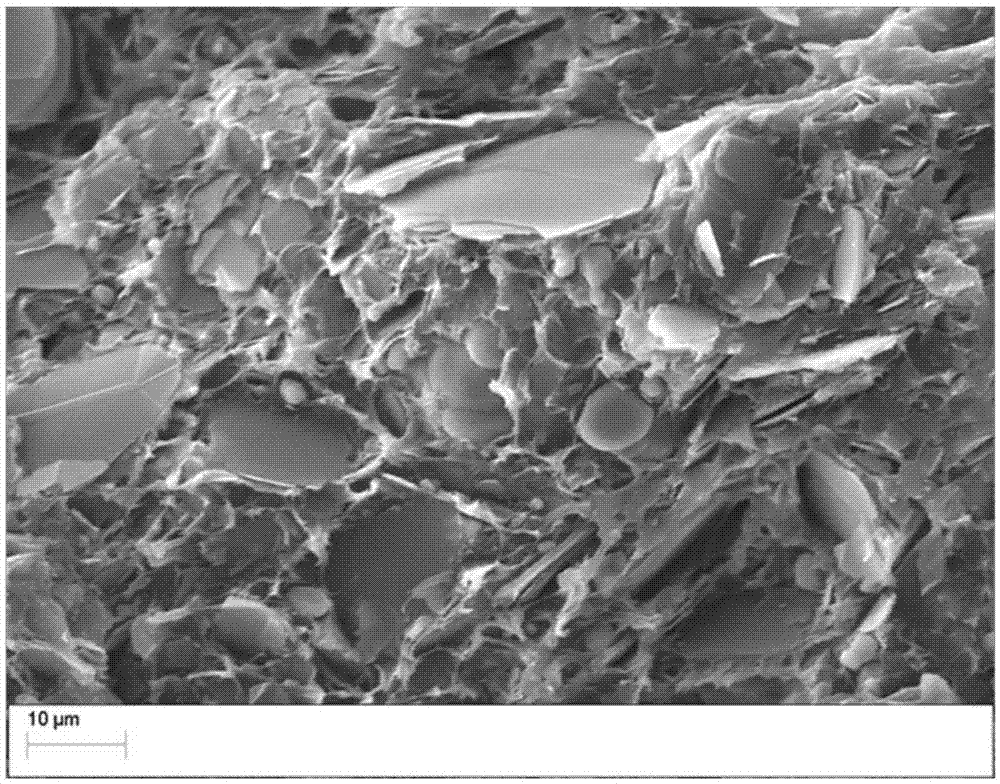
Impact-resistant scratch-resistant thermal-conduction nylon composite material and preparation method thereof
A nylon composite material and composite material technology are applied in the field of impact-resistant and scratch-resistant thermally conductive nylon composite materials and their preparation, and can solve the problems of poor scratch resistance, poor toughness and low temperature resistance, and poor toughness of thermally conductive composite materials.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0051] The preparation method (i.e. "two-step melt blending method") of the composite material involved in the first aspect of the present invention related to the second aspect of the present invention includes:
[0052] Step A, uniformly mixing the thermally conductive component, coupling agent and optional anti-scratch agent to prepare a pretreatment;
[0053] Step B, uniformly mixing the pretreated material with the nylon resin to obtain a mixture I;
[0054] Step C, using a melt blending method, melt-extruding and granulating the mixture I through a twin-screw extruder to obtain a masterbatch;
[0055] Step D, uniformly mixing the masterbatch with a flame retardant and an antioxidant to obtain a mixture II;
[0056] In step E, the mixture II is melt-extruded and granulated by a twin-screw extruder by a melt-blending method to obtain an impact-resistant, scratch-resistant, and heat-conducting nylon composite material.
[0057] In the preparation method of the above-menti...
Embodiment 1
[0087] Example 1: Preparation of thermally conductive nylon composite material by two-step melt blending method
[0088] (1) Add 1200g of spherical alumina and 9g of KH550 into a heatable homogenizer, adjust the temperature of the homogenizer to 60°C, and mix at a high speed for 3 minutes to obtain a pretreated product;
[0089] (2) Add 1500g copolymerized nylon (relative viscosity is 2.8, number average molecular weight is 15000, molecular weight distribution index is 1.8, and the molar ratio of nylon 6 structural unit and nylon 66 structural unit in the copolymerized nylon is 4:1) in the pretreatment product The resin was uniformly mixed at high speed for 3 minutes to obtain mixture I;
[0090] (3) The mixture I is melt-extruded and granulated through a twin-screw extruder to obtain a heat-conducting, scratch-resistant masterbatch; the process conditions of the twin-screw extruder are: temperature in the first zone: 220°C; temperature in the second zone: 240°C; the temperat...
Embodiment 2
[0094] Example 2: Preparation of thermally conductive nylon composite material by two-step melt blending method
[0095] (1) Add 300g of boron nitride, 900g of spherical alumina and 9g of KH550 into a heatable homogenizer, adjust the temperature of the homogenizer to 60°C, and mix at a high speed for 3 minutes to obtain a pretreated product;
[0096] (2) Add 1500g copolymerized nylon (relative viscosity is 3.2, number average molecular weight is 18000, molecular weight distribution index is 2.2, and the molar ratio of nylon 6 structural unit and nylon 66 structural unit in the copolymerized nylon is 4:1) in the pretreatment product The resin was uniformly mixed at high speed for 3 minutes to obtain mixture I;
[0097] (3) The mixture I is melt-extruded and granulated through a twin-screw extruder to obtain a heat-conducting, scratch-resistant masterbatch; the process conditions of the twin-screw extruder are: temperature in the first zone: 220°C; temperature in the second zone...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com