Antibacterial peptide and antibiotic combined antibacterial drug and use method thereof
A technology of antibacterial drugs and polypeptide antibiotics, which is applied in antibacterial drugs, pharmaceutical formulas, active ingredients of heterocyclic compounds, etc., can solve problems such as high medical expenses, bacterial aggravation, long hospital stay and death, and achieve good bactericidal effect, antibacterial Improve the effect and reduce the effect of side effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
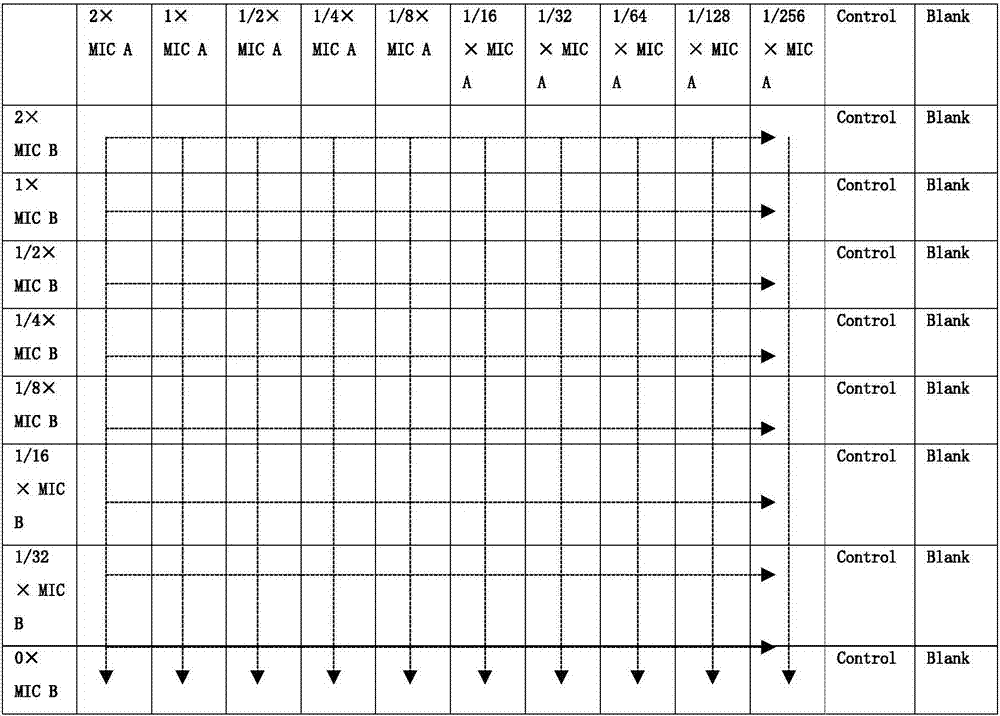
[0042] Example 1 The synergistic antibacterial effect of DP7 combined with various antibiotics on various clinically isolated drug-resistant bacteria and the synergistic antibacterial effect comparison with CLS001:
[0043] The antimicrobial peptide DP7 (amino acid sequence VQWRIRVAVIRK-NH2, with amidation at the carbon terminus) was combined with the antibiotic drugs vancomycin (VAN), gentamicin (GEN), azithromycin (AZT) and amoxicillin (AMO) with checkerboard Antibacterial experiments were carried out by drug combination, and selected clinically isolated drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains (SAU series), clinically isolated drug-resistant Escherichia coli strains (ECO series), and clinically isolated drug-resistant Escherichia coli strains (ECO series) obtained from Chongqing Southwest Hospital and Sichuan Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Three isolated drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains (PAER series) and three clinically isolated drug-...
Embodiment 2
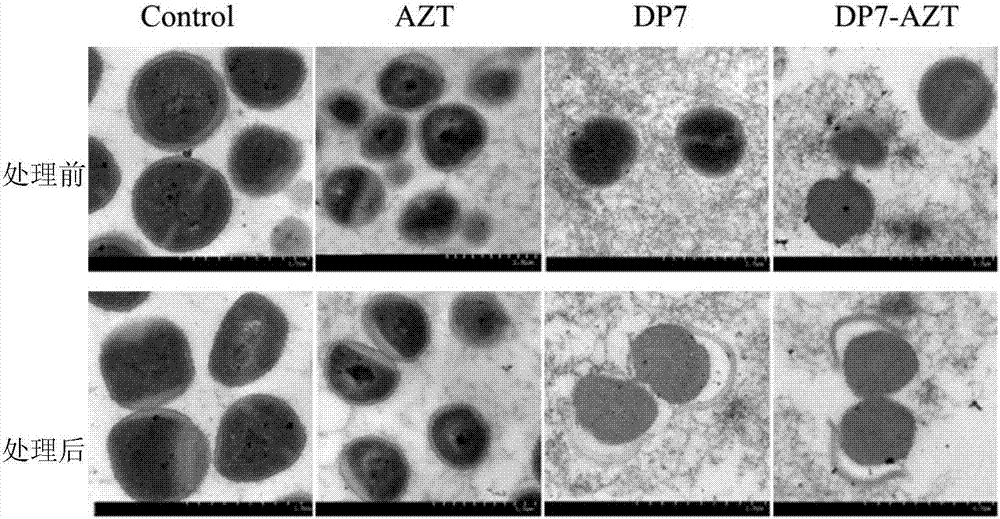
[0067] Example 2 The expansion experiment of DP7 combined with vancomycin and azithromycin for antibacterial
[0068] When the antimicrobial peptide DP7 is used in combination with vancomycin and azithromycin, it has a better synergistic antibacterial effect on the clinically isolated drug-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, so we expand the combination of DP7 with vancomycin and azithromycin The number of strains of Staphylococcus aureus clinically isolated drug-resistant bacteria and Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinically isolated drug-resistant bacteria in the joint antibacterial experiment is used to further study the synergistic antibacterial effect.
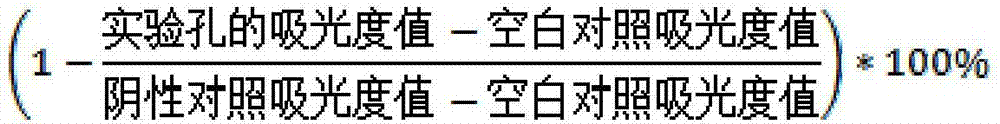
[0069] Real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR) was used to determine the accuracy of clinical isolation of drug-resistant bacteria. Use DNeasyBlood&Tissue Kit (Qiagen) to extract the total DNA of bacteria, and detect the DNA concentration with a Thermo Scientific NanoDrop2000 spectrophotometer. The c...
Embodiment 3
[0074] Example 3 The relationship between the synergistic effect of DP7 and azithromycin and the azithromycin resistance gene
[0075] Based on the synergistic antibacterial effect of DP7 combined with azithromycin or vancomycin and the resistance of each strain to azithromycin or vancomycin, we used real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR) to clinically isolate drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and The clinical isolation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa drug-resistant bacteria has carried out the identification and analysis of common vancomycin resistance genes and azithromycin resistance genes. The drug resistance genes involved in this example are vancomycin resistance genes (vanB, vanC) and azithromycin resistance genes. Drug resistance genes (ermA, ermB, ermC, mefA, msrA).
[0076] The results are shown in Table 4 and Table 5. We concluded from the qPCR gene identification results that the isolated Staphylococcus aureus drug-resistant bacteria and Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinically i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com