On-line analysis method for real-time monitoring of dose of radiotherapy patient
A technology of real-time monitoring and analysis methods, applied in radiation therapy, X-ray/γ-ray/particle irradiation therapy, treatment, etc., can solve the problems of no statistical analysis of dose distribution differences, measured patients, and inability to reflect patient doses, etc., to achieve Optimize the remaining radiation dose, calculate quickly and accurately, and improve the effect of radiotherapy effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0041] The present invention will be described in further detail below by means of specific embodiments:
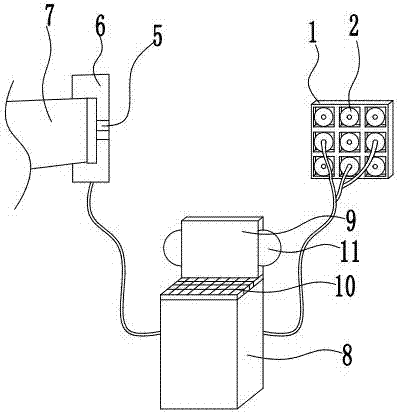
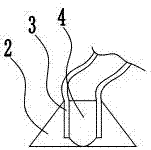
[0042] The reference signs in the drawings of the specification include: fixed plate 1, suction cup 2, connecting pipe 3, second probe 4, first probe 5, bracket 6, machine head 7, shell 8, display screen 9, input device 10, alarm Device 11.
[0043] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the on-line analyzer used in this embodiment for real-time monitoring of the patient dose of radiotherapy includes a first group of detectors arranged on the head 7 of the radiotherapy equipment, a second group of detectors arranged on the surface of the human body, and the first group of detectors arranged on the surface of the human body. Chassis to which the first group of detectors and the second group of detectors are connected.
[0044] The first group of detectors includes a bracket 6 used to be fixedly connected to the head 7 of the radiotherapy equipment and a first probe se...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com