Method for computing twin-crystal forming ability of solid solution materials
A solid solution and twinning technology, which is applied in the field of twinning, can solve the problems that the influence of solute atoms on the formation ability of solid solution twinning cannot be accurately calculated, the unit cell is small, and the distribution of solute atoms cannot be accurately described. Lower cost and better accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention more clear, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the examples. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention.
[0028] The application principle of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
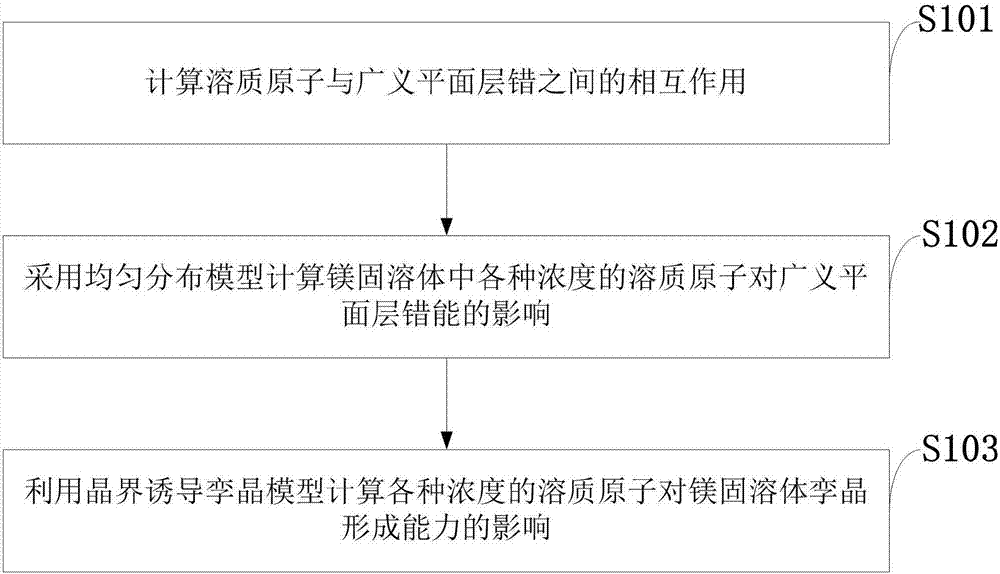
[0029] like figure 1 As shown, the method for calculating the twin formation ability of solid solution materials provided by the embodiments of the present invention includes the following steps:
[0030] S101: Calculate the interaction between solute atoms and generalized planar faults;
[0031] S102: Using the uniform distribution model to calculate the influence of various concentrations of solute atoms in the magnesium solid solution on the generalized planar fault energy;
[00...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com