Sphingomonas paucimobilis strain and application thereof
A technology of single cell bacteria and less active sheaths, applied in the direction of bacteria, microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problem of low yield, achieve the effect of increasing sources, simple process, and easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Embodiment 1, the isolation of the bacterial strain FJAT-10625:
[0027] (1) Weigh 5g of kumquat leaves from Shunchang County, Nanping City, Fujian Province, rinse the leaves with tap water first, blot the water on the surface of the leaves, then soak them in 75% alcohol for 30s, and then soak them with 10% sodium hypochlorite for 5 minutes , and then rinse the leaves 3 times with sterile water;
[0028] (2) In order to test the effect of surface sterilization, clamp the leaves treated in step (1) with sterilized tweezers, and make the surface of the leaves contact with the NA plate for 2 minutes, and then place the NA plate at 30°C for 2 days. , if no colonies are found on the NA plate, it proves that the surface of the leaf is completely sterilized and can be used as a follow-up operation, otherwise it cannot be used.
[0029] (3) Take the thoroughly sterilized leaves after the inspection in step (2), under aseptic operation, cut the leaves into pieces in a mortar an...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Embodiment 2, the identification of this bacterial strain FJAT-10625
[0032] (1) Identification of physiological and biochemical characteristics:
[0033] The physiological and biochemical characteristics of the strain FJAT-10625 obtained from the screening were measured, and the main morphological characteristics of the strain were as follows: small colonies, round, yellow, smooth and moist surface, slightly raised, neat edges, opaque, and migratory .
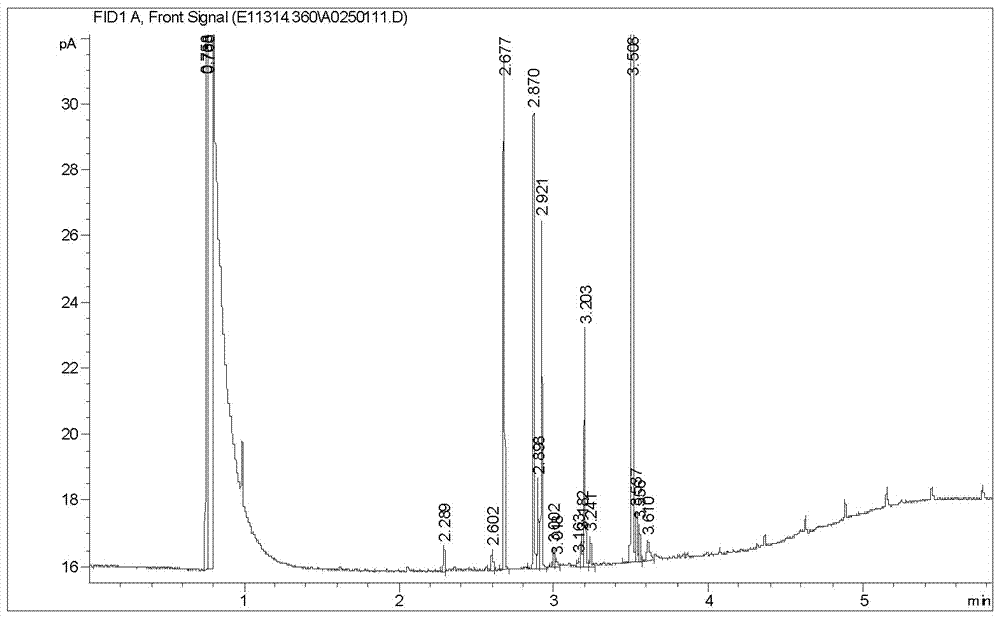
[0034] (2) Sherlock-MIDI system identification: the microbial automatic identification system (Sherlock Microbial Identification System) produced by American MIDI Company was used to analyze the fatty acid of the bacterial strain FJAT-10625, and the analysis results showed that the fatty acid of the bacterial strain FJAT-10625 had the same The similarity coefficient of the fatty acid of the standard Sphingomonas paucimobilis strain in the system is 0.709; the fatty acid map of the strain FJAT-10625 is shown figure 1 ...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Example 3, using the bacterial strain FJAT-10625 to prepare exopolysaccharide
[0037] Activation of the bacterial strain FJAT-10625: Streak the described Sphingomonas paucimobilis bacterial strain FJAT-10625 on the NA plate with an inoculation loop, and cultivate it in a constant temperature incubator for 48h, and the cultivation temperature is 30°C;
[0038] Preparation of seed solution: Inoculate a single colony of Sphingomonas paucimobilis strain FJAT-10625 obtained by activating the strain FJAT-10625 into the seed medium, and place it in a constant temperature shaking shaker for 16 hours at a temperature of 30 ℃, speed 170rpm·min -1 , get the seed solution;
[0039] Preparation of fermented liquid: Transfer the obtained seed liquid to a sterilized fermentation medium for 72 hours at an inoculum size of 2% by volume, at a temperature of 30°C and a rotational speed of 190rpm·min -1 , to obtain the fermentation broth;
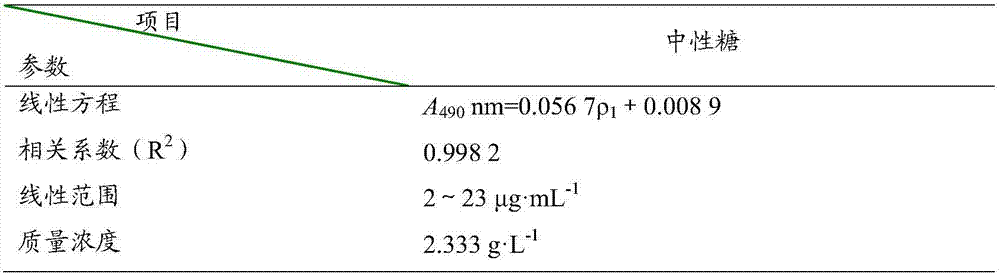
[0040] Extraction of exopolysaccharide: the o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com