Technology for promoting direct trans-differentiation of umbilical cord blood CD34 positive cells into mesenchymal stem cells
A technology of positive cells and hematopoietic stem cells, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of low efficiency of MSCs, and achieve the effect of far-reaching medical application value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
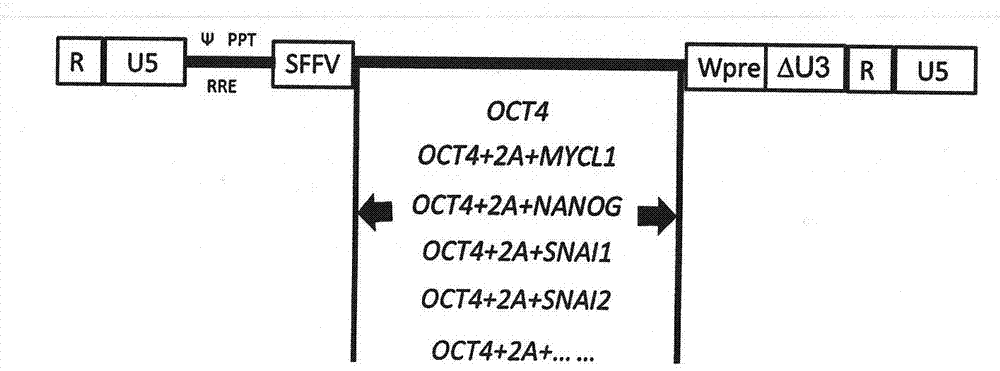
[0022] This embodiment provides a method for obtaining MSCs by using lentivirus to infect CD34-positive hematopoietic stem cells derived from umbilical cord blood, which includes the following steps:
[0023] 1. Enrichment and storage of CD34 positive cells:
[0024] 1) The umbilical cord blood and hydroxyethyl starch 5:1 were thoroughly mixed, and left at room temperature for 40 minutes to precipitate red blood cells.
[0025] 2) Dispense 15ml of lymphocyte separation solution into a 50ml centrifuge tube and place at room temperature to equilibrate.
[0026] 3) Aspirate the supernatant in 1), and slowly add it to the lymphocyte separation medium that has been equilibrated to room temperature, taking care not to disturb the liquid level of the separation medium, the total volume can reach 50ml. The centrifuge was set to de-brake and centrifuged at 400G for 25 minutes.
[0027] 4) Aspirate the buffy coat layer between the two liquid phases, add 5 times the volume of PBS and mix...
Embodiment 2
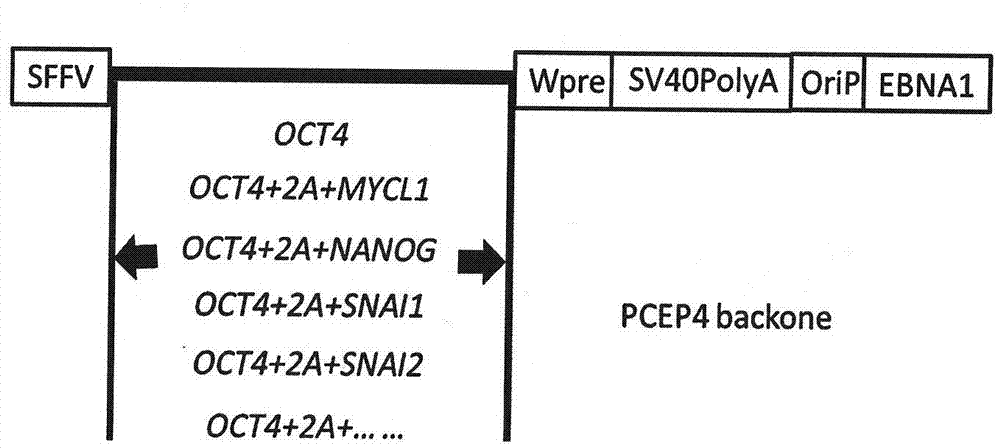
[0036] This embodiment provides a method for using a non-integrating vector to transdifferentiate umbilical cord blood-derived CD34-positive hematopoietic stem cells to obtain iMSCs, which includes the following steps:
[0037] 1. Construction of non-integrating vector
[0038] 1) In order to better meet the standards of clinical cell therapy, we developed a transdifferentiation method for MSCs using non-integrating vectors. We first tested an episomal vector based on EBNA1. One week after nucleofection of cord blood CD34-positive cells, we obtained MSC-like cells.
[0039] 2) From Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA). The hygromycin resistance gene element and the CMV promoter were removed by two restriction enzyme sites, NruI and BamHI, and at least one of the nucleotide sequence combinations of the six genes OCT4, NANOG, MYCL1, SNAI1, SNAI2, and TWIST1 An episomal vector cut from lentiviral vector and inserted into pCEP4. figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of the non-integrated e...
Embodiment 3
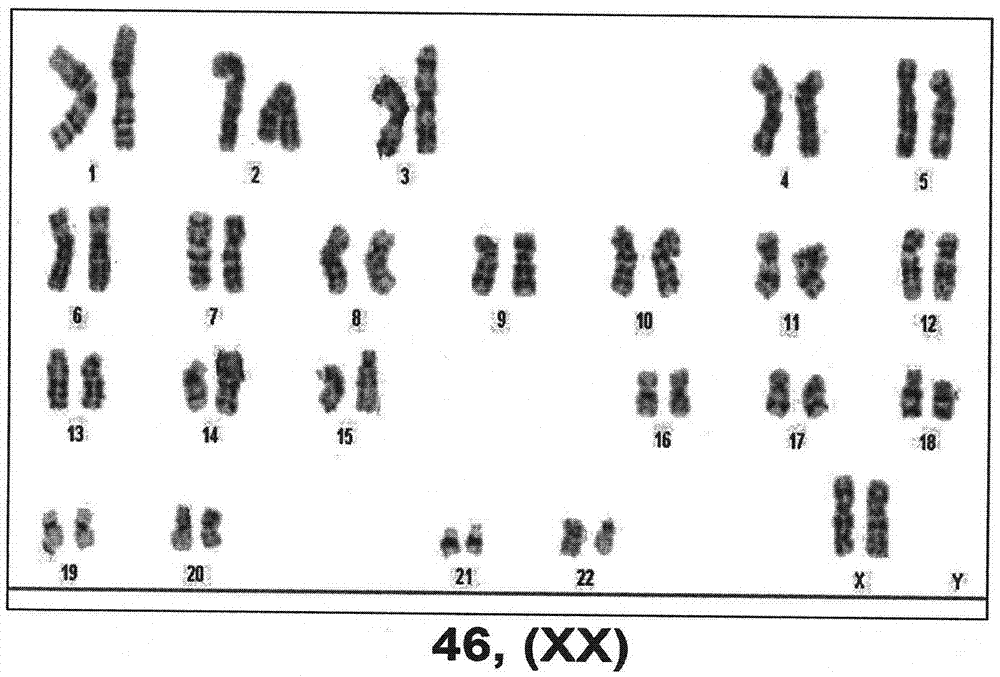
[0047] Example 3 Long-term culture of iMSCs and identification of genome stability
[0048] In this example, the iMSCs obtained in Example 2 were cultured for a long period of time, and the genome stability was identified according to the following steps:
[0049] 1. We cultured bone marrow iMSCs for more than 40 passages under MSCs culture conditions, and the population doubling time was 18-36 hours. Specific methods of cell culture and subculture:
[0050] 1) 24-well plates were pretreated with fibronectin (RetroNectin) (CH-296; Takara Bio, Inc., Shiga, Japan) according to the product instructions. After standing at room temperature for 2 hours or overnight at 4, wash with PBS to remove residual fibronectin and it can be used.
[0051] 2) MSCs were cultured in culture plates pretreated with RetroNectin. Every 2-3 days, iMSCs were treated with Accutase or trypsin for five minutes to digest the iMSCs into single cells, and passaged 4-6 times.
[0052] 2. After long-term in ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com