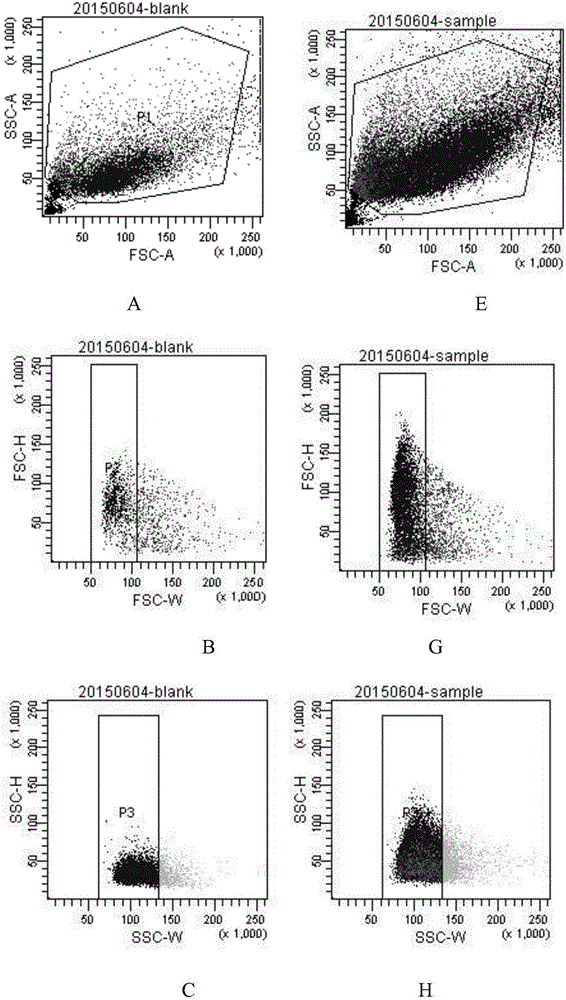
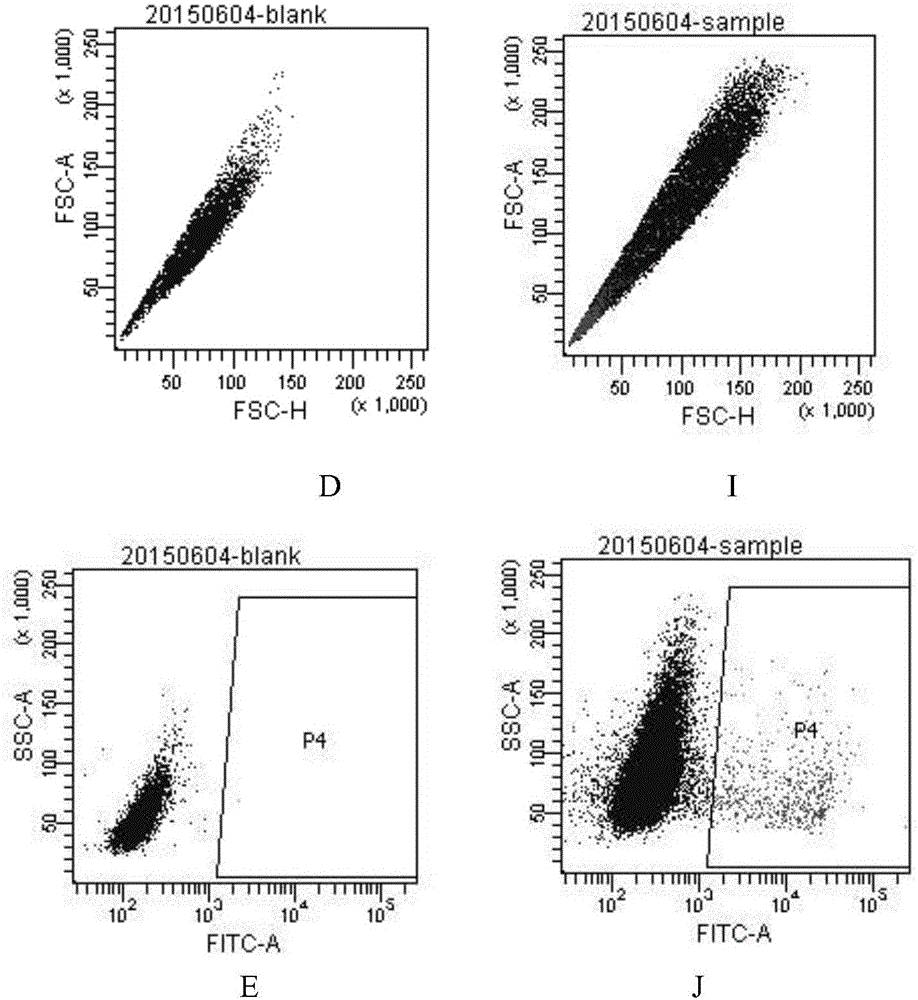
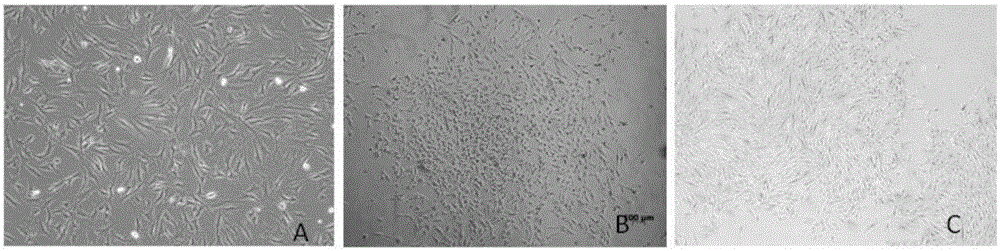
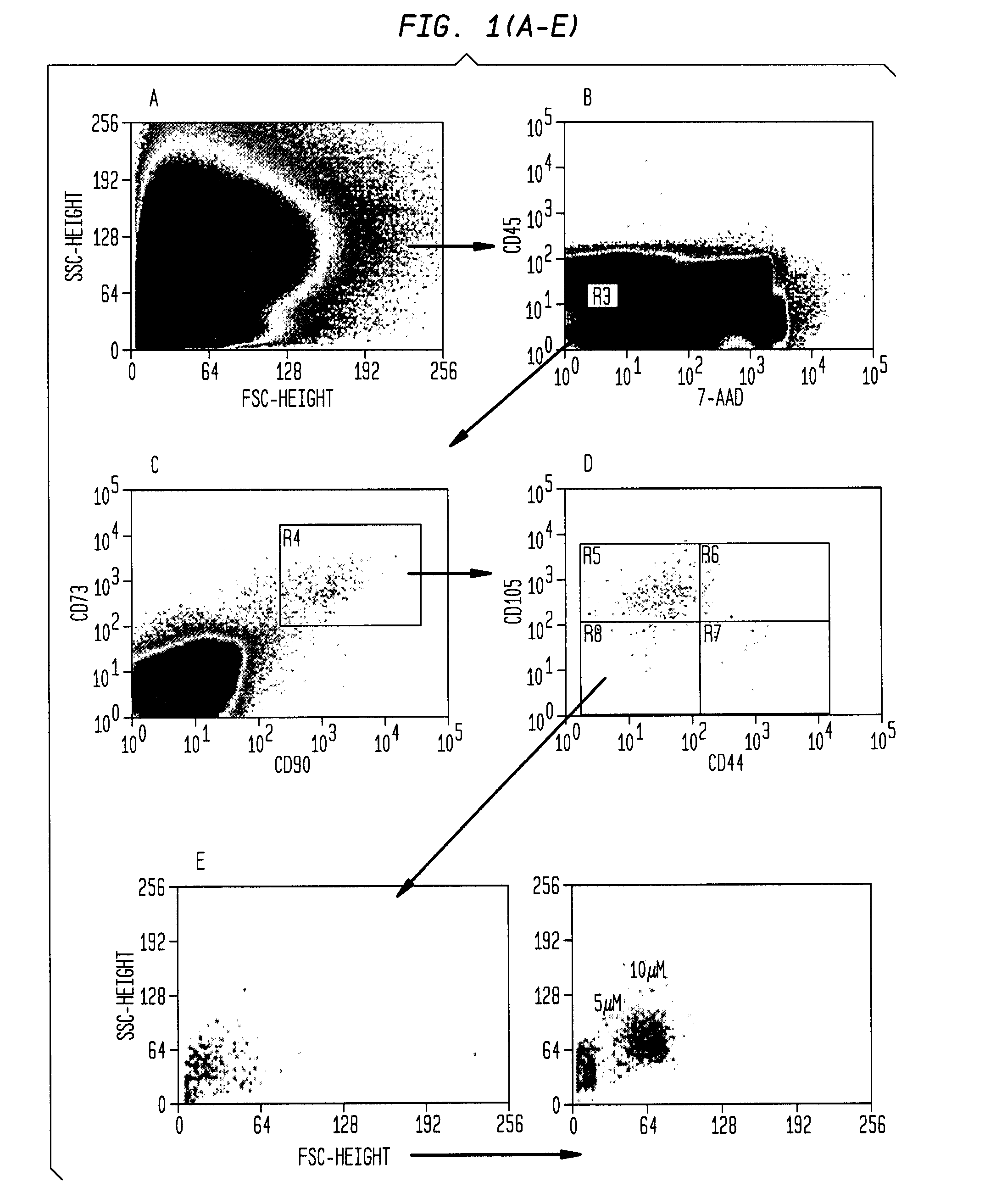
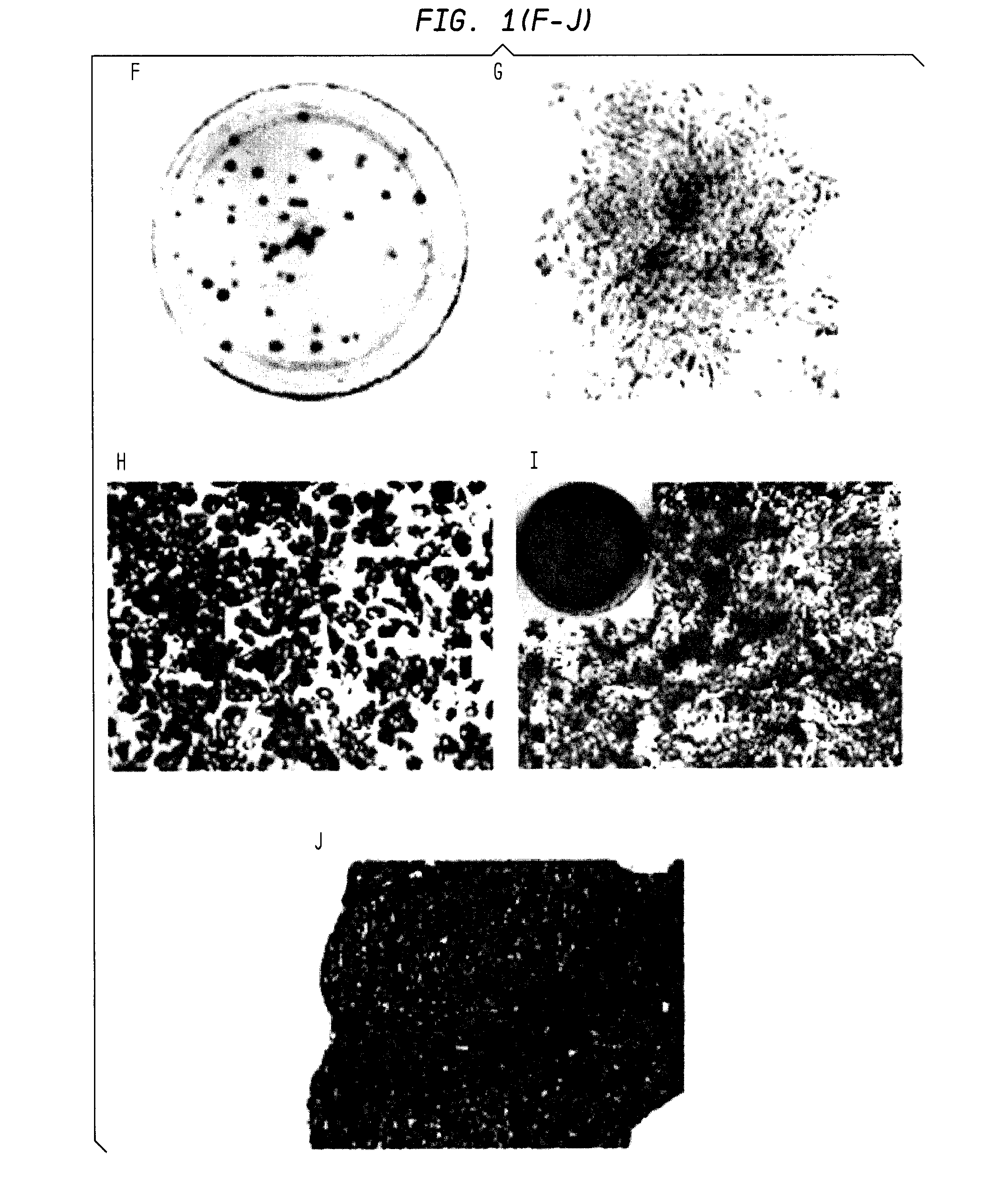
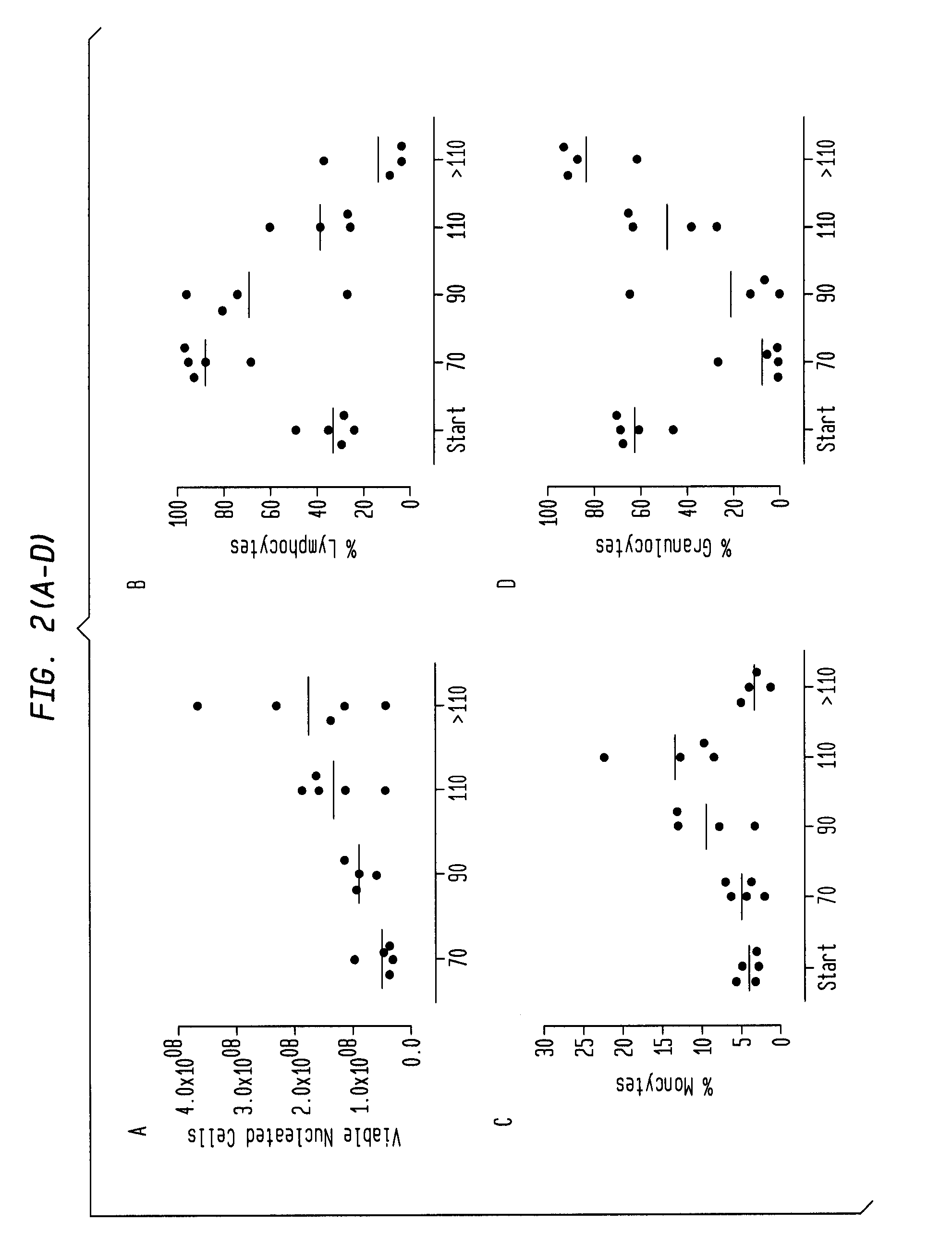
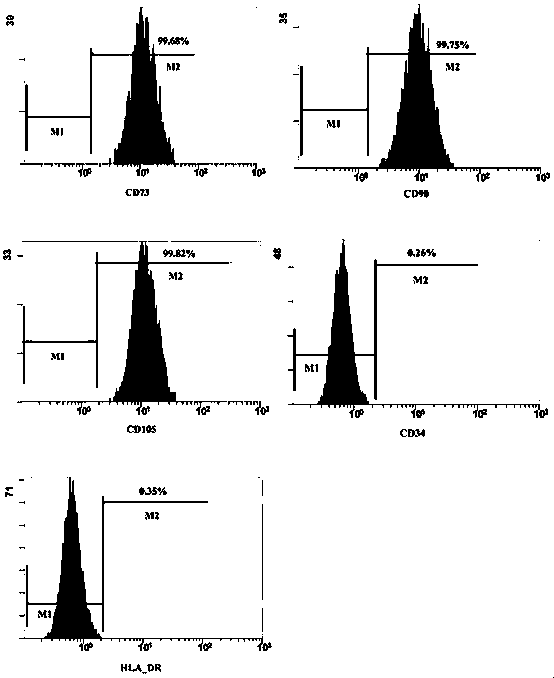
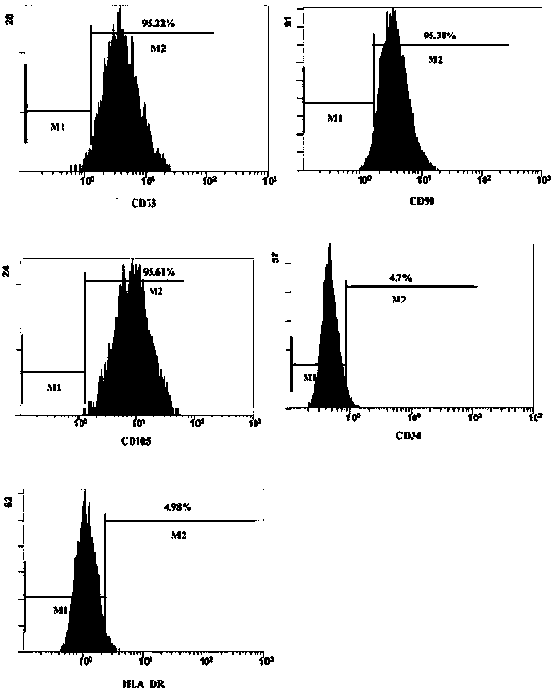
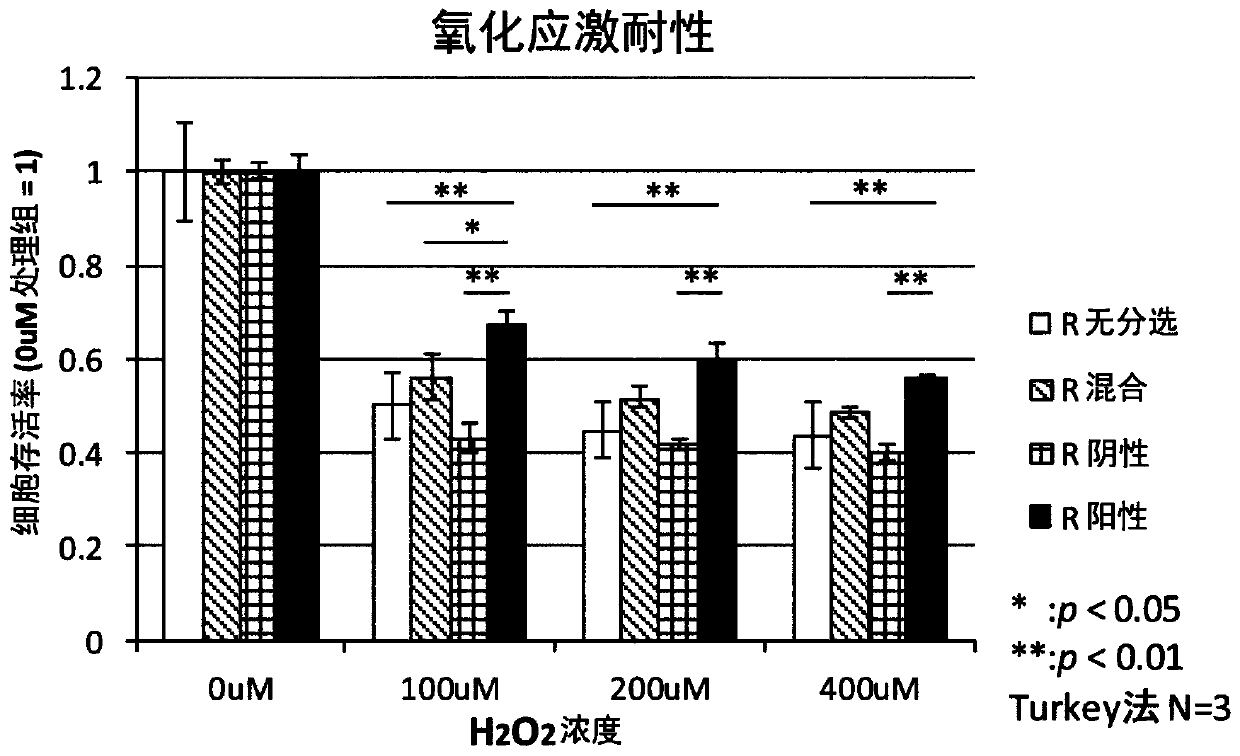
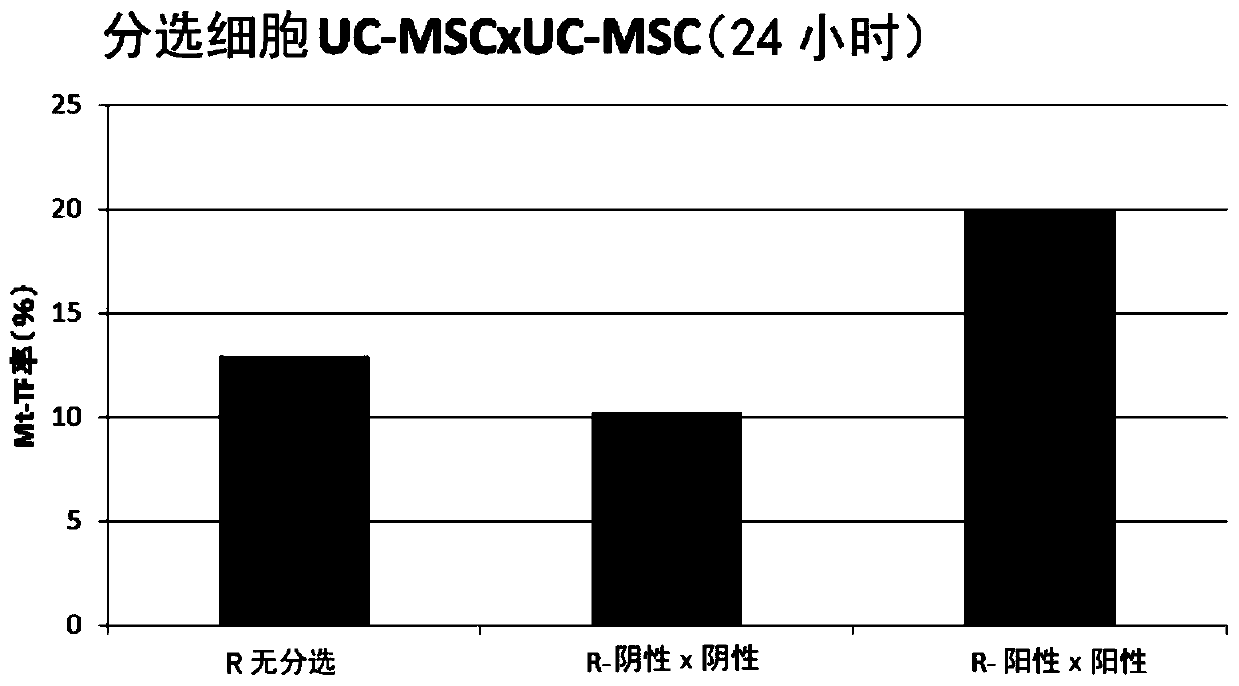
Patents
Literature
124 results about "CD90" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
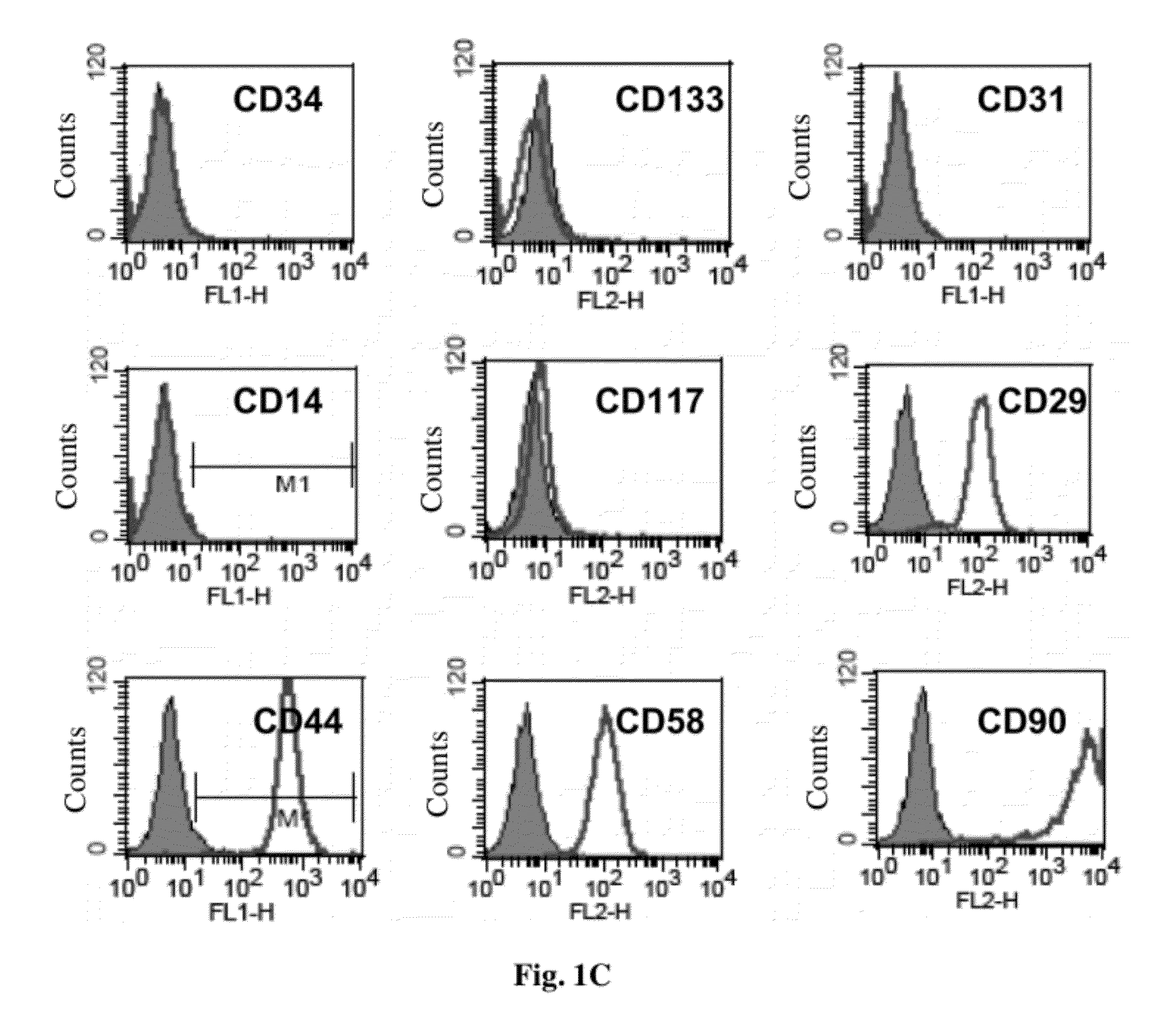
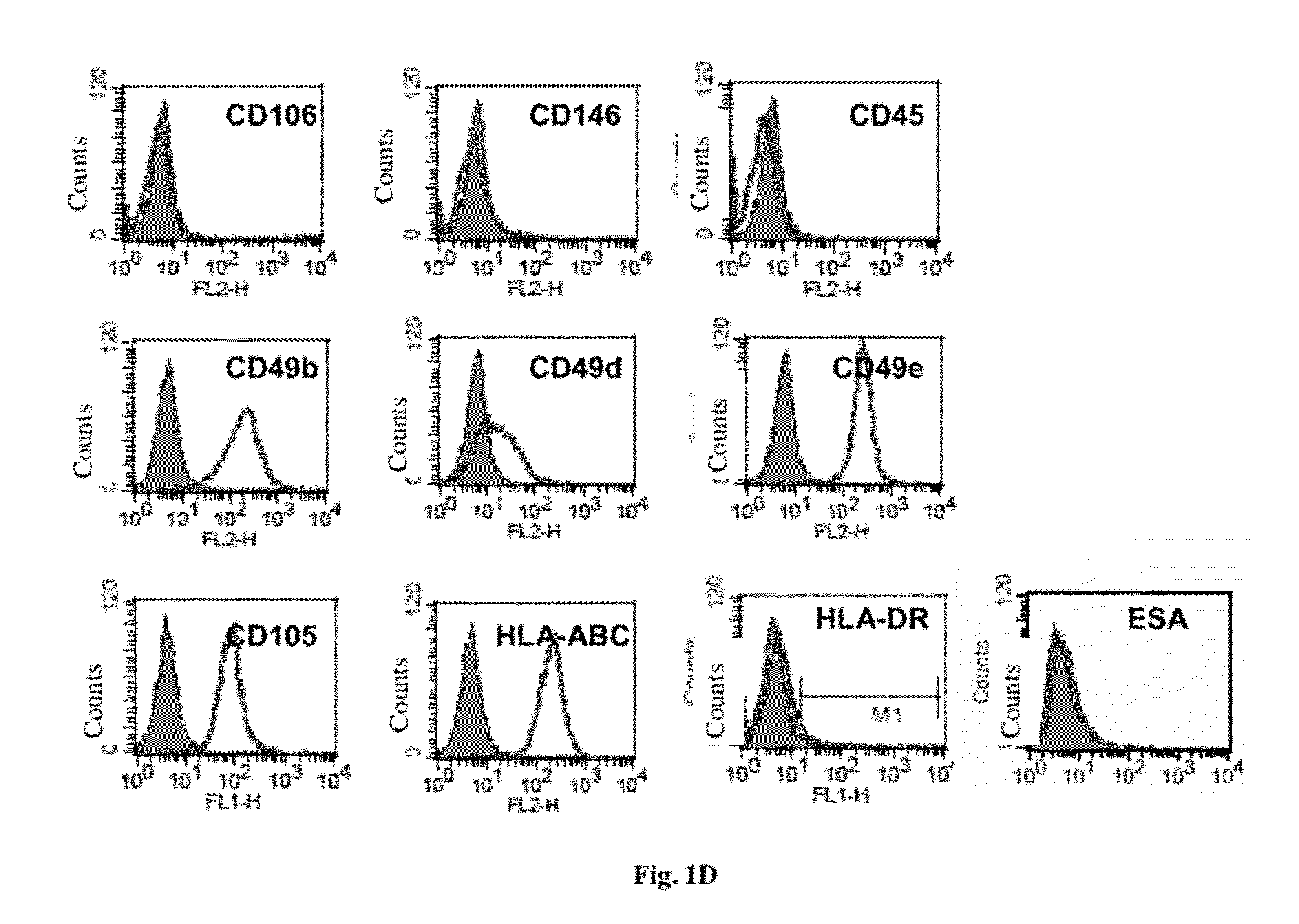
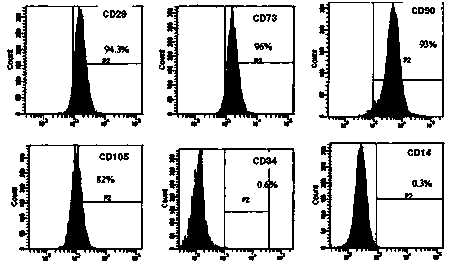
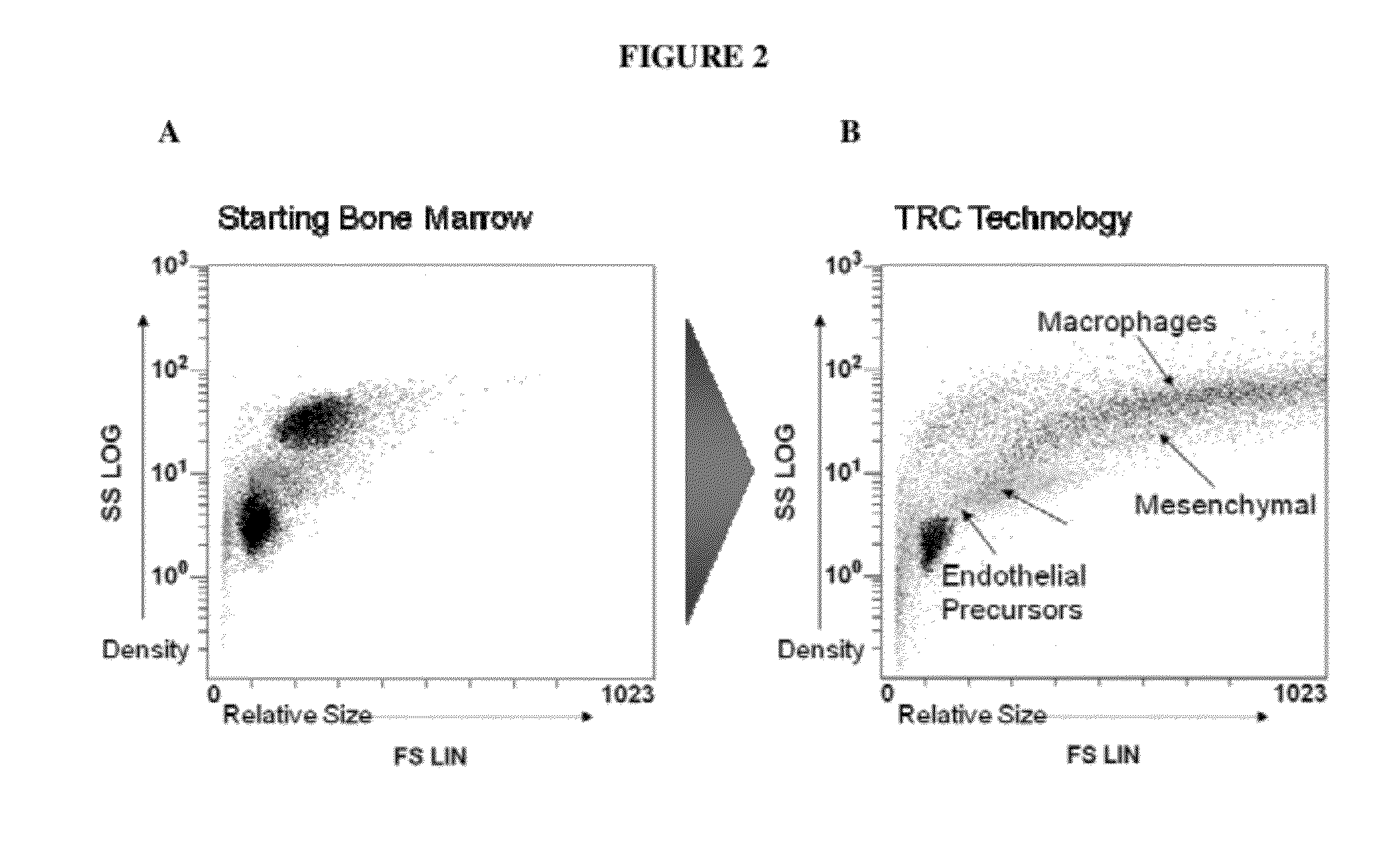
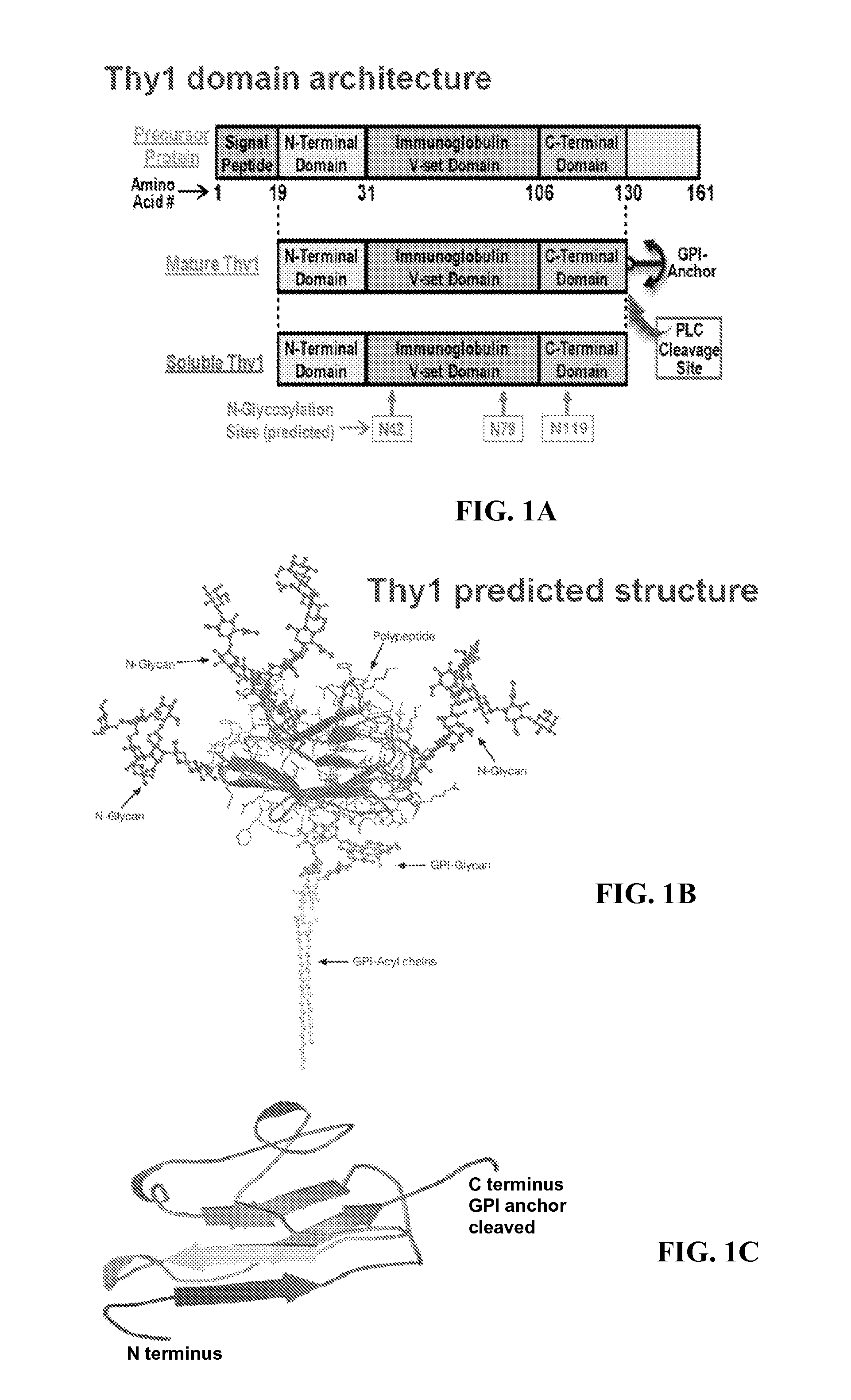
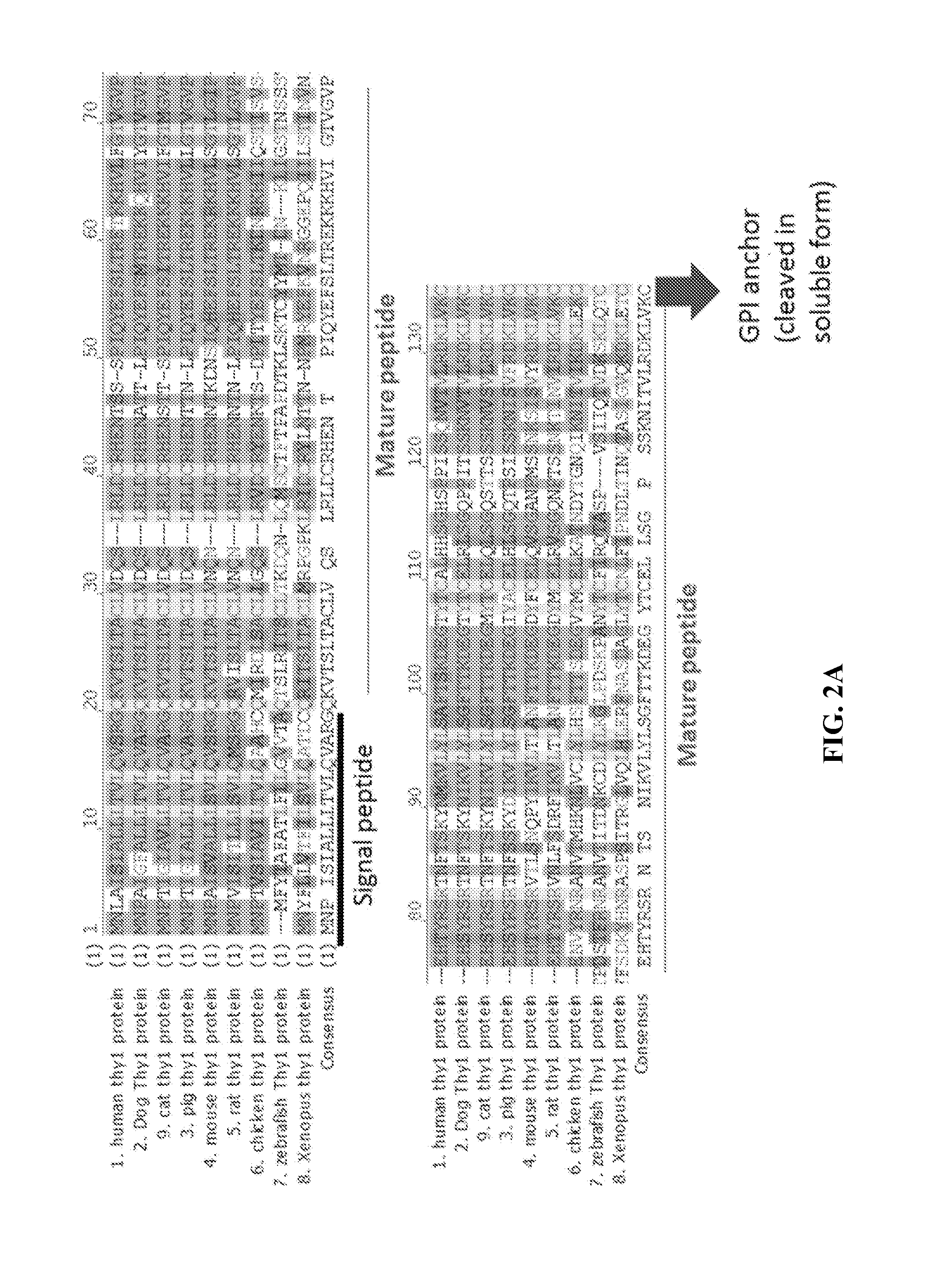
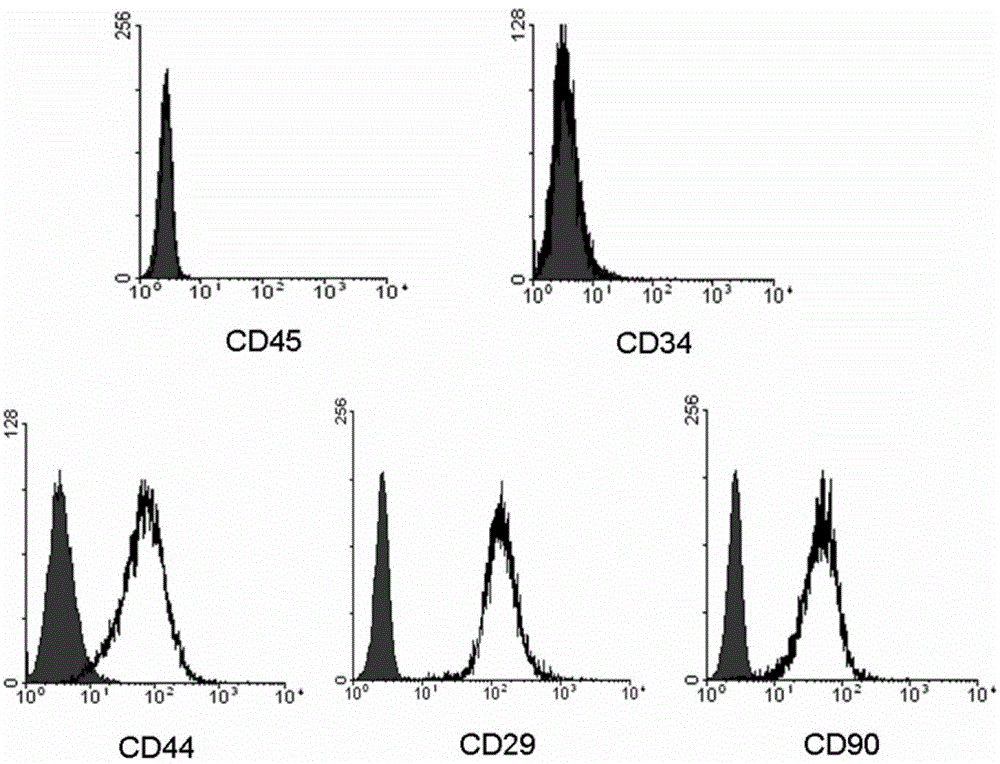
Thy-1 or CD90 (Cluster of Differentiation 90) is a 25–37 kDa heavily N-glycosylated, glycophosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchored conserved cell surface protein with a single V-like immunoglobulin domain, originally discovered as a thymocyte antigen. Thy-1 can be used as a marker for a variety of stem cells and for the axonal processes of mature neurons. Structural study of Thy-1 led to the foundation of the Immunoglobulin superfamily, of which it is the smallest member, and led to some of the initial biochemical description and characterization of a vertebrate GPI anchor and also the first demonstration of tissue specific differential glycosylation.
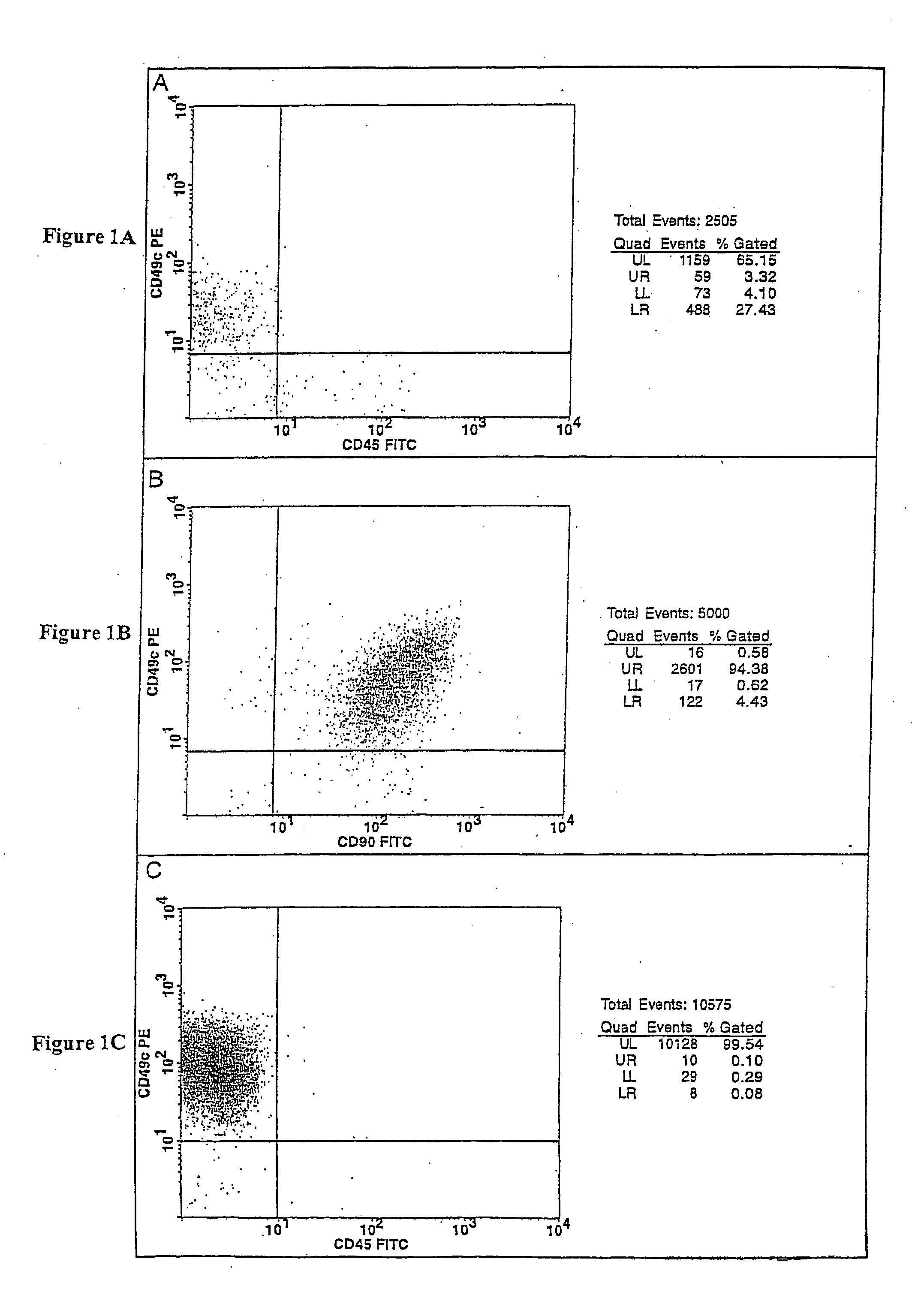
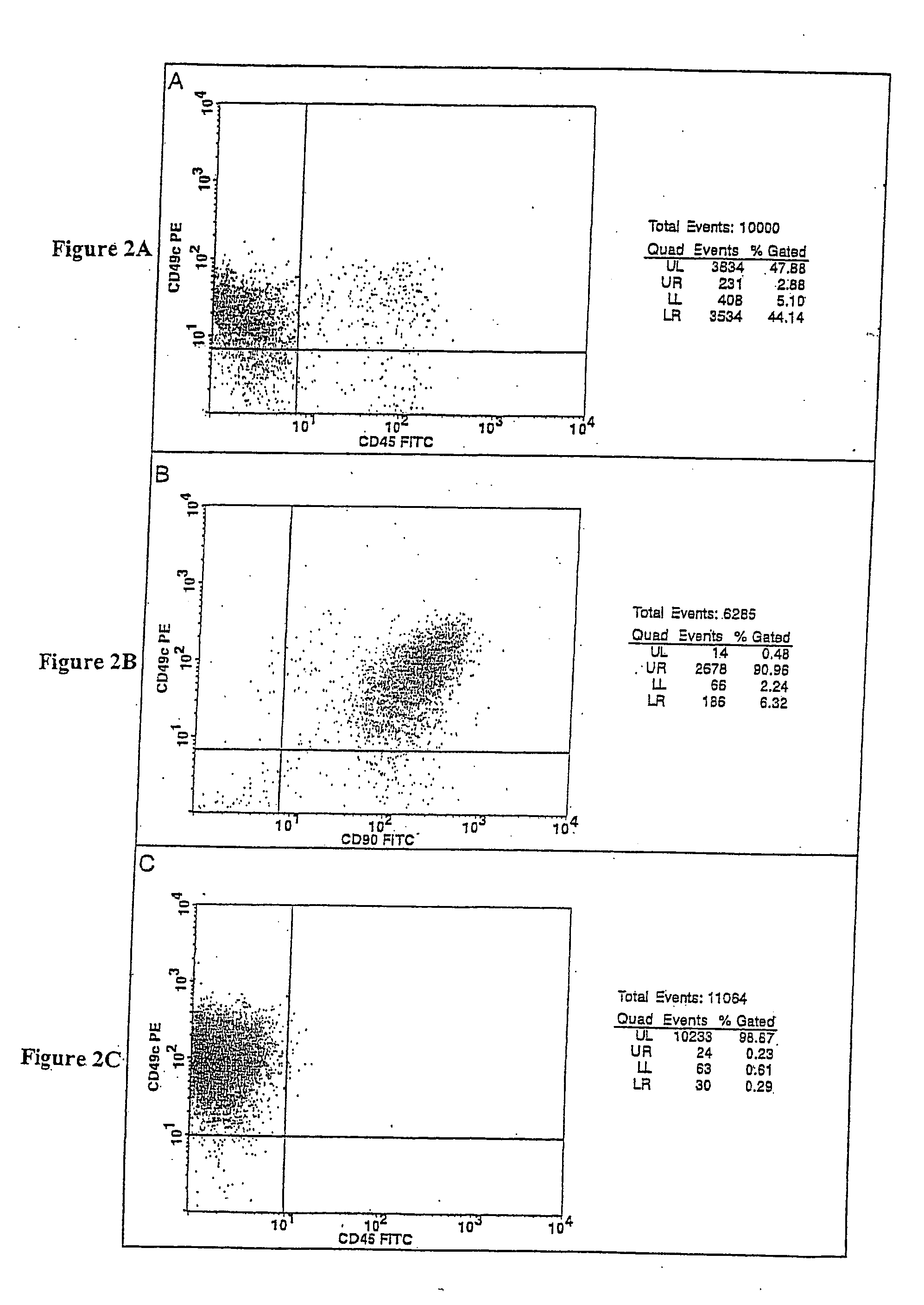
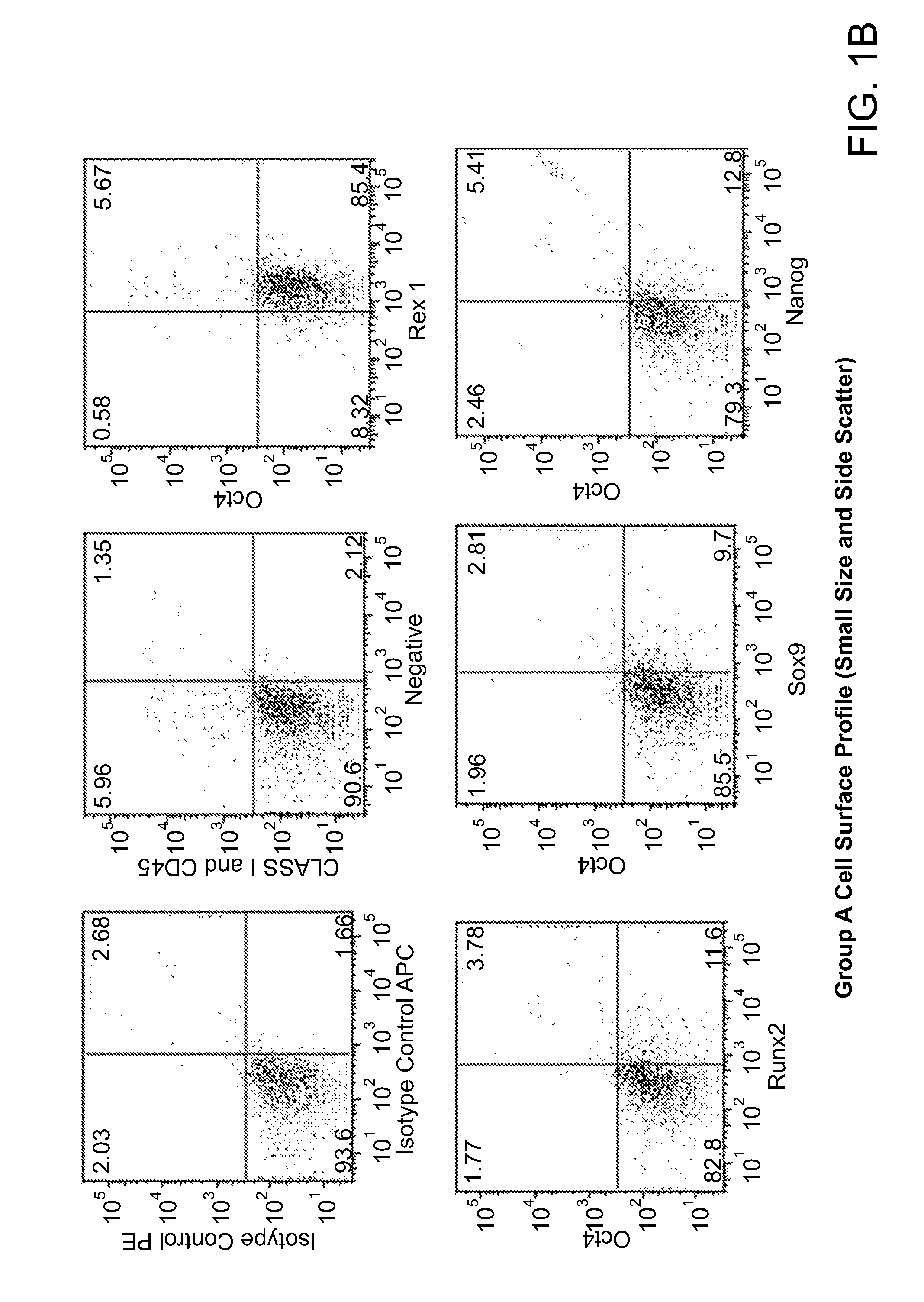
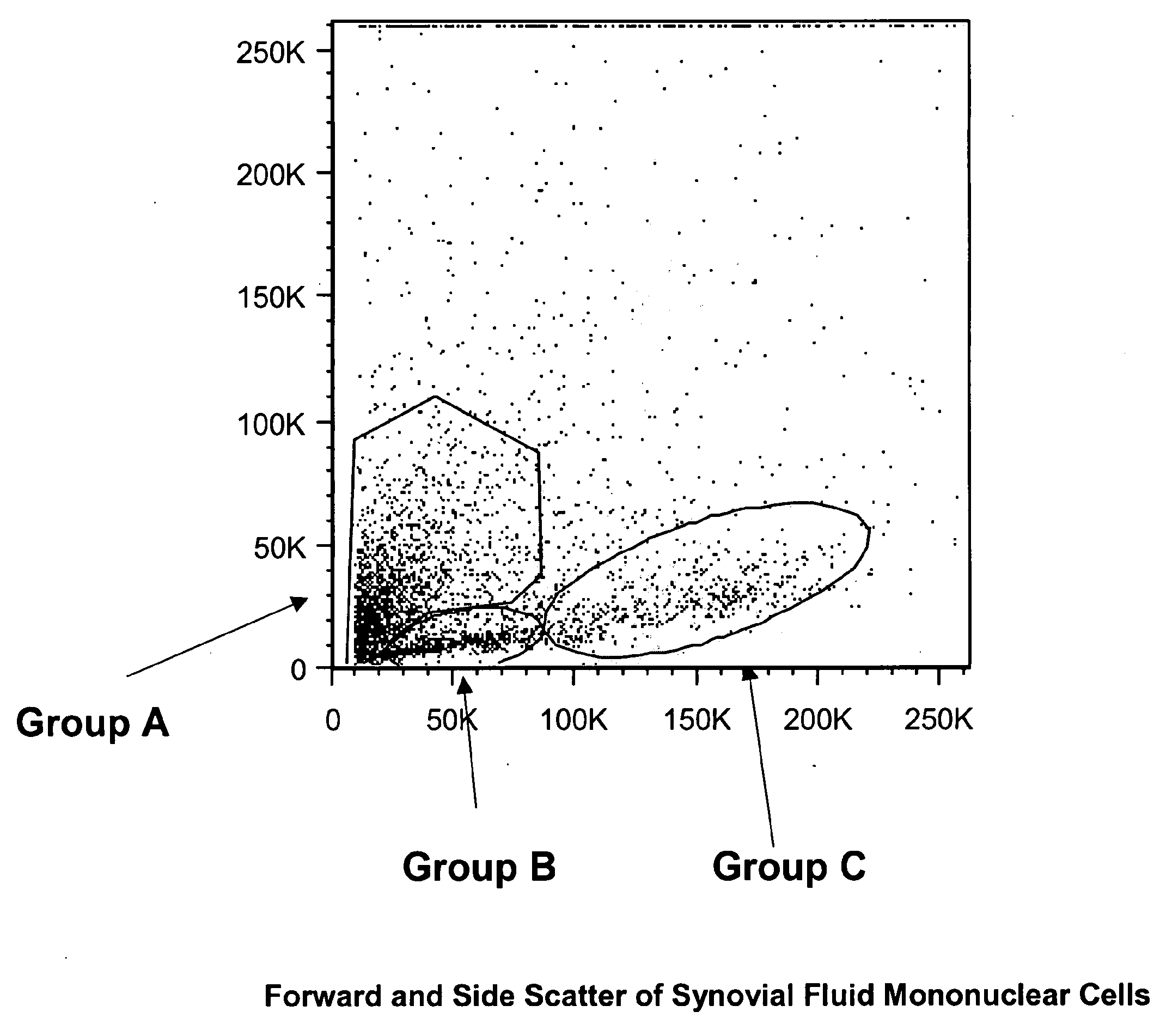
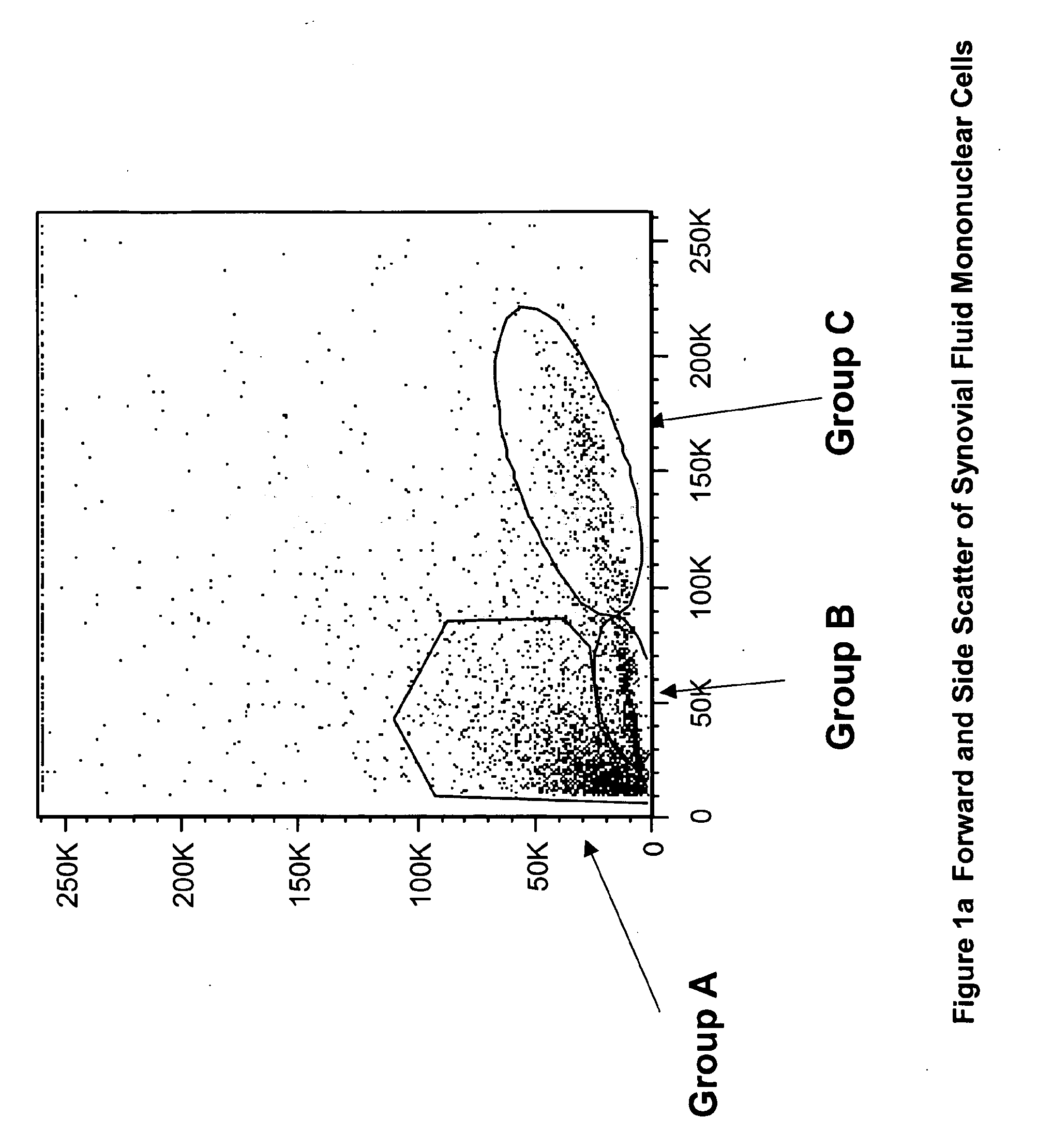
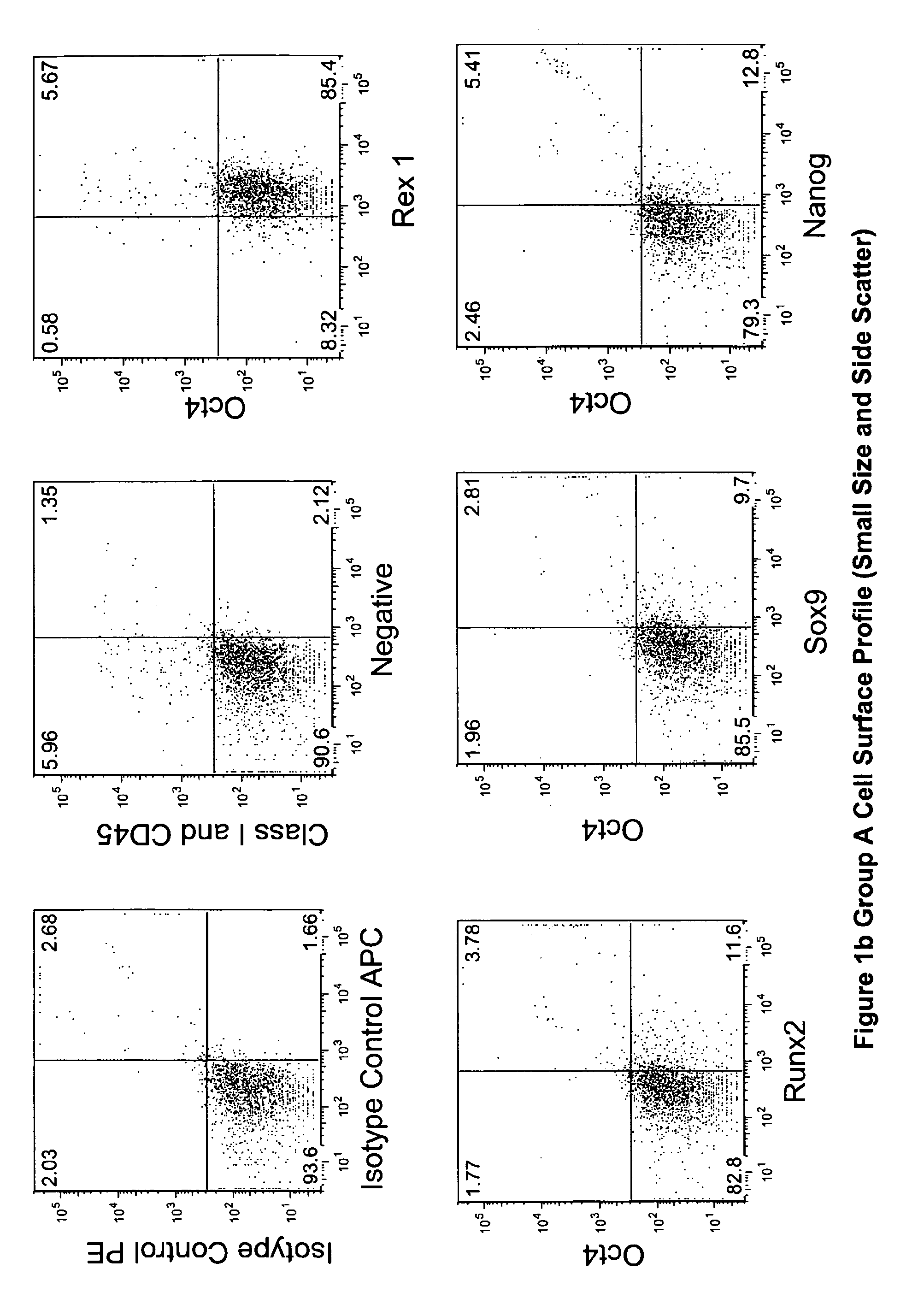
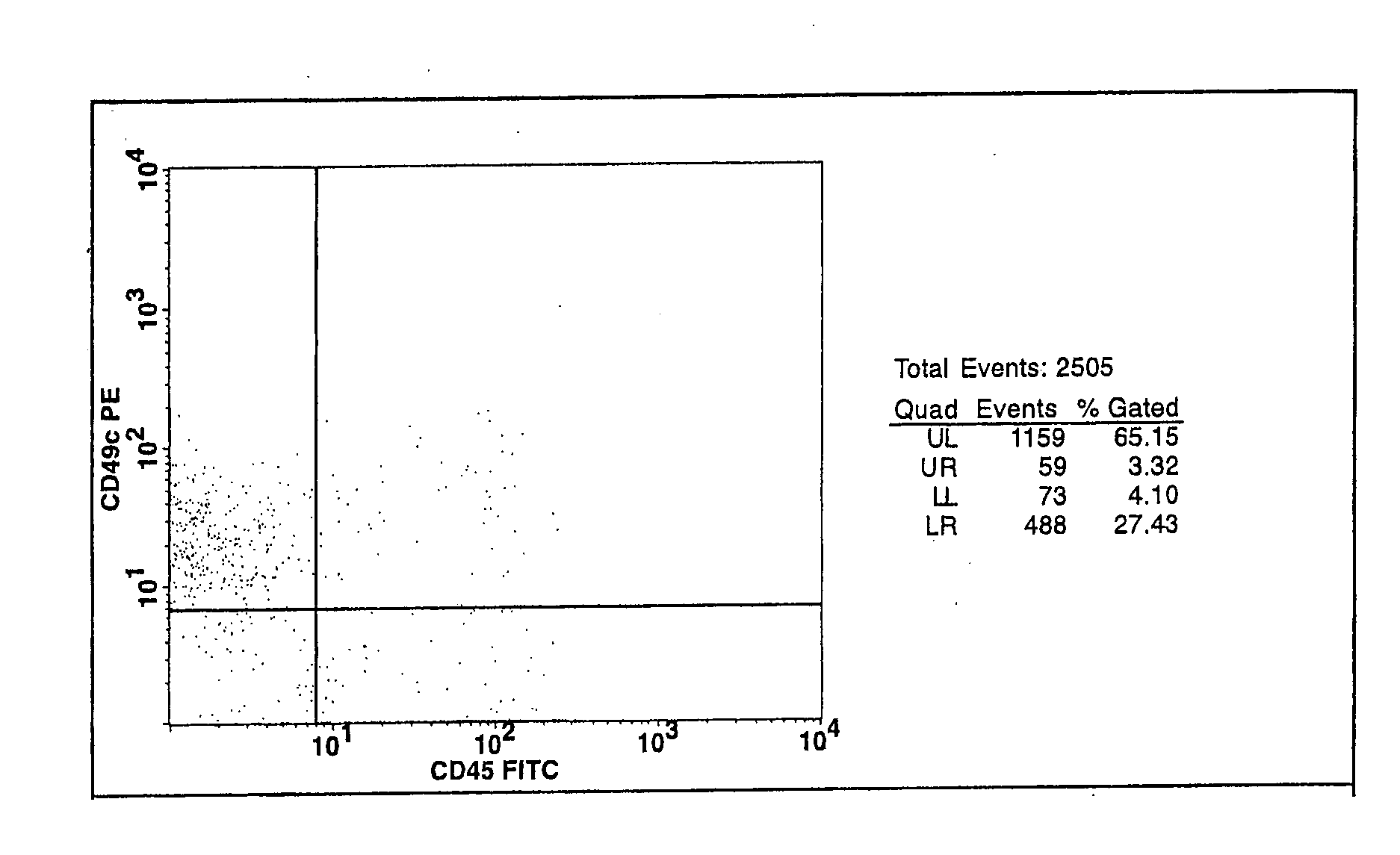
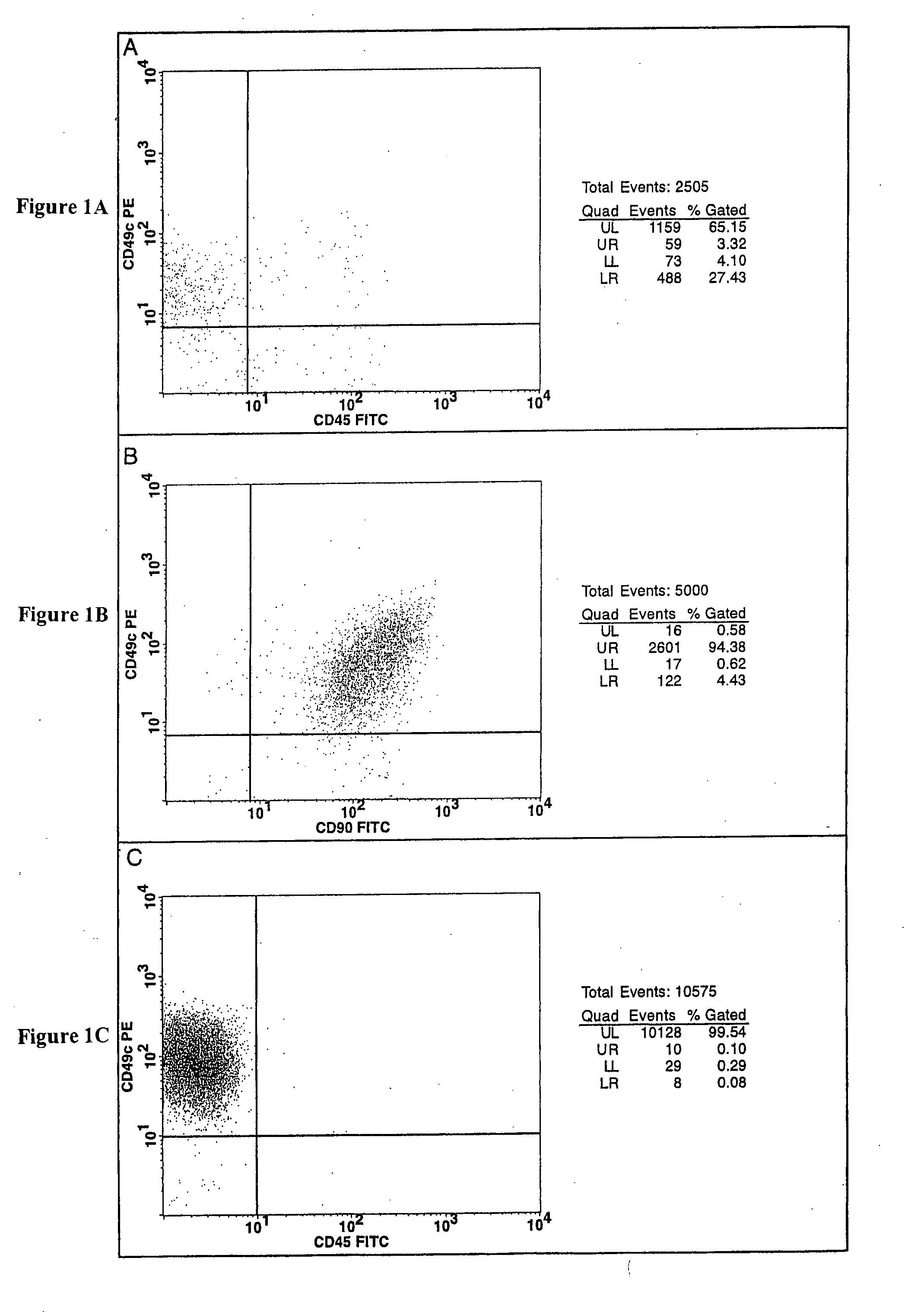
Cell populations which co-express CD49c and CD90
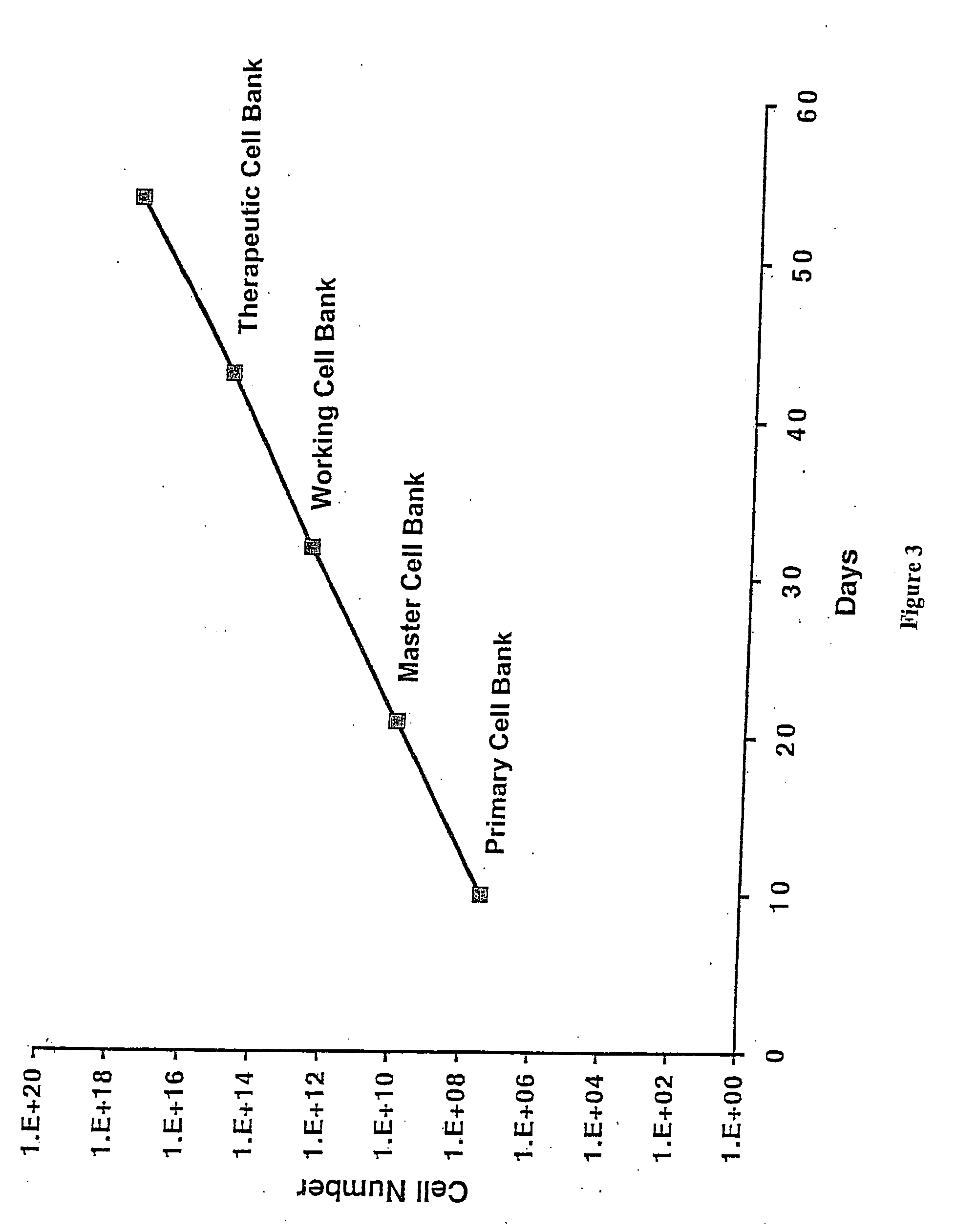
ActiveUS20050233452A1Promote repairIncreasing of life life expectancyBone marrow stroma cellsNervous disorderTelomeraseProgenitor
Substantially homogenous cells populations which co-express CD49c, CD90 and telomerase are made. In one embodiment, humans suffering from a degenerative, traumatic, acute injury, cardiac or neurological condition are treated with the substantially homogenous cells populations which co-express CD49c, CD90 and telomerase. In another embodiment, committed progenitor cells are made are made by selecting from a cultured source of a cell population which co-express CD49c and CD90 and modifying the cell population. The committed progenitor cells can be employed to treat a human suffering from a degenerative, traumatic, acute injury, cardiac or neurological condition and formulate pharmaceutical compositions.
Owner:GARNET BIOTHERAPEUTICS
Multipotent stem cells derived from placenta tissue and cellular therapeutic agents comprising the same
InactiveUS20070243172A1Negative immunological responseBiocideArtificial cell constructsGerm layerDisease
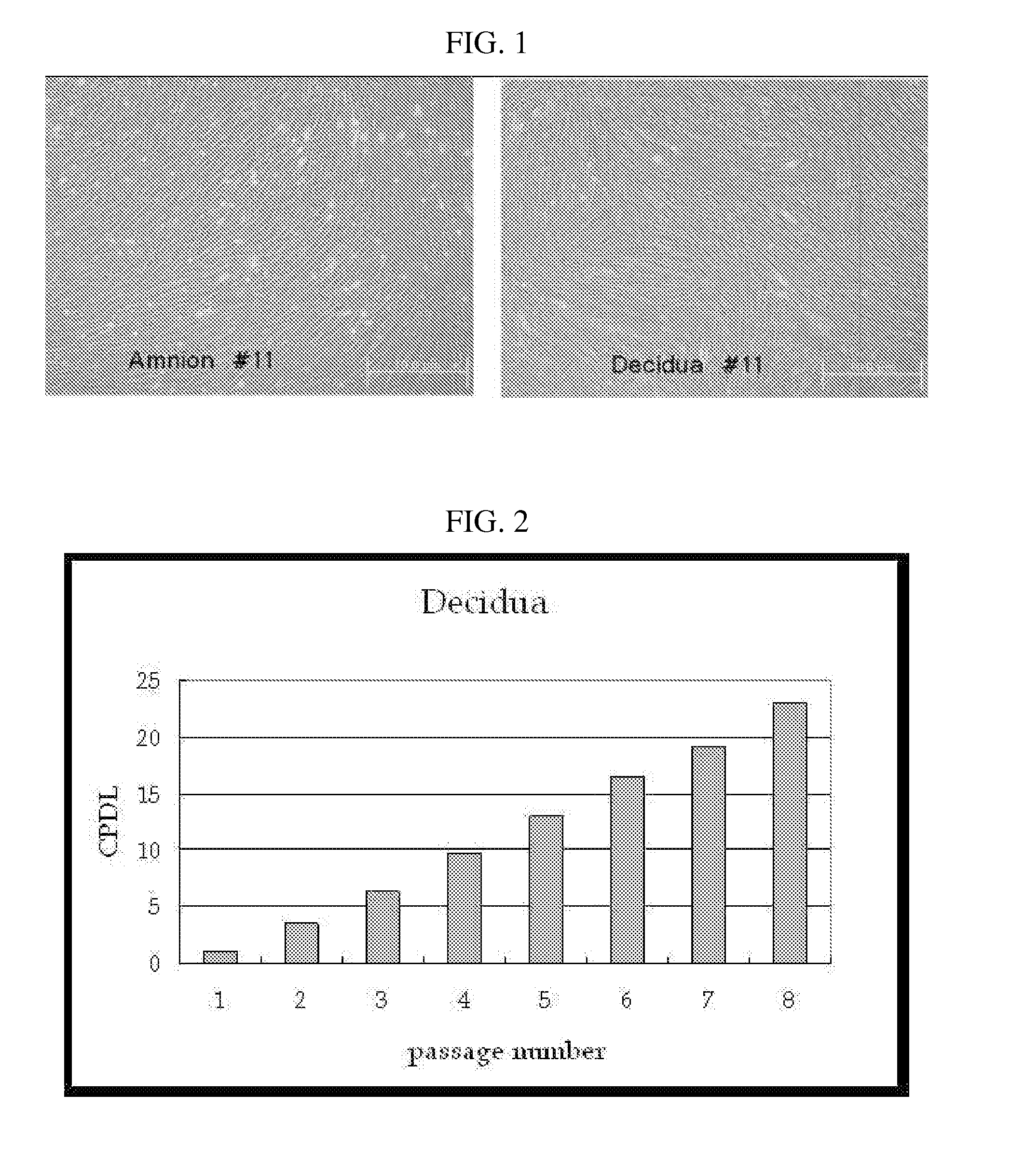
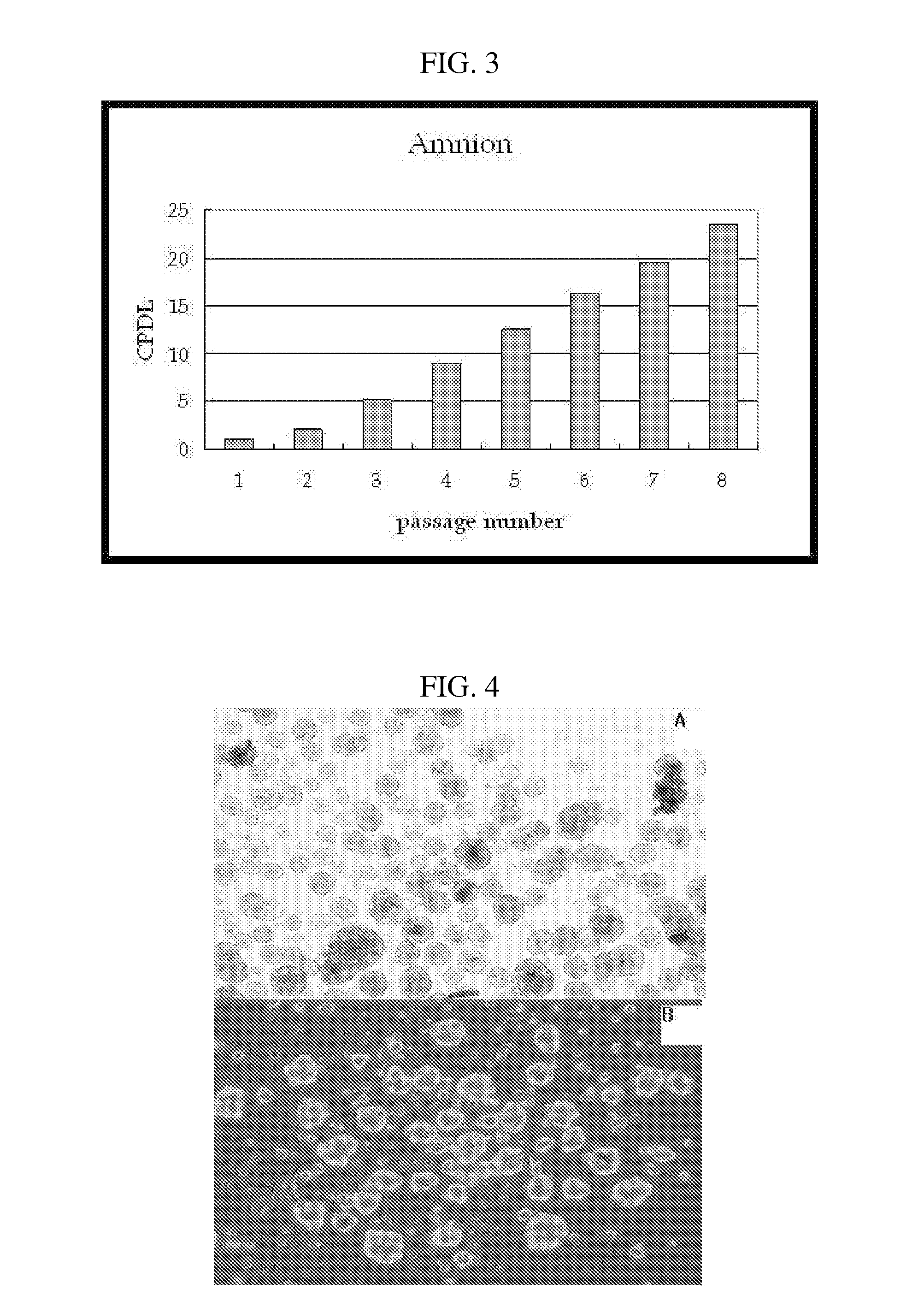
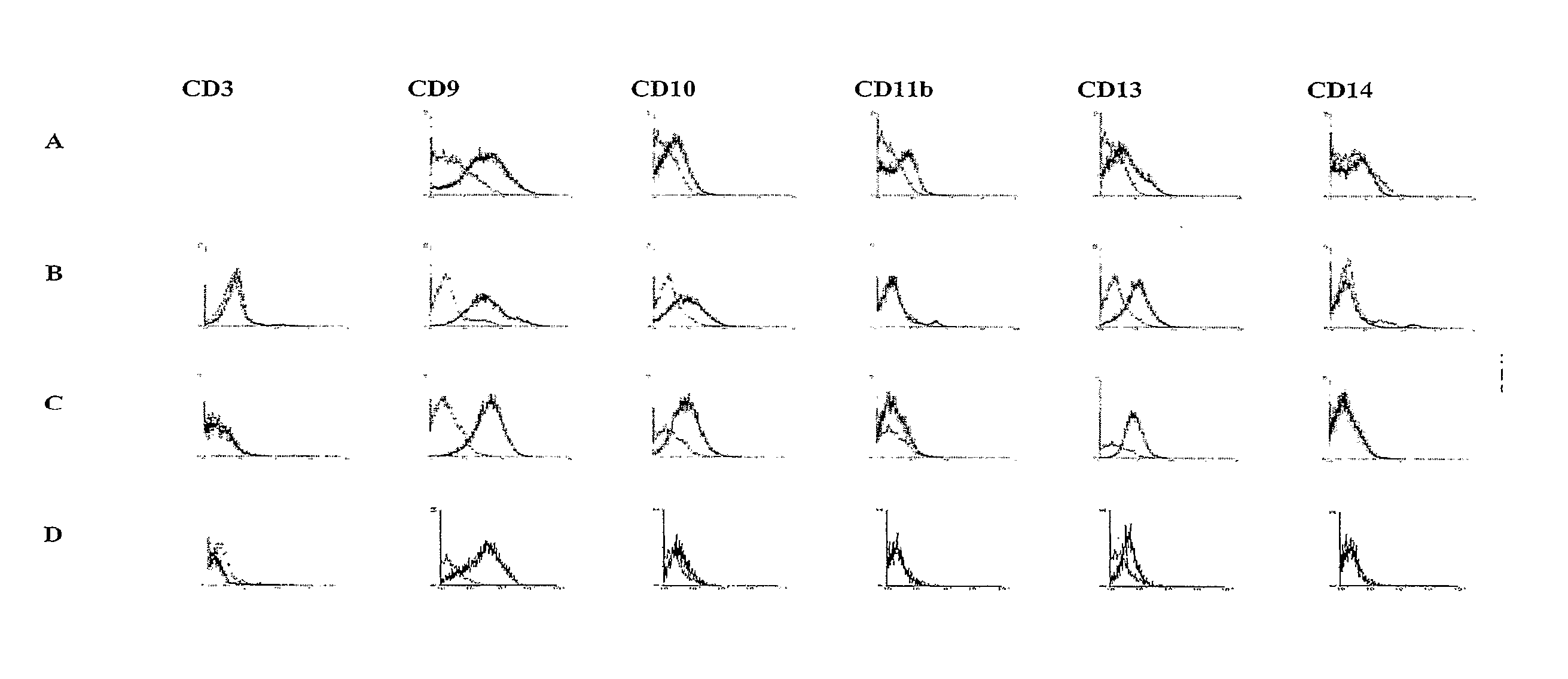
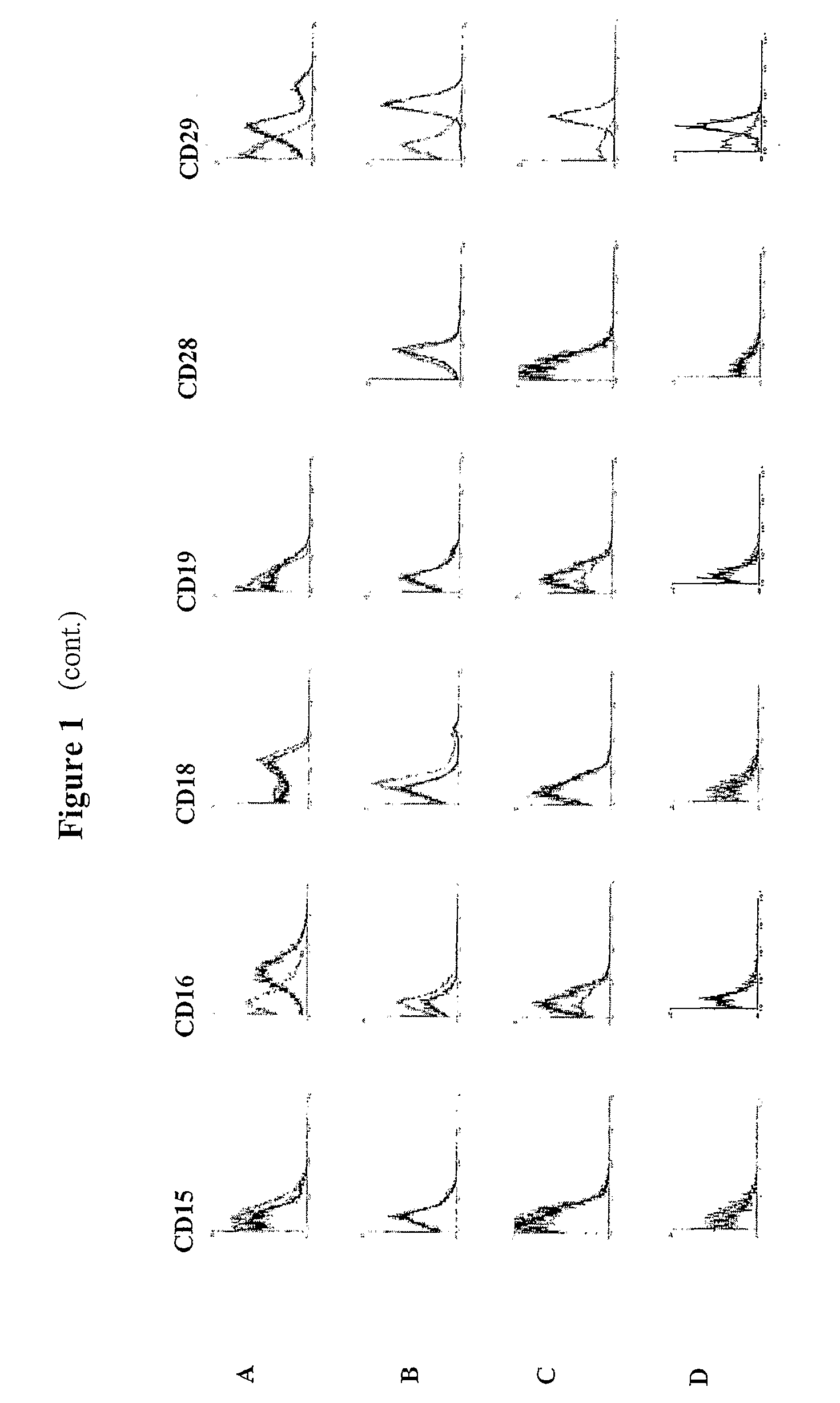
The present invention relates to placenta tissue-derived multipotent stem cells and cell therapeutic agents containing the same. More specifically, to a method for producing placenta stem cells having the following characteristics, the method comprising culturing amnion, chorion, decidua or placenta tissue in a medium containing collagenase and bFGF and collecting the cultured cells: (a) showing a positive immunological response to CD29, CD44, CD73, CD90 and CD105, and showing a negative immunological response to CD31, CD34, CD45 and HLA-DR; (b) showing a positive immunological response to Oct4 and SSEA4; (c) growing attached to plastic, showing a round-shaped or spindle-shaped morphology, and forming spheres in an SFM medium so as to be able to be maintained in an undifferentiated state for a long period of time; and (d) having the ability to differentiate into mesoderm-, endoderm- and ectoderm-derived cells. Also the present invention relates to placenta stem cells obtained using the production method. The inventive multipotent stem cells have the ability to differentiate into muscle cells, vascular endothelial cells, osteogenic cells, nerve cells, satellite cells, fat cells, cartilage-forming cells, osteogenic cells, or insuline-secreting pancreatic β-cells, and thus are effective for the treatment of muscular diseases, osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, nervous diseases, diabetes and the like, and are useful for the formation of breast tissue.
Owner:RNL BIO
Identification and Isolation of Multipotent Cells From Non-Osteochondral Mesenchymal Tissue
Identification and isolation of multipotent cells from non-osteochondral mesenchymal tissue. This invention relates to the identification and isolation of multipotent cells from non-osteochondral mesenchymal tissue. Specifically, it relates to an adult multipotent cell or a cell population or composition comprising said cell, isolated from non-osteochondral mesenchymal tissue, characterized in that it is positive for the following markers: CD9, CD10, CD13, CD29, CD44, CD49A, CD51, CD54, CD55, CD58, CD59, CD90 and CD105 and because it lacks expression of the following markers: CD11b, CD14, CD15, CD16, CD31, CD34, CD45, CD49f, CD102, CD104, CD106 and CD133.
Owner:AUTONOMOUS UNIVERSITY OF MADRID +1
Stem Cell Populations and Methods of Use
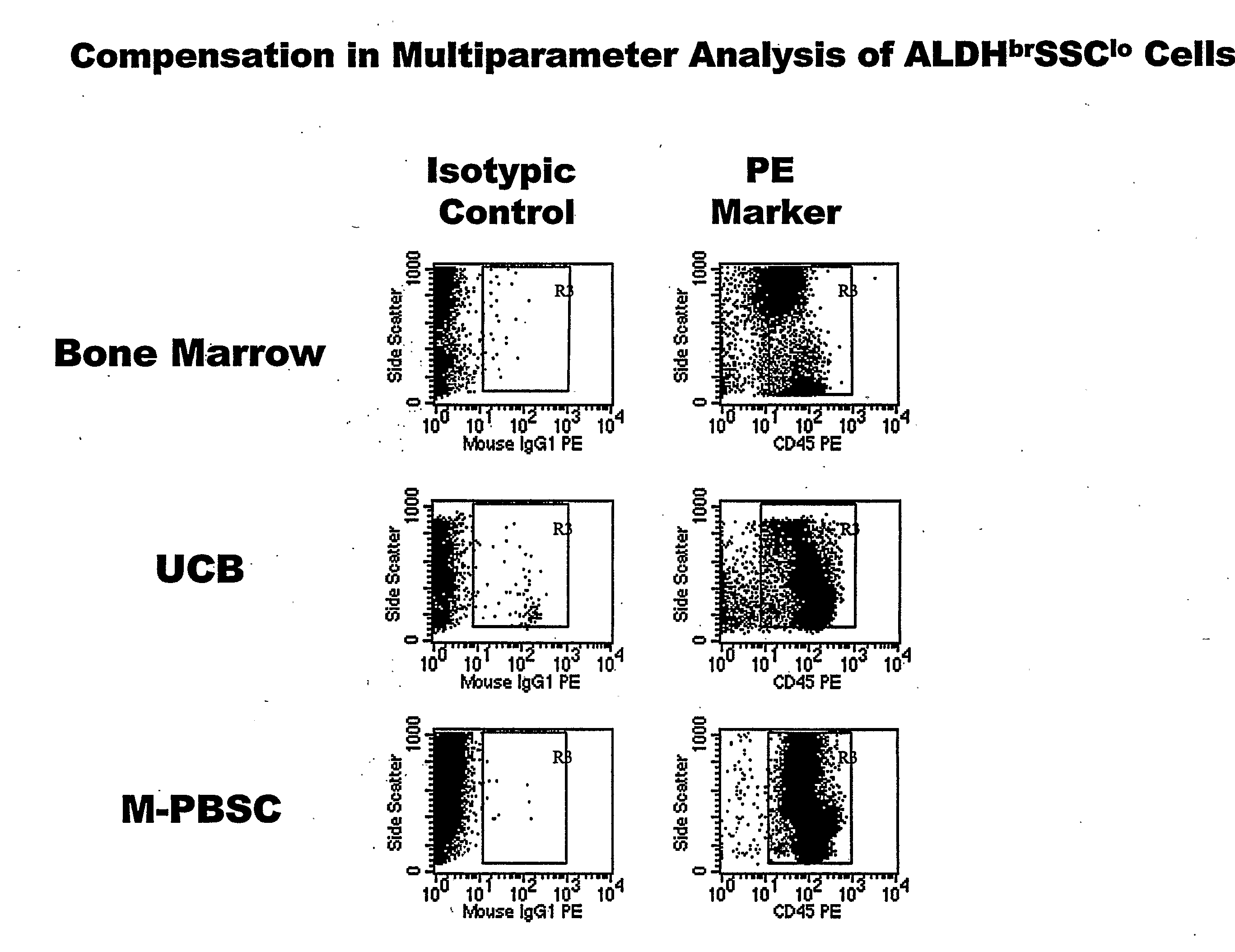
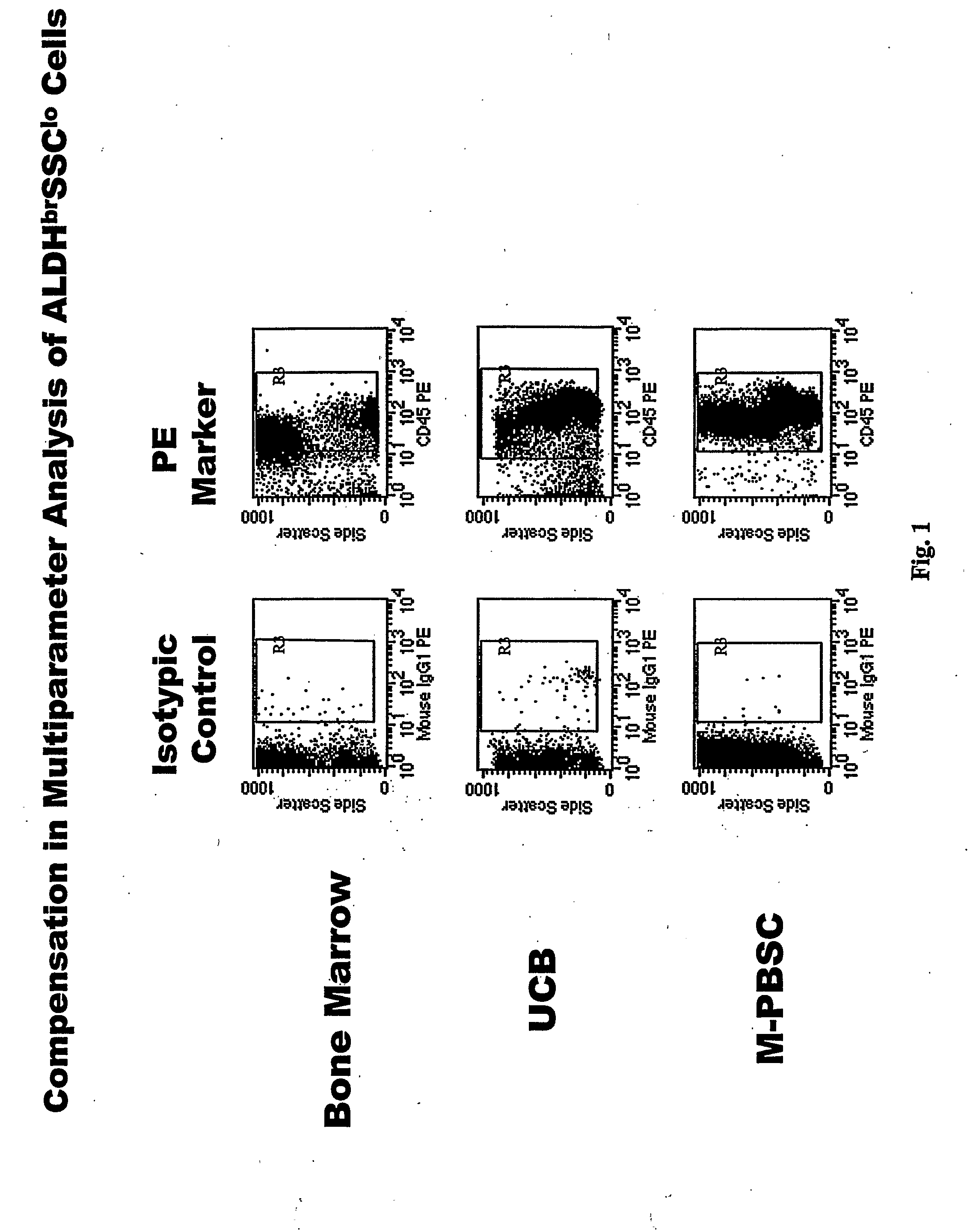
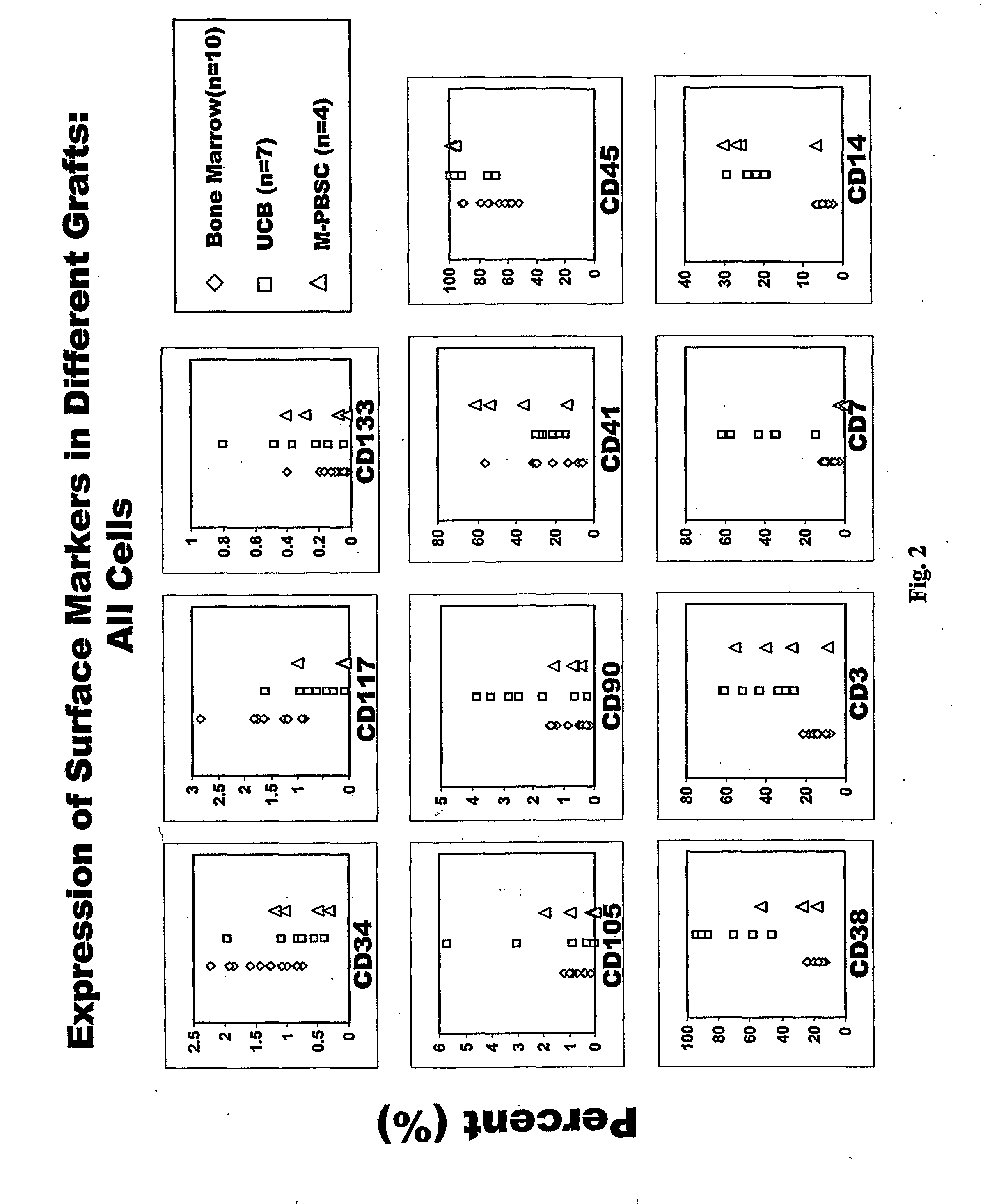
Populations of stem cells and methods for their isolation and use are provided. These stem cell populations comprise aldehyde dehydrogenase positive (ALDHbr) cells isolated from bone marrow, and ALDHbr CD105+ cells derived from any stem cell source. These populations may also comprise cells expressing such surface markers as CD34, CD38, CD41, CD45, CD105, CD133, CD135, CD117, and HLA-DR, and / or are substantially free from such cell surface markers as CD3, CD7, CD 10, CD 13, CD 14, C1319, CD33, CD35, CD56, CD 127, CD 138, and glycophorin A. The population may also comprise cells expressing CD90. The stem cell populations of the invention are isolated from a stem cell source such as bone marrow, peripheral blood, umbilical cord blood, and fetal liver. Methods of the invention comprise isolating and purifying stem cell populations from stem cell sources, and methods of using these cells to reconstitute, repair, and regenerate tissues.
Owner:ALDAGEN
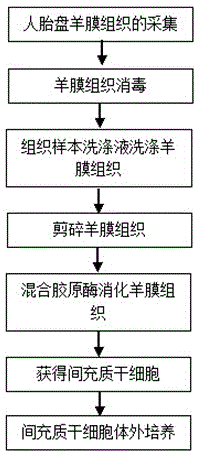
Isolated culture method of human amnia mesenchymal stem cells
InactiveCN105062959AGood repeatabilityShort training periodSkeletal/connective tissue cellsEmbryonic cellsDigestionCancer research
The invention discloses an isolated culture method of human amnia mesenchymal stem cells, which comprises the following steps: carrying out human placenta amnia tissue acquisition, amnia tissue disinfection, washing, shredding and mixed collagenase digestion to obtain mesenchymal stem cells, and carrying out mesenchymal stem cell in-vitro culture. The method can obtain abundant mesenchymal stem cells, which have the advantages of uniform and stable phenotype and high multiplication capacity and have the multidirectional differentiation potential, from the human amnia tissues; and the culture medium in-vitro amplification is performed to purify the cells, thereby satisfying the quantity for cryopreservation or clinical use. The method has the advantages of short cell culture period and high repetitiveness. The stem cells obtained by the method have the phenotypes of CD105<+>, CD90<+> and CD73<+>.
Owner:GENESIS STEMCELL REGENERATIVE MEDICINE ENG CO LTD
Multipotent stem cells and uses thereof
ActiveUS20110070205A1Easily attainable embryonic-likePromote wound healingBiocideNervous disorderGerm layerMHC class I
The invention provides a quiescent stem cell having the capacity to differentiate into ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm, and which does not express cell surface markers including MHC class I, MHC class II, CD44, CD45, CD13, CD34, CD49c, CD73, CD105 CD90, CD66A, CD66E, CXCR4, CD133 or an SSEA. The invention further provides a proliferative stem cell, which expresses genes including Oct-4, Nanog, Sox2, GDF3, P16INK4, BMI, Notch, HDAC4, TERT, Rex-1, TWIST, KLF-4 and Stella but does not express cell surface markers including MHC class I, MHC class II, CD44, CD45, CD13, CD34, CD49c, CD73, CD105, CD90, CD66A, CD66E, CXCR4, CD133 or an SSEA. The cells of the invention can be isolated from adult mammals, have embryonic cell characteristics, and can form embryoid bodies. Methods for obtaining the stem cells, as well as methods of treating diseases and differentiated the stem cells, are also provided.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Multipotent stem cells and uses thereof
InactiveUS20100291042A1Easily attainable embryonic-likePromote wound healingBiocidePancreatic cellsDiseaseMHC class I
The invention provides a quiescent stem cell having the capacity to differentiate into ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm, and which does not express cell surface markers including MHC class I, MHC class II, CD44, CD45, CD13, CD34, CD49c, CD73, CD105 and CD90. The invention further provides a proliferative stem cell, which expresses genes including Oct-4, Nanog, Sox2, GDF3, P16INK4, BMI, Notch, HDAC4, TERT, Rex-1 and TWIST but does not express cell surface markers including MHC class I, MHC class II, CD44, CD45, CD13, CD34, CD49c, CD73, CD105 and CD90. The cells of the invention can be isolated from adult mammals, have embryonic cell characteristics, and can form embryoid bodies. Methods for obtaining the stem cells, as well as methods of treating diseases and differentiated the stem cells, are also provided.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Cells for therapy of the heart, method of obtaining a cell preparation, and cell preparation
InactiveUS20100040587A1Improving patient ' cardiac outputHigh outputBiocideCell dissociation methodsMedicineFibroblast
Fibroblast-like cells obtained from heart muscle biopsies, which are CD90 negative, CD105 positive, CD117 negative and / or CD166 positive as well as cell preparations of such cells for therapy of heart diseases, as well as a method for providing the latter. The cells are characterized by a good cultivability in cell culture. Furthermore a method for obtaining the cells and cell preparations according to the invention are disclosed.
Owner:CHARITE UNIVS MEDIZIN BERLIN
Method for separating and culturing umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells
ActiveCN104630144AIncrease growth rateHigh recovery rateSkeletal/connective tissue cellsPrimary cellBottle
The invention provides a method for separating and culturing umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells. The method comprises the steps of carrying out secondary separation on umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells by using a separating medium, and then inoculating the umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells into a culture bottle in which fibronectin and CD90 monoclonal antibodies are coated; and culturing for 4-5 days by using a serum-free culture system and simulating the in-vivo low-oxygen growth environment of the mesenchymal stem cells, then, removing suspension cells, further culturing adherent cells, and subculturing after the fusion rate of primary cells is up to 60%. By using the method for separating and culturing umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells, provided by the invention, the problems of adherence infirmness, low culture success rate, low purity and the like caused in the extraction and culture processes of the umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells are effectively solved, and the safety in clinical application is improved. In addition, the application ranges of the umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells are widened, the utilization values of the umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells are developed, and the clinical application prospects of the umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells are widened.
Owner:中国医科大学 +1
Macs-based purification of stem cell-derived retinal pigment epithelium
Provided herein are methods of enriching a retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cell population derived from stem cells. Such a method may comprise removing contaminating cells through the depletion of CD24 positive cells, CD56 positive cells, and / or CD90 positive cells from a starting population of RPE cells.
Owner:FUJIFILM CELLULAR DYNAMICS INC
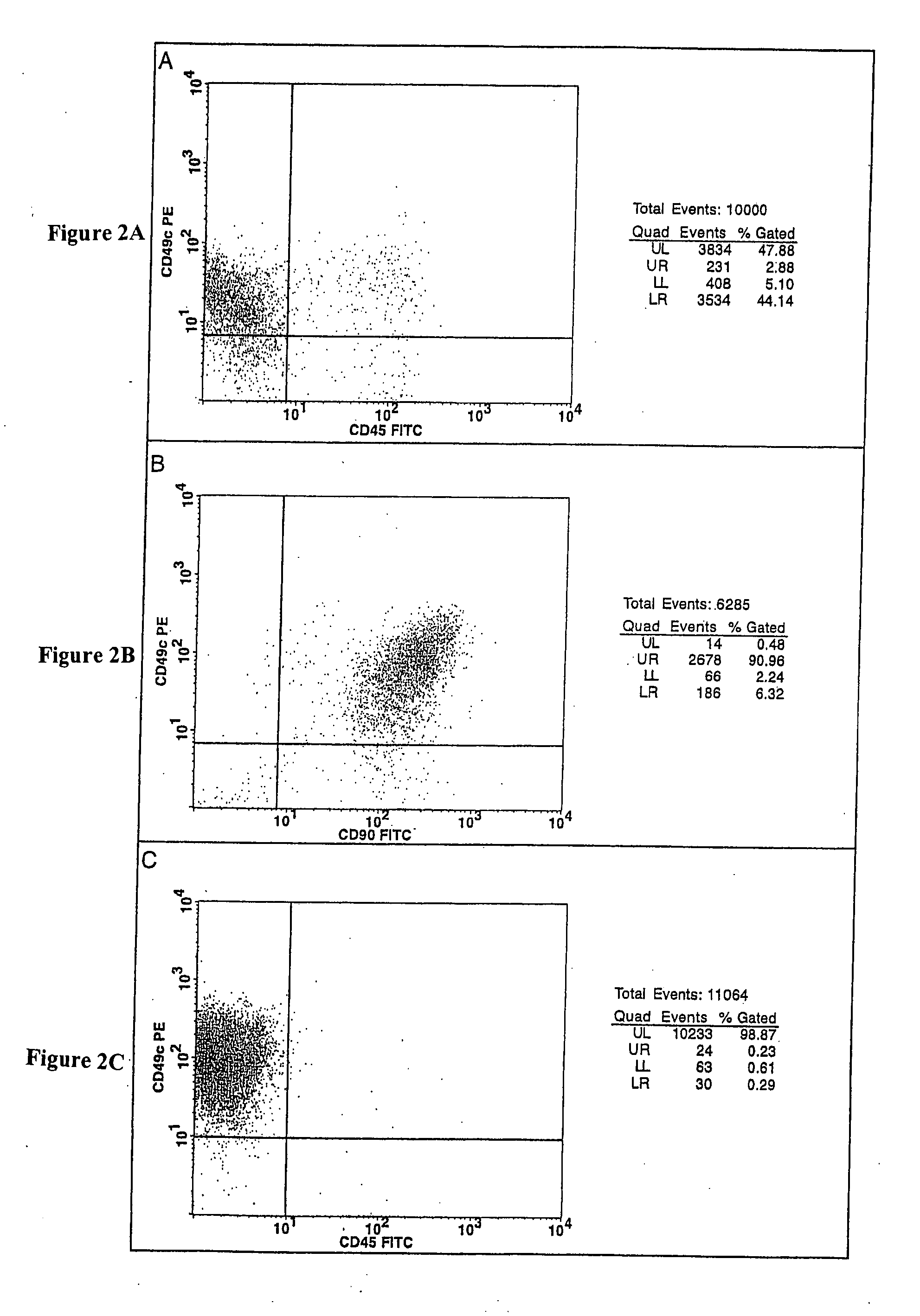
Cell populations which co-express CD49c and CD90
InactiveUS20070231309A1Promote repairIncreasing quality of life and life expectancyBiocideBone marrow stroma cellsTelomeraseProgenitor
Substantially homogenous cells populations which co-express CD49c, CD90 and telomerase are made. In one embodiment, humans suffering from a degenerative, traumatic, acute injury, cardiac or neurological condition are treated with the substantially homogenous cells populations which co-express CD49c, CD90 and telomerase. In another embodiment, committed progenitor cells are made are made by selecting from a cultured source of a cell population which co-express CD49c and CD90 and modifying the cell population. The committed progenitor cells can be employed to treat a human suffering from a degenerative, traumatic, acute injury cardiac or neurological condition and formulate pharmaceutical compositions.
Owner:GARNET BIOTHERAPEUTICS
Regenerative Dot cells
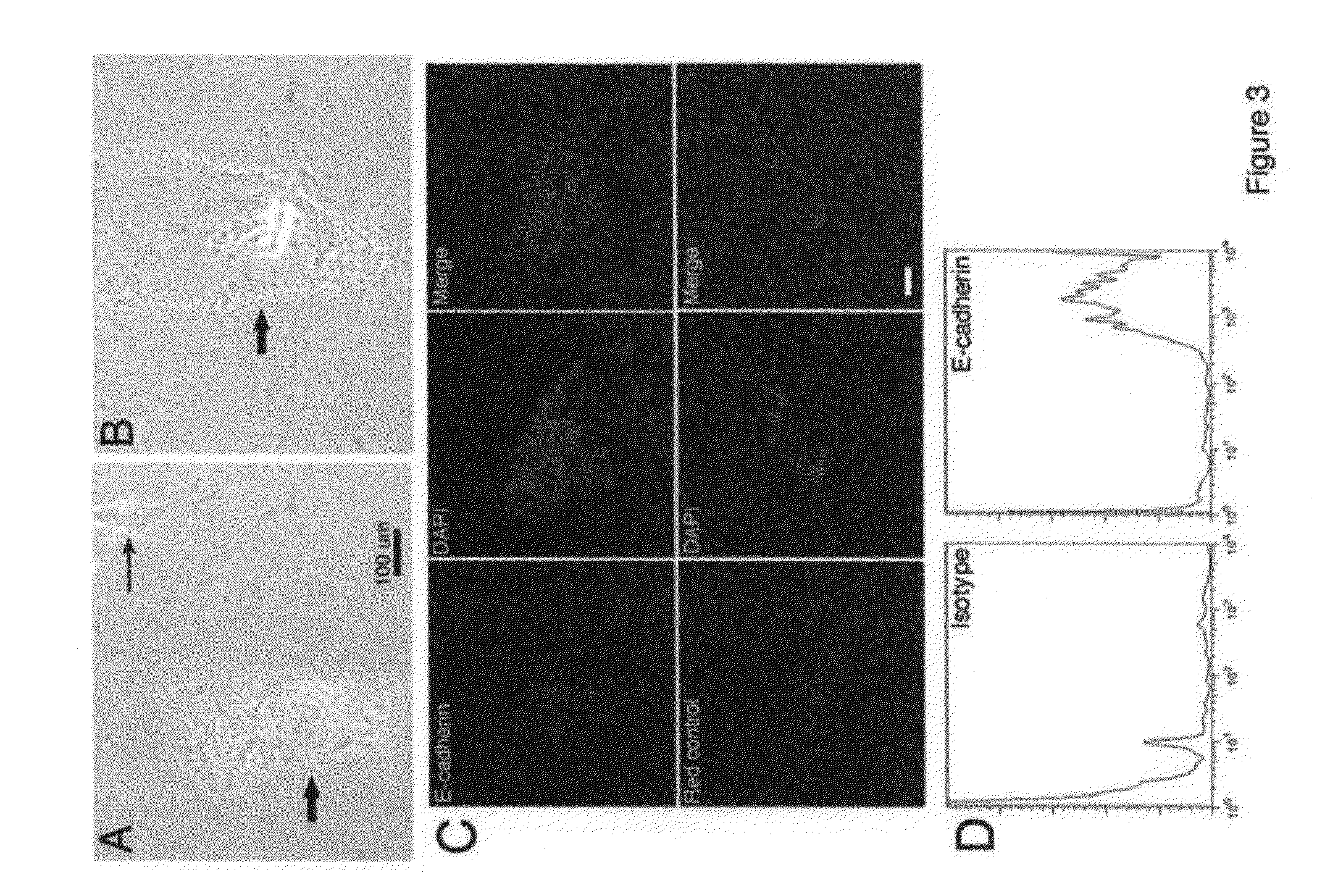
InactiveUS20090155226A1Promote regenerationBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsCXCR4Mammalian cell
Methods and compositions are provided for the isolation, culture and use of highly regenerative somatic mammalian cells. The cells are very small, and have an undefined nuclear structure. The cells may be isolated from fetal or adult tissues, and are found in tissue including, without limitation, fetal dermal tissue, blood, and bone marrow. The cells are characterized as expressing one or more markers selected from E-cadherin, integrin β1, CXCR4, CD90 and CD34, and may be selected on the basis of such expression patterns.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
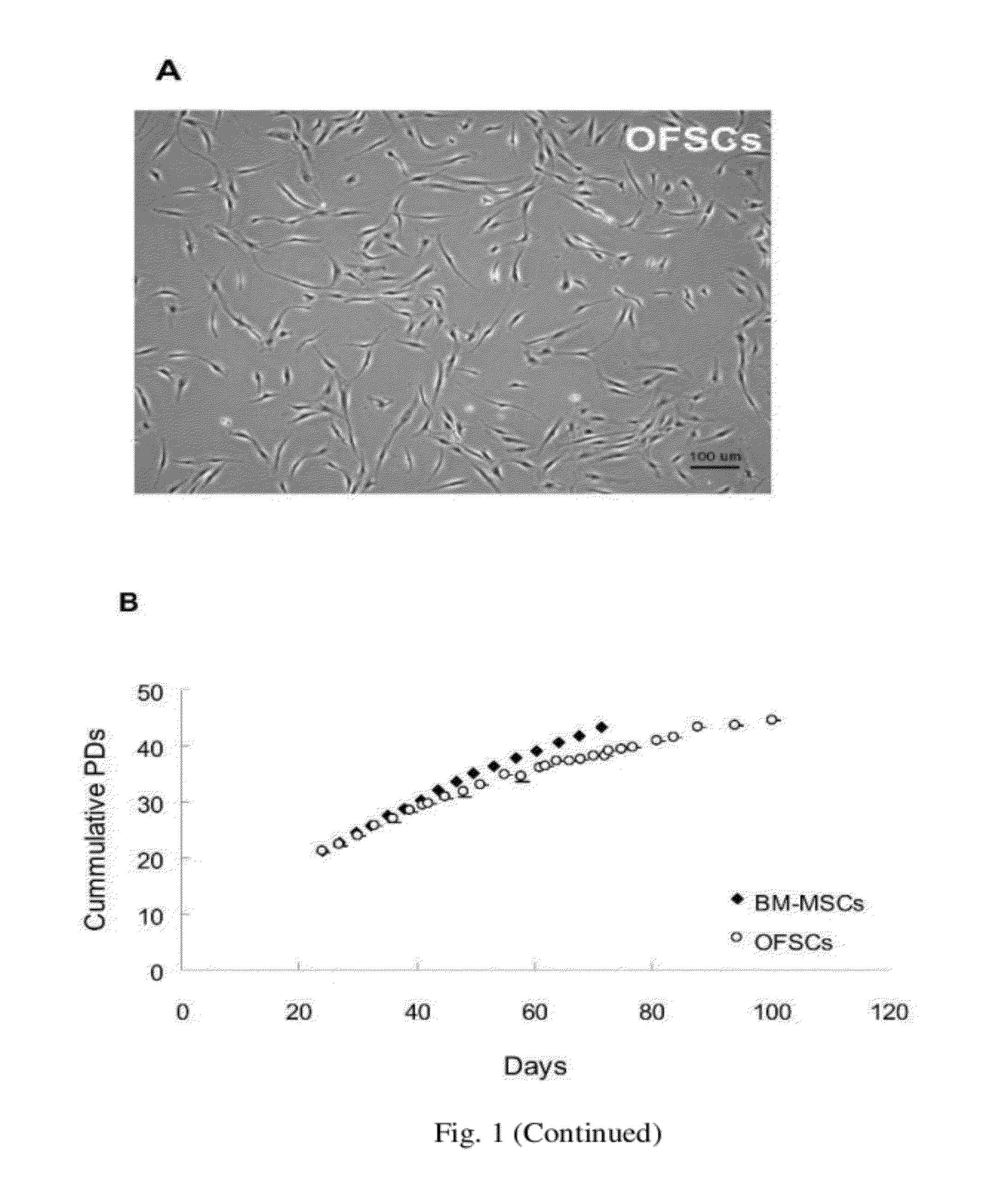
Cell population comprising orbital fat-derived stem cells (OFSCS) and their isolation and applications
The invention relates to a cell population comprising minimal volume of orbital fat-derived stem cells (OFSCs) and its isolation, purification, characterization and application. The OFSCs of the invention are capable of multilineage development and express at least CD90 and CD 105 but not hematopoietic and epithelial markers. The OFSCs have colony formation ability and multi-lineage differentiation ability. They possess at least osteogenic, chondrogenic and adipogenic differentiation capacity; besides mesodermal tri-linage differentiation, the OFSCs have corneal epithelial differentiation potential. Taking together, orbital fat tissues are a novel source for multi-potent stem cells which possess multiple therapeutic potential. Therefore, the OFSCs can be used in cell therapy and tissue engineering.
Owner:TAIPEI MEDICAL UNIV
Stem cell preparation for treating primary liver cancer and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103861088AImprove survivalGood conditionPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemSolventImmunogenicity
The invention discloses a stem cell preparation for treating primary liver cancer and a preparation method thereof. The preparation contains (60-100)*10<6> pieces / ml of mesenchymal stem cells, 20ng / ml of HGF and 10ng / ml of FGF-4, and takes autologous platelet-rich plasma lysate as a solvent. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (1) collecting an umbilical cord, and carrying out primary culture to obtain cells; (2) detecting by using a flow cytometry, wherein such cells express CD29, CD73, CD90 and CD105; (3) collecting cells, namely dissolving (60-100)*10<6> mesenchymal stem cells of the human umbilical cord in 1 ml of autologous platelet-rich plasma lysate, and adding 20ng of HGF and 10ng of FGF-4 to be prepared into 1 ml of a stem cell preparation. According to the stem cell preparation disclosed by the invention, the source of raw materials is rich, the raw materials are easy to obtain, the umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells are weakly immunogenic, and platelet-rich plasma is taken from the patients, so no immunogenicity exists.
Owner:奥思达干细胞有限公司
Compositions and methods of treating no-option critical limb ischemia (CLI)
InactiveUS20120100108A1Improve the quality of lifeImprove mobilityBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsTissue repairGangrene
The present invention provides methods for treating critical limb ischemia (CLI), including increasing wound healing, decreasing wound size, increasing survival-free amputation, preventing amputation, preventing or delaying de novo gangrene, increasing survival probability, and preventing or delaying death, in subjects who prevent a vascular occlusion that cannot be resolved by using a standard method of revascularization, i.e. a subject with “no-option” CLI. Methods of the invention include administering to a subject with no-option CLI an isolated cell composition for tissue repair comprising a mixed population of cells of hematopoietic, mesenchymal and endothelial lineage, wherein the viability of said cells is at least 80% and the composition contains: a) about 5-75% viable CD90+ cells with the remaining cells in said composition being CD45+; b) less than 2 μg / ml of bovine serum albumin; c) less than 1 μg / ml of a enzymatically active harvest reagent; and d) substantially free of mycoplasma, endotoxin, and microbial contamination.
Owner:AASTROM BIOSCI
Purifying method of adipose-derived stem cells and application of stem cells on osteogenic induction and chondrogenesis
ActiveCN106047804AImprove efficiencyImprove repair effectCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsTissue engineeringDerived stem
The invention provides a purifying method of adipose-derived stem cells. The method comprises the following steps: primary adipose-derived stem cell culture and CD90+ cell population purification. The invention further provides application of the purified adipose-derived stem cells in the aspects of osteogenic induction and chondrogenesis. Obtained CD90+ cell population in ADSCs has high stem cell differentiative potential, using efficiency and repairing effect of ADSCs in tissue engineering can be improved, and under the same induction condition, osteogenesis and chondrogenesis are improved by 3-5 times and 5-7 times respectively.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Adult mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) compositions and methods for preparing the same
The described invention provides a composition comprising mesenchymal progenitor cells (MPC) and processes for isolating or enriching the mesenchymal progenitor cells (MPCs) having a cell surface antigenic profile of CD34(−) / CD133(−) / CD45(−) / CD73(+) / CD90(+) / CD105(+) / CD44(−). The described invention also provides methods for differentiating the mesenchymal progenitor cells (MPCs) into various cell types.
Owner:NEOSTEM
Human placenta mesenchymal stem cell suspension protection agent
The invention discloses a human placenta mesenchymal stem cell suspension protection agent, which is prepared from the following ingredients including human serum albumin, mycose, vitamin C, dextran sodium chloride injection and NaCl solution for injection. The preparation of the human placenta mesenchymal stem cell suspension protection agent is completed through the steps of basic solution preparation, ingredient addition and storage. The activity, the dryness performance and the uniformity of the placenta mesenchymal stem cells can be effectively maintained; the ingredients are specific; the different source animal serum is not contained; the safety is high; in addition, the storage method provided by the invention can effectively maintain the stem cell activity; high efficiency and time saving are realized; the scaled production is facilitated; experiments show that after the human placenta mesenchymal stem cells are stored in the cell storage agent for 48h at 4 to 8 DEG C; the cellular morphology is uniform; the survival rate is still maintained at a value being 90 percent or higher; the mesenchymal stem cell specific surface mark CD73, CD105 and CD90 expression rate is higherthan 95 percent.
Owner:GENESIS STEMCELL REGENERATIVE MEDICINE ENG CO LTD
Multipotent stem cells and uses thereof
ActiveUS8574567B2Easily attainable embryonic-likePromote wound healingBiocideNervous disorderMHC class ISurface marker
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Thy1 (CD90) as a novel therapy to control adipose tissue accumulation
The present invention relates to methods of treating a condition involving excessive adipogenesis. This method relates to selecting a subject having a condition involving excessive adipogenesis and administering to the selected subject a composition comprising a Thy1 protein or polypeptide fragment thereof, or an agent that enhances Thy1 expression, under conditions effective to treat the condition. The present invention also relates to isolated nucleic acid molecules encoding a Thy1 protein or the fragment thereof and pharmaceutical formulations including such a protein or fragment thereof or an agent that enhances Thy1 expression and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The present invention also relates to methods of inhibiting adipogenesis and / or decreasing adipocyte size, as well as methods of screening a candidate compound for its ability to influence adipogenesis.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
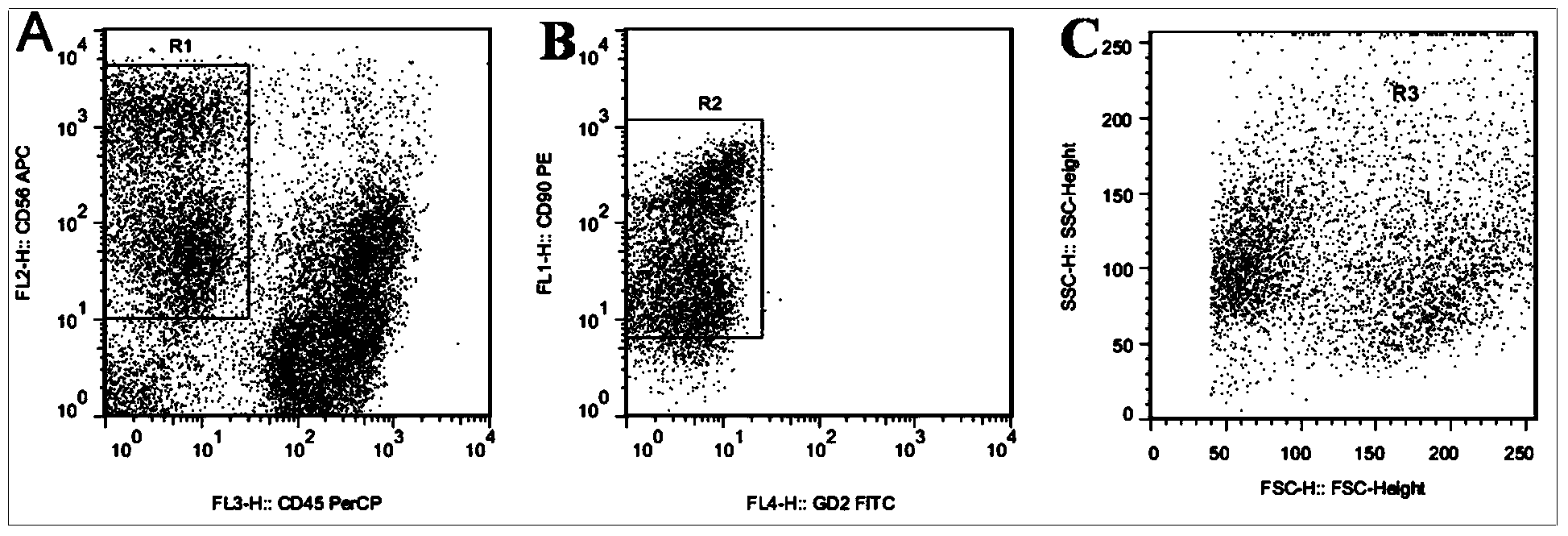
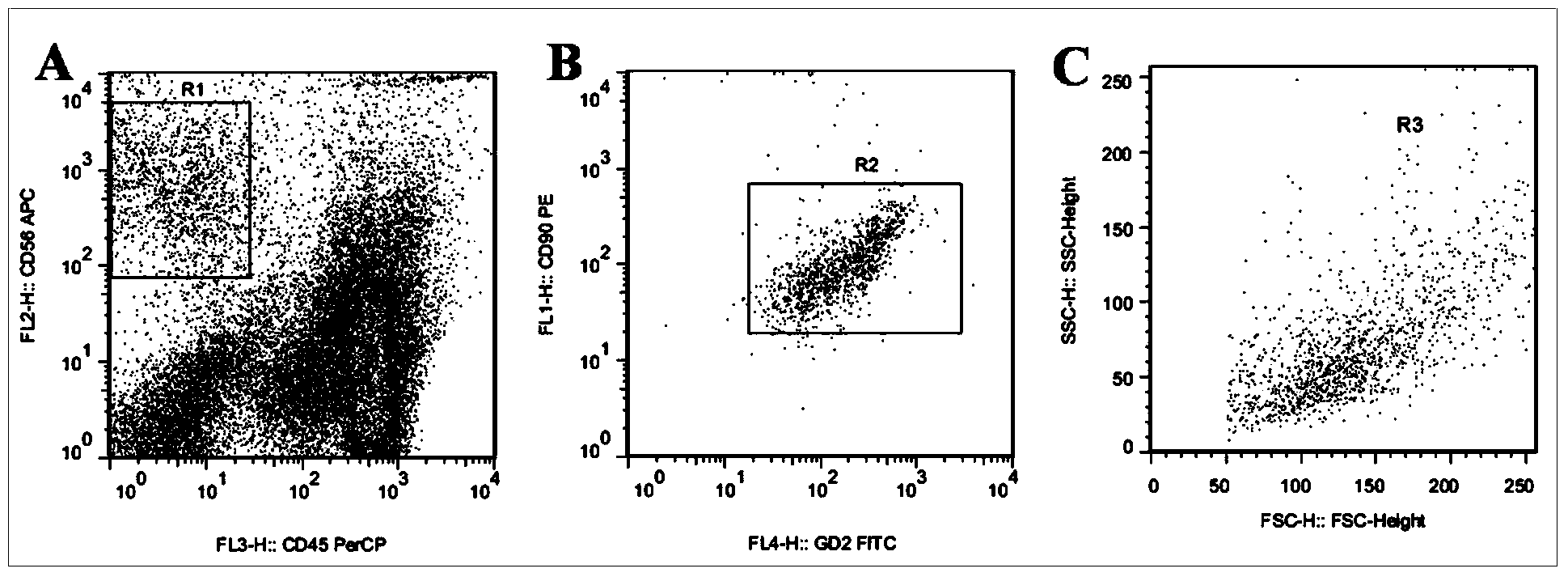
Fluorescent probe and kit for carrying out differential diagnosis on leukemia and bone marrow metastasis of rhabdomyosarcoma and neuroblastoma by using flow cytometry
InactiveCN103675277ANo cross reactionImprove featuresIndividual particle analysisFluorescenceAcute leukemia
The invention discloses a fluorescent probe and a kit for carrying out differential diagnosis on leukemia and bone marrow metastasis of rhabdomyosarcoma and neuroblastoma by using flow cytometry. The fluorescent probe comprises four fluorescence labeled antibodies; the four fluorescence labeled antibodies comprise a GD2 antibody, a CD90 antibody, a CD45 antibody and a CD56 antibody which take fluorescence labels; the different antibodies take the different fluorescence labels. The kit comprises a probe solution, a hemolytic agent, a phosphate buffer and a positive standard product. The fluorescent probe can be respectively and specifically combined with cells of the rhabdomyosarcoma and the neuroblastoma in bone marrow and original cells of acute leukemia; three tumor cells which are common in the child bone marrow, such as the bone marrow metastasis of the rhabdomyosarcoma and the neuroblastoma and the leukemia cells, can be rapidly and accurately identified by the flow cytometry, so as to guide clinical treatment; the application prospect is very good.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
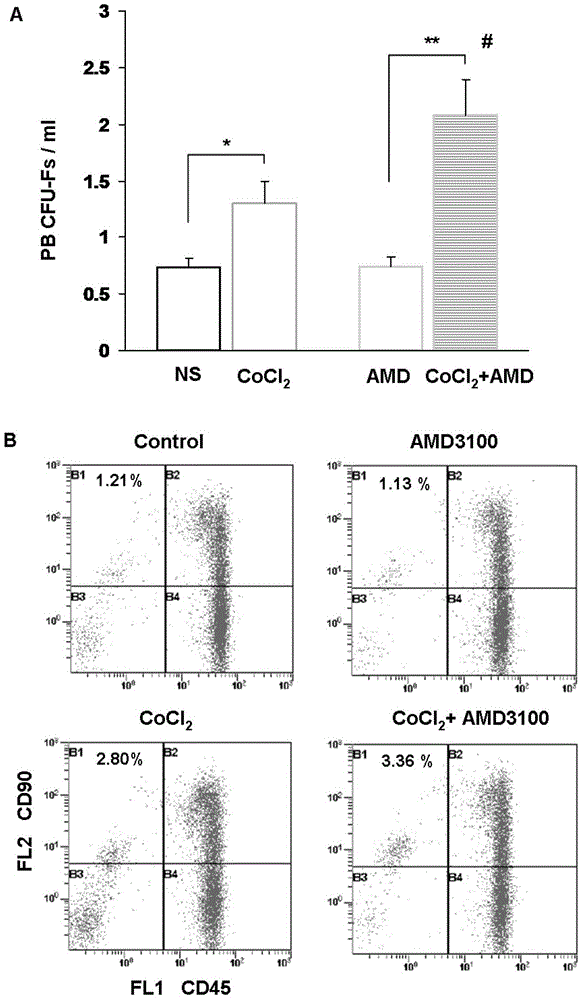
Preparation for mobilizing mesenchymal stem cells and method for separating mesenchymal stem cells
InactiveCN103146646AHigh mobilization efficiencySkeletal/connective tissue cellsLymphocytic cellRegenerative medicine
The invention provides a preparation for mobilizing mesenchymal stem cells and a method for separating the mesenchymal stem cells. The preparation for mobilizing the mesenchymal stem cells comprises CoCl2, wherein the CoCl2 is a hypoxia mimetic agent, and the dosage is in a range of 5-20mg / kg. The CoCl2 and AMD3100 are used in a combined manner. The dosage of the AMD3100 is 5mg / kg. According to the method for separating the mesenchymal stem cells by using the preparation, the preparation is used for actuating the mesenchymal stem cells to be mobilized, enter peripheral blood and then be separated. The method comprises the following separation steps of: sampling the periphery blood, separating mononuclear cells by using a lymphocyte separating medium, performing resuspension by using a DMEM (dulbeccos modified eagle medium) containing 20% of fetal bovine serum, inoculating to a culture flask, culturing for 7 days, and changing a culture solution, thus obtaining the mesenchymal stem cells of the peripheral blood on the 10th day. The mesenchymal stem cells of the peripheral blood highly express CD90, CD29 and CD44, do not express CD45 and CD34, and have the capacities of in vitro bone formation, fat formation and cartilage differentiation formation. The preparation is high in MSCs (mesenchymal stem cells) mobilization efficiency, and an effective preparation and an effective method are provided for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Diagnosis of anemia and optimizing treatment for heart repair
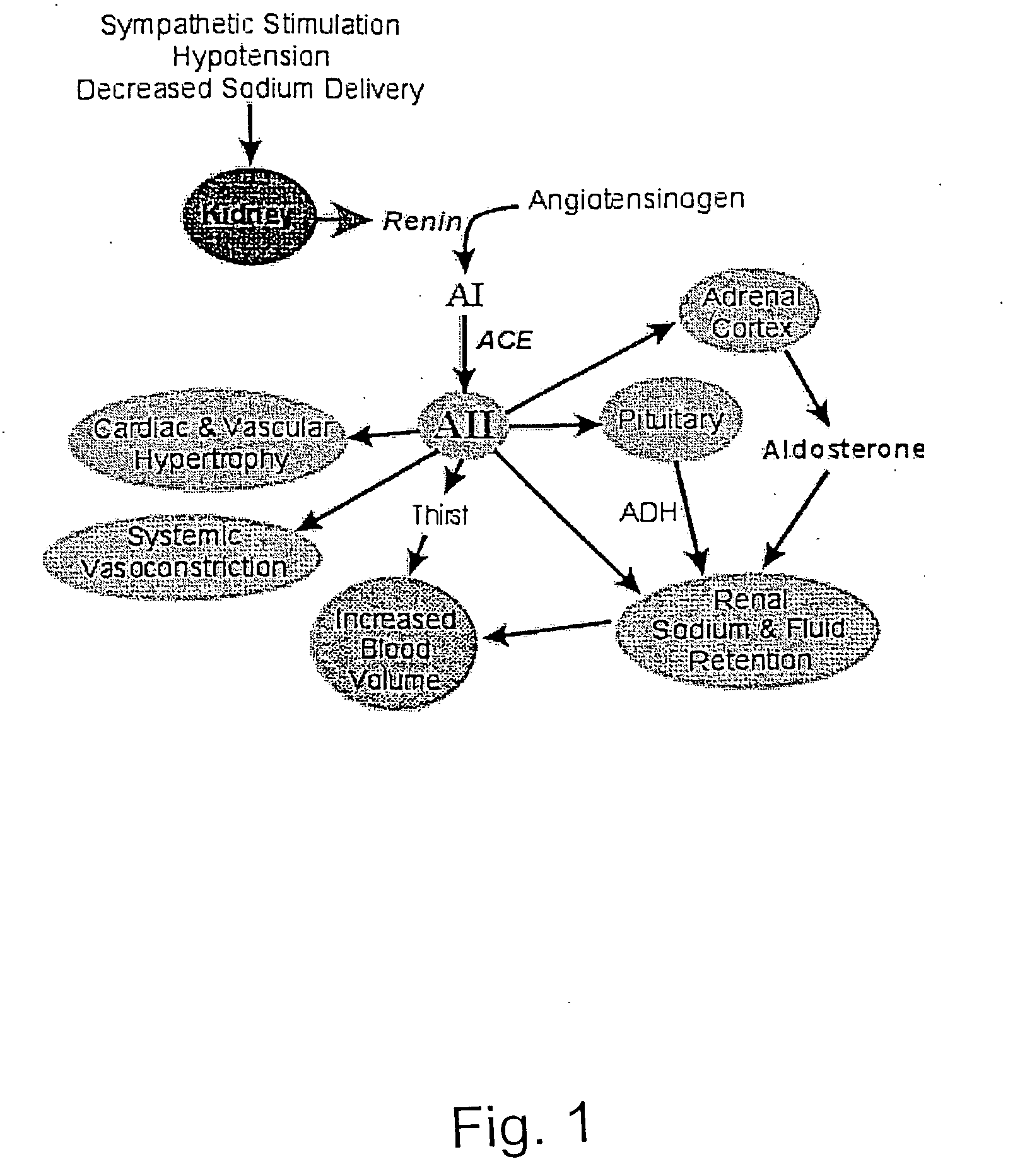
InactiveUS20060046268A1Good curative effectIncrease vascularizationDisease diagnosisBiological testingHeart repairCell Surface Proteins
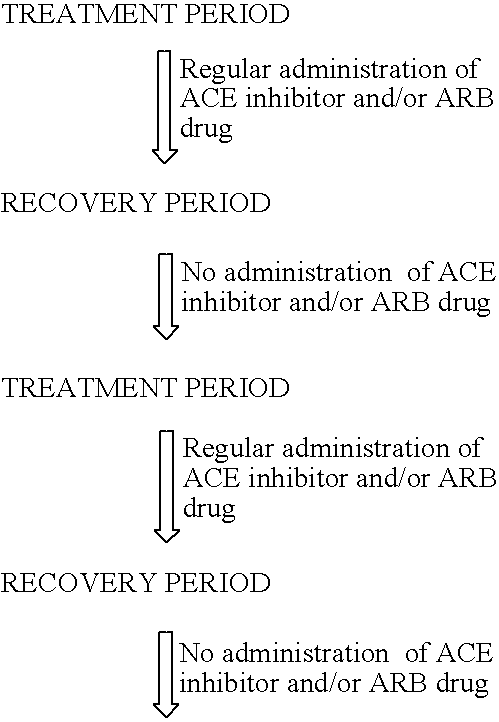
A method of diagnosis of anemia is disclosed whereby blood is withdrawn from a patient and the level of hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) in the blood are determined by detecting a cell surface protein chosen from ACE+, CD34+, CD38, CD90+ (thyl) and Lin−. Patients with low levels of HSC are treated and in particular patients whose levels have been reduced by drugs such as ACE inhibitors are treated using an intermittent treatment regimine of the invention.
Owner:AUSTRALIAN STEM CELL CENT
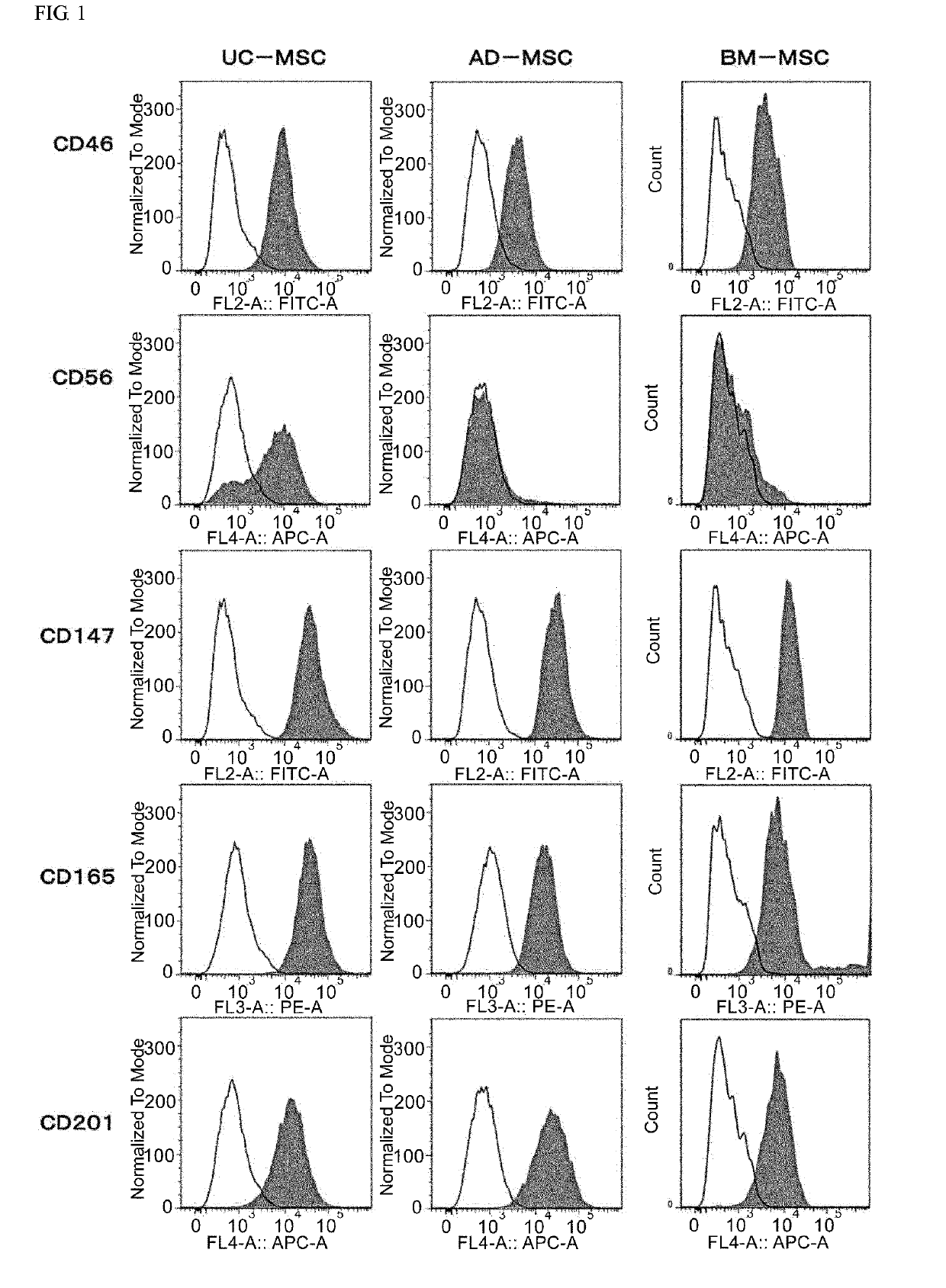
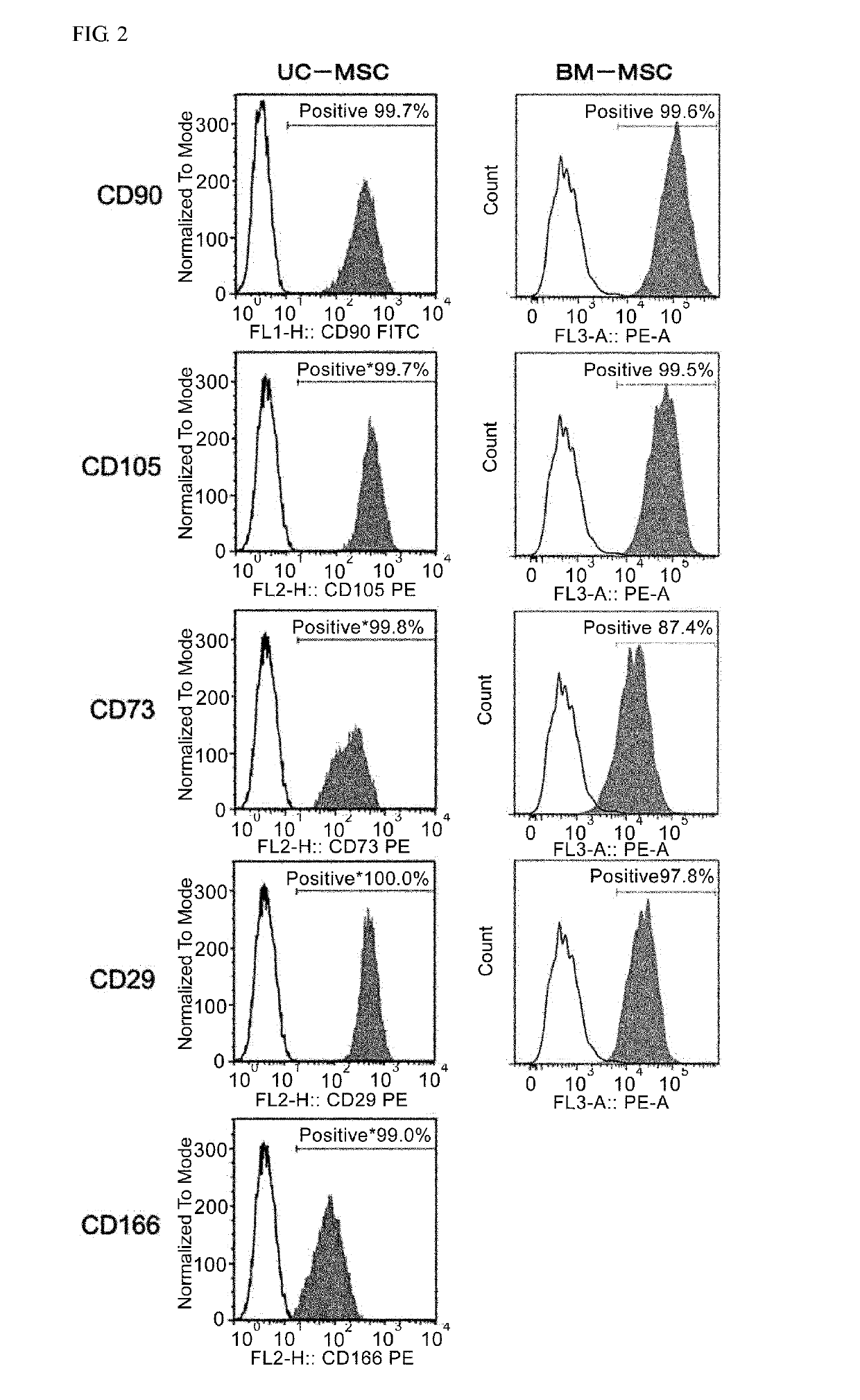
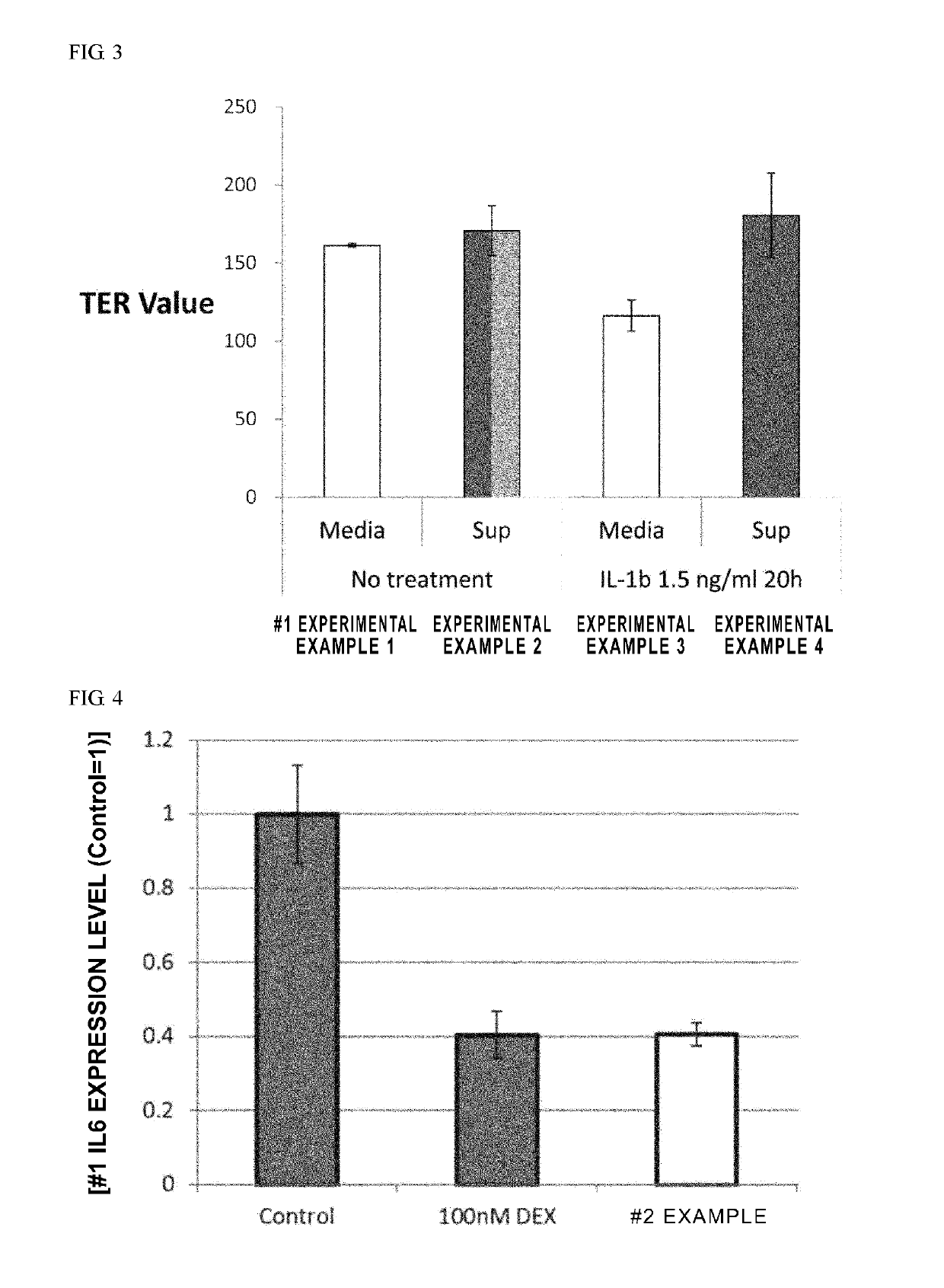
Mesenchymal stem cell expressing at least one cell surface marker selected from the group consisting of cd201, cd46, cd56, cd147, and cd165, method for preparing the same, pharmaceutical composition containing the mesenchymal stem cells, and method for preparing the same
An object of the present invention is to provide novel mesenchymal stem cells demonstrating superior therapeutic effects for various diseases, a novel pharmaceutical composition containing the mesenchymal stem cells, and methods for preparing these. The present invention provides mesenchymal stem cells expressing at least one cell surface marker selected from the group consisting of CD201, CD46, CD56, CD147 and CD165. The mesenchymal stem cells expressing such a specific marker are positive for CD29, CD73, CD90, CD105 and CD166, and maintain an undifferentiated state.
Owner:ROHTO PHARM CO LTD
Ror1-positive mesenchymal stem cells and method for preparing same, pharmaceutical composition containing ror1-positive mesenchymal stem cells and method for preparing same, and method for preventing or treating diseases by using ror1-positive mesenchymal stem cells
ActiveCN108350427ANot easy to damageImprove mobilityMetabolism disorderGenetically modified cellsDiseaseMedicine
The purpose of the present invention is to provide: new mesenchymal stem cells having excellent therapeutic effect on various diseases, a new pharmaceutical composition containing the mesenchymal stemcells, and a method for preparing the same. The present invention is ROR1-positive mesenchymal stem cells. Preferably, the ROR1-positive mesenchymal stem cells are CD29-, CD73-, CD90-, CD105-, and CD166-positive, and are derived from an umbilical cord or fat.
Owner:ROHTO PHARM CO LTD
Hepatic progenitor cells and uses thereof
The invention provides a preparation method and uses of hepatic progenitor cells. The preparation method comprises acquiring processed materials having cultured multifunctional zooblasts. The processed materials show a positive reaction to the mark of a group selected from CD29, CD44, CD49b, CD49d, CD73, CD90, CD105, CD 13 and HLA-DR, and shows a negative reaction to the mark of a group selected from CD14, CD34 and CD45. The preparation method also comprises the step of culturing zooblasts and liver tissues in nutrient solution for a certain period of time, and collecting the progeny of the multifunctional zooblasts cultured together to obtain hepatic progenitor cells. The multifunctional zooblasts are Wharton's jelly extracted from an umbilical cord of a first experiment object. The multifunctional hepatic progenitor cells can treat hepatopathy and other relevant problems.
Owner:GWOXI STEM CELL APPL TECH CO LTD
Method for isolating stem cells and their use in cell therapy
The invention relates to a method for isolating muscle-derived stem cells that can be used in cell therapy, said method comprising the steps of (i) dissociating cells from at least one muscle sample, (ii) plating the cells obtained at the end of step (i) on a non-coated cell container, (iii) isolating the cells present in the supernatant of the non-coated cell container obtained at the end of step (ii), (iv) plating the cells obtained at the end of step (iii) on a coated cell container, (v) isolating the cells present in the supernatant of the coated cell container obtained at the end of step (iv), (vi) repeating, or not, the steps (iii) and (iv) at least one or two times, (vii) plating and culturing the cells isolated from the supernatant of the coated cell container obtained at the end of step (vi) until said cells have reached a confluence level of at least 50%, (viii) isolating, at the end of step (vii), the stem cells which can be used in cell therapy, wherein after expansion (a) at least 95% of said cells express CD44, CD73, (b) at least 95% of said cells express CD29, (c) at least 70% of said cells express CD90, and (d) said cells do not express CD4, CD8, CD34, CD45, CD31, CD1 17, CD144 and CD133. The invention also relates to said isolated stem cells and pharmaceutical compositions containing them.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL DE LA RECHERCHE AGRONOMIQUE +1
A method of converting human hematopoietic progenitor cells into hematopoietic stem cells
ActiveCN109207426AIncrease the number ofPotential for lineage differentiationBlood/immune system cellsCell culture active agentsHematopoietic cellHematopoietic progenitor
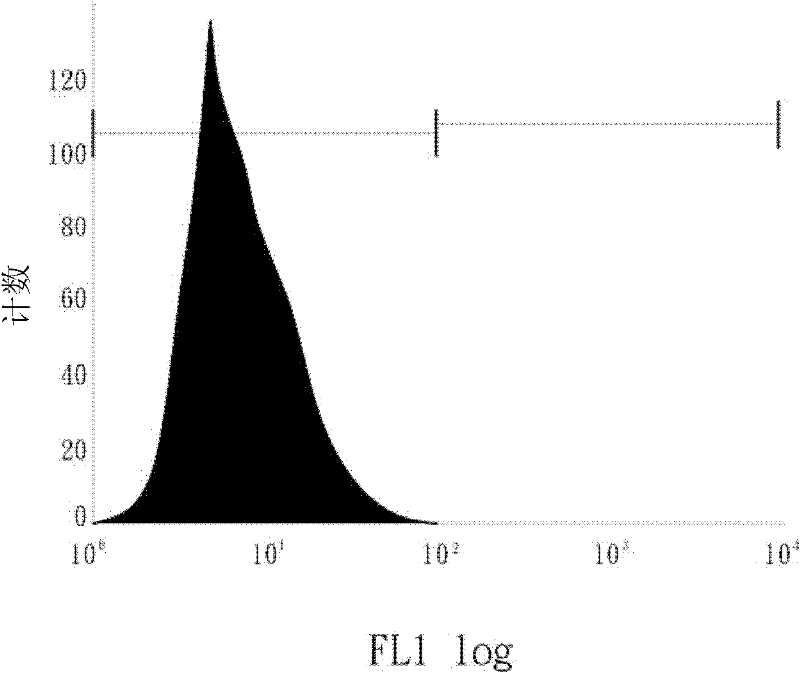
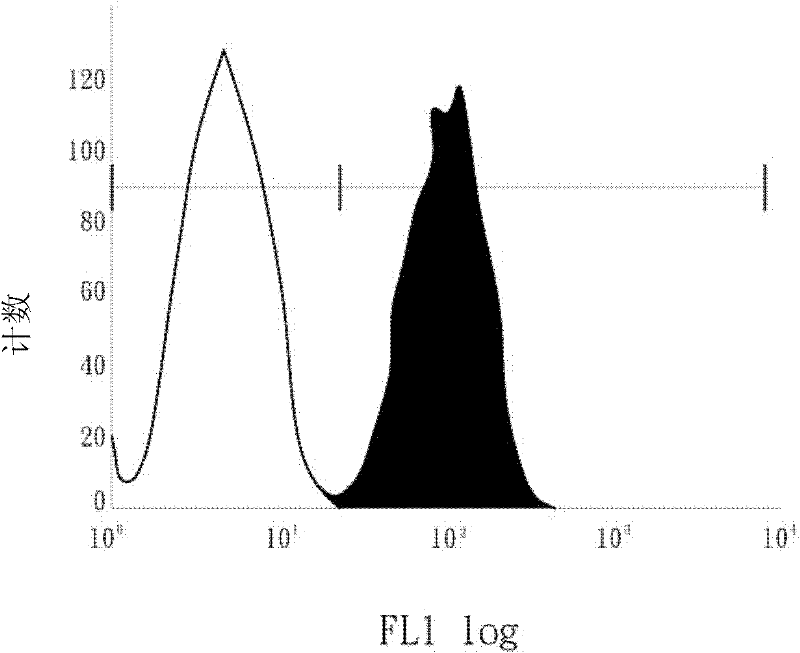
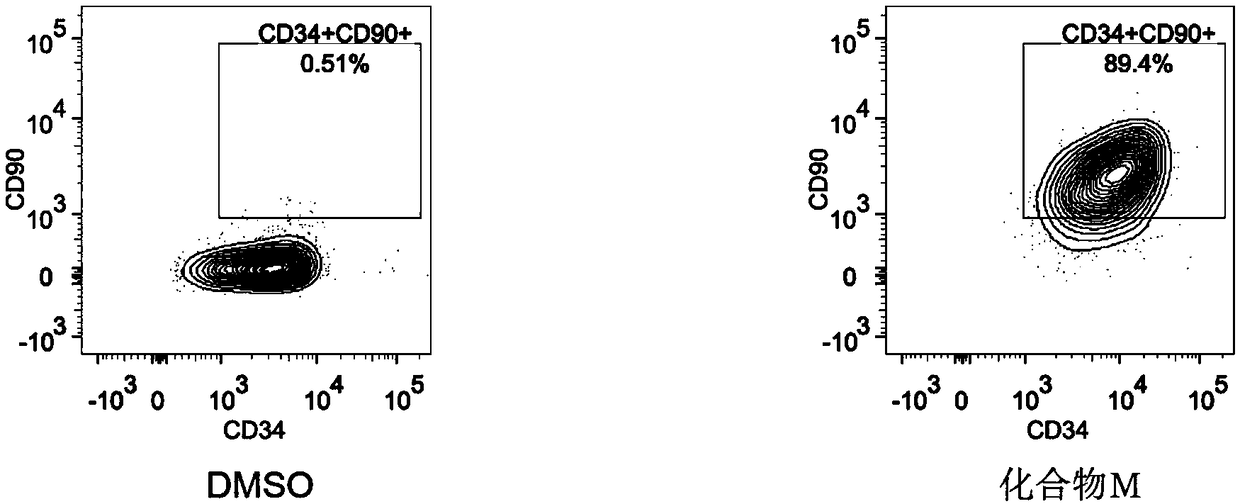
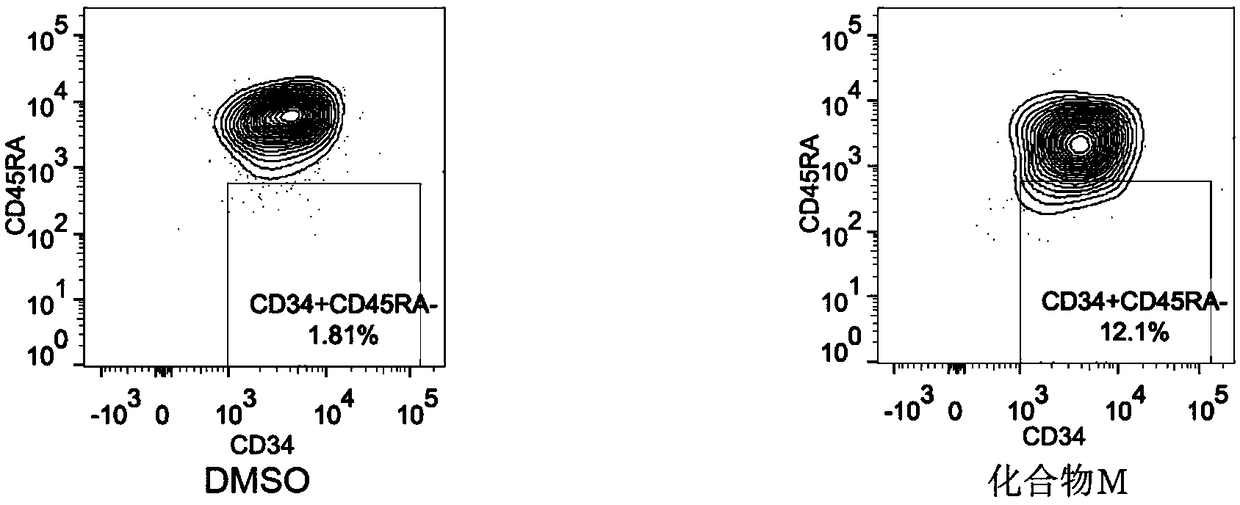
The invention discloses a method for preparing human hematopoietic stem cells by using human hematopoietic progenitor cells, comprising the following steps: S1 preparing CD34+CD90- and CD34+CD45RA+ umbilical cord hematopoietic progenitor cells from human umbilical cord blood; S2) suspending the CD34+CD90- and CD34+CD45RA+ umbilical cord hematopoietic progenitor cells in a medium specially used forumbilical cord hematopoietic stem cells transformation and culturing the cells, the medium adopting a StemSpan SFEM II serum-free culture medium and 100ng / ml SCF, 100ng / ml FLT3 and 50ng / ml TPO beingadded into the medium, wherein the cell seeding density in 24-well plate is 0.55 *10<4> cells / well for CD34+CD90-cells, and 0.13 *10<4> cells / well CD34+CD45RA+ cells; 1[mu]M of MS-275 is added, and culture is performed at 37 DEG C in an incubator with the CO2 concnetration being 5%. The method has the beneficial effects that the hematopoietic stem cells prepared by using the human hematopoietic progenitor cells are high in quantity and have the differentiation potential of each lineage, and can provide a hematopoietic stem cell donor for clinical application.
Owner:NEWISH TECH (BEIJING) CO LTD
Stem cell-based medicinal product for treating diabetes and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN105456293ALow immunogenicityRich sourcesMetabolism disorderSkeletal/connective tissue cellsPharmacy medicineMesenchymal stem cell
The invention discloses a stem cell-based medicinal product for treating diabetes. The stem cell-based medicinal product contains mesenchymal stem cells separated and extracted from the human umbilical cord, the expression of stem cell surface markers CD73, CD90 and CD105 is higher than 95%, and the expression of cell surface markers CD14, CD34, CD45, CD19 and HLA-DR is lower than 3%. The stem cell-based medicinal product can be differentiated into pancreatic beta cells under induction, so that insulin is secreted and blood sugar concentration is effectively reduced, and then a new method is provided for overcoming the defect that diabetes treatment depends on insulin and radically curing diabetes. The invention further provides a method for preparing the stem cell-based medicinal product. The method is easy to operate, raw material sources are wide, ethic limitation is avoided, and large-scale production can be conducted.
Owner:SHENZHEN BEIKE BIOTECH +1
Ror1-positive mesenchymal stem cell-containing pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating disease associated with fibrosis, method for preparing same, and method for preventing or treating disease associated with fibrosis using ror1-positive mesenchymal stem cells
InactiveCN110418645AImprove mobilityGood treatment effectDigestive systemCulture processDiseaseFibrosis
The purpose of the present invention is to provide the following: novel mesenchymal stem cells having an excellent therapeutic effect on various diseases, particularly diseases associated with fibrosis; and a pharmaceutical composition containing such mesenchymal stem cells. The present invention is a therapeutic agent for fibrosis that contains ROR1-positive mesenchymal stem cells and / or a culture supernatant thereof and that is for preventing or treating a disease associated with fibrosis. The mesenchymal stem cells are CD29-, CD73-, CD90-, CD105-, and CD166-positive and are preferably derived from the umbilical cord or fat. In addition, the abovementioned disease associated with fibrosis is preferably a liver disease, a lung disease, a kidney disease, or a heart disease.
Owner:ROHTO PHARM CO LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com