In-situ classification and identification method and device of marine phytoplankton by microscopic fluorescence spectral imaging
A spectral imaging and micro-fluorescence technology, which is applied in the field of in-situ classification and identification of marine phytoplankton in micro-fluorescence spectral imaging and devices, can solve the problems of difficulty in automatic image classification and identification, difficulty in species identification, etc. Sensitive effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Example 1 A method for in-situ classification and identification of marine phytoplankton by microscopic fluorescence spectroscopy
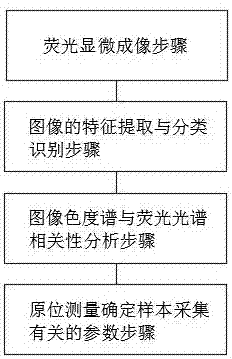
[0040] Such as Figure 1-3 As shown, the present invention provides a method for in-situ classification and identification of marine phytoplankton by microscopic fluorescence spectroscopy, comprising the following steps:
[0041] Step 1, fluorescence microscopy imaging step;
[0042]Step 2, the feature extraction and classification recognition steps of the algae image;
[0043] Step 3, image chromaticity spectrum and fluorescence spectrum correlation analysis step;
[0044] Step 4, in-situ measurement to determine parameters related to sample collection.
[0045] in,
[0046] Step 1, fluorescence microscopic imaging step: including laboratory microscopic fluorescence spectrum imaging step,
[0047] Including laboratory microscopic fluorescent spectrum imaging steps: using xenon lamp as excitation light source, using Leica DMILM fluores...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Example 2: A method for in-situ classification and identification of marine phytoplankton by microscopic fluorescence spectroscopy
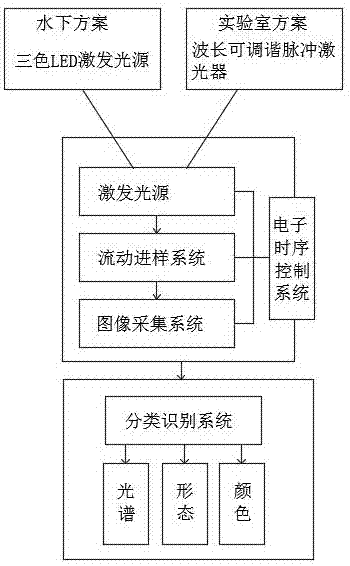
[0058] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the present invention provides a method for in-situ classification and identification of marine phytoplankton by microscopic fluorescence spectroscopy, comprising the following steps:
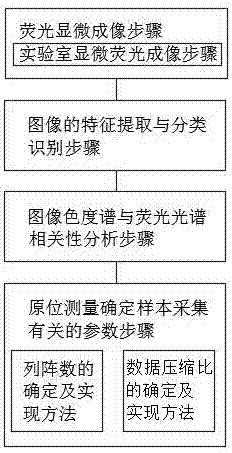
[0059] Step 1, fluorescence microscopy imaging step;
[0060] Step 2, the feature extraction and classification recognition steps of the algae image;
[0061] Step 3, image chromaticity spectrum and fluorescence spectrum correlation analysis step;
[0062] Step 4, in-situ measurement to determine parameters related to sample collection.
[0063] in:
[0064] Step 1, the fluorescent microscopic imaging step: including the underwater fluorescent microscopic imaging step;
[0065] The underwater fluorescence microscopy imaging step uses an in-situ microfluorescence spectroscopy imaging system, using pigtail-LEDs that can...
Embodiment 3
[0076] Example 3: A device for in-situ classification and identification of marine phytoplankton by microscopic fluorescence spectroscopy
[0077] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the present invention provides a microscopic fluorescence spectrum imaging marine phytoplankton in situ classification and identification device, comprising:
[0078] It includes an excitation light source system 1, a flow sample cell 2, and a CCD imaging system 3.
[0079] The excitation light source system 1 includes a light source device 11 and an optical system 12 .
[0080] The light source device 11 includes excitation light source, imaging and image acquisition system.
[0081] The laser light source adopts a xenon lamp as an excitation light source; the excitation light source adopts a surface excitation method. The planar excitation method is to simultaneously excite the entire observation area and detect the fluorescence signal of the entire area at the same time, with fast imaging speed, whi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com