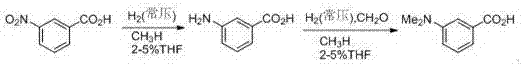
Method for producing m-dimethylaminobenzoic acid
A technology of dimethylaminobenzoic acid and production room, applied in the direction of chemical instruments and methods, preparation of organic compounds, organic chemistry, etc., can solve problems such as unfavorable, large residual hydrogen, and cost reduction, so as to reduce investment cost and save The effect of hydrogen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
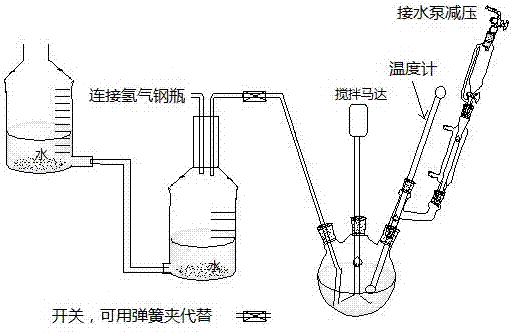
[0014] In a 250mL glass three-neck flask, add 95mL of methanol and 3mL of tetrahydrofuran, 16.7g of m-nitrobenzoic acid, 0.2g of 5% palladium carbon, and add 15.2mL of 37% formaldehyde aqueous solution in a constant pressure dropping funnel. The air in the reaction system was pumped away, and then hydrogen gas at normal pressure was introduced. Raise the temp to 64 o C, stirring the reaction until no more hydrogen is absorbed. Add formaldehyde solution from the dropping funnel, and continue to stir and hydrogenate at this temperature until hydrogen is no longer absorbed. Stirring was stopped, the catalyst was recovered by filtration, the filtrate was concentrated, and the product was precipitated. Collect the product by filtration, wash the product with a small amount of water, and then re-100 o C was dried to obtain 15.3 g of product m-dimethylaminobenzoic acid, and the productive rate was 93%. After the catalyst is recovered, it is washed with a reaction solvent and used...
example 2
[0016] In a 250mL glass three-neck flask, add 100mL of tetrahydrofuran, 16.7g of m-nitrobenzoic acid, 0.2g of 5% palladium carbon, and add 15.2mL of 37% formaldehyde solution in a constant pressure dropping funnel. The air in the reaction system was pumped away, and then hydrogen gas at normal pressure was introduced. Raise the temperature to 66 o C, stirring the reaction until no more hydrogen is absorbed. Add formaldehyde solution from the dropping funnel, and continue to stir and hydrogenate at this temperature until hydrogen is no longer absorbed. Stirring was stopped, the catalyst was recovered by filtration, the filtrate was concentrated, and the product was precipitated. Collect the product by filtration, wash the product with a small amount of water, and then re-100 o C was dried to obtain 15.2 g of product m-dimethylaminobenzoic acid, and the productive rate was 92%. After the catalyst is recovered, it is washed with a reaction solvent and used for the next reacti...
example 3
[0018] In a 250mL glass three-neck flask, add 98mL of methanol and 2mL of butyl ether, 16.7g of m-nitrobenzoic acid, and 0.2g of 5% palladium carbon, and add 15.2mL of 37% formaldehyde aqueous solution into a constant pressure dropping funnel. The air in the reaction system was pumped away, and then hydrogen gas at normal pressure was introduced. Raise the temperature to 65 o C, stirring the reaction until no more hydrogen is absorbed. Add formaldehyde solution from the dropping funnel, and continue to stir and hydrogenate at this temperature until hydrogen is no longer absorbed. Stirring was stopped, the catalyst was recovered by filtration, the filtrate was concentrated, and the product was precipitated. Collect the product by filtration, wash the product with a small amount of water, and then re-100 o C was dried to obtain 14.9 g of product m-dimethylaminobenzoic acid, and the productive rate was 90%. After the catalyst is recovered, it is washed with a reaction solvent...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com