A single-stage photovoltaic off-grid inverter and its control method
An inverter, single-stage technology, applied in the electrical field, can solve the problems of difficult to increase power, need two inductors, and high control difficulty, and achieve the effect of reducing the voltage distortion rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
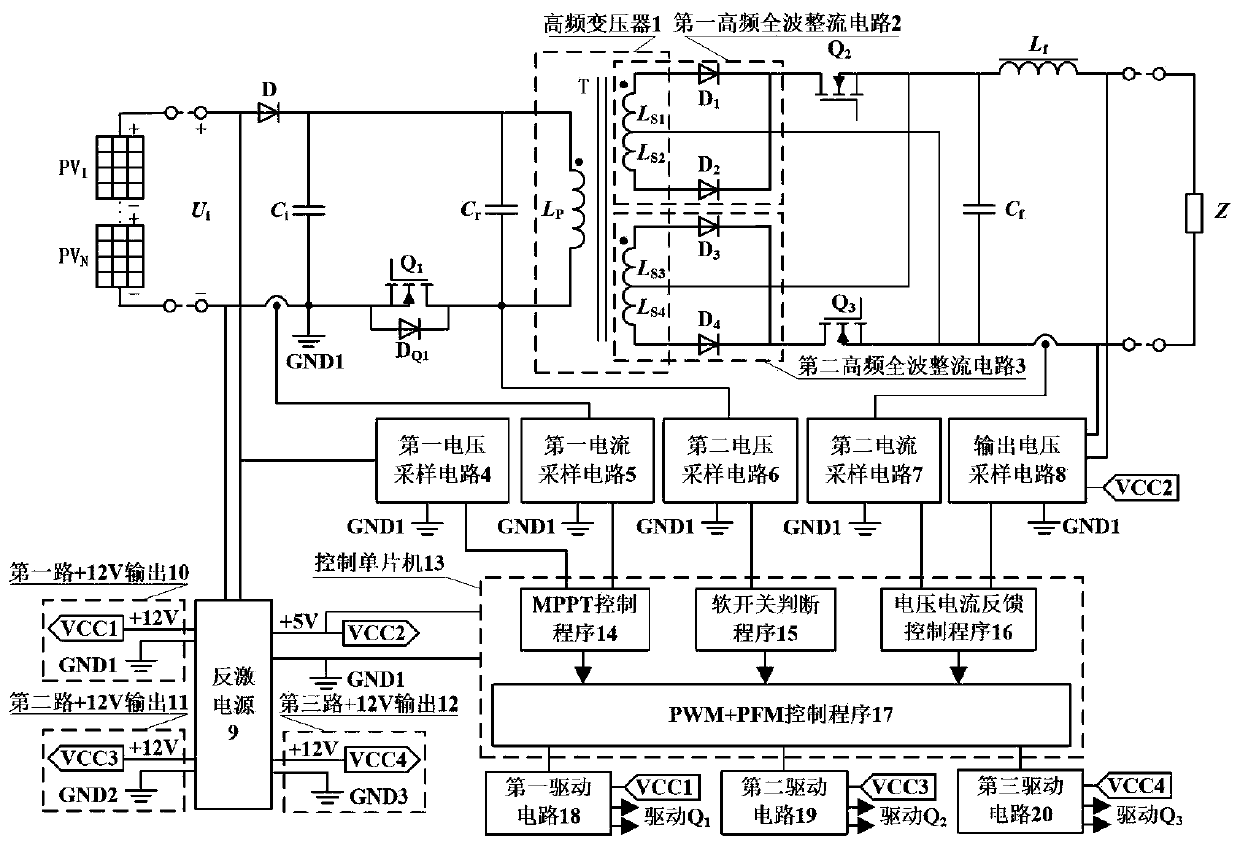
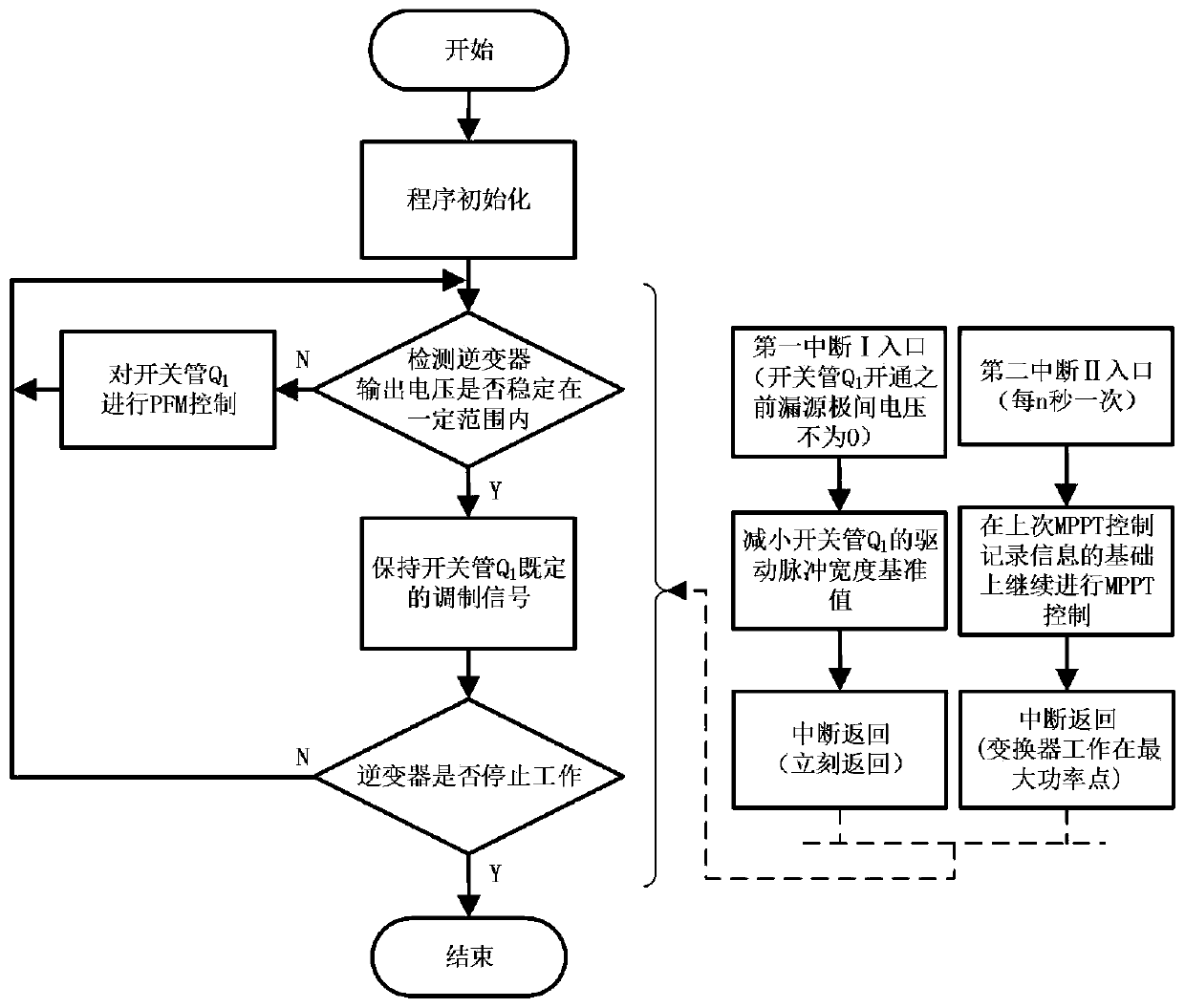
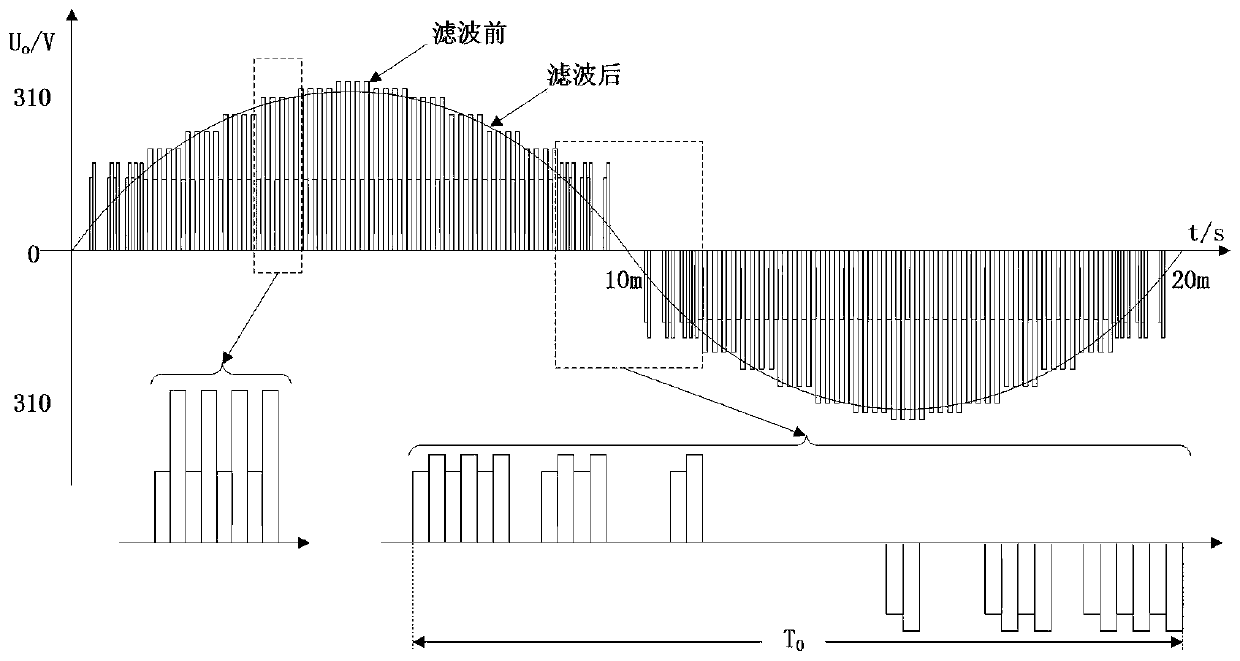
[0020] The main structure of the single-stage photovoltaic off-grid inverter described in this embodiment includes a reverse cut-off diode D, a capacitor C i , Resonant capacitance C r , the first switching tube Q 1 , Freewheeling diode D Q1 , high-frequency transformer 1, first high-frequency full-wave rectifier circuit 2, second high-frequency full-wave rectifier circuit 3, second switching tube Q 2 , the third switching tube Q 3 , filter capacitor C f , filter inductance L f , a first voltage sampling circuit 4, a first current sampling circuit 5, a second voltage sampling circuit 6, a second current sampling circuit 7, an output voltage sampling circuit 8, a flyback power supply 9, a control microcontroller 13, a first drive circuit 18, The second drive circuit 19 and the third drive circuit 20; input voltage U i through the reverse blocking diode D and by the capacitor C i After filtering, it is used as the input of the following circuit, where the input voltage U ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com