Method and reagent for detecting small and dense low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in sample
A low-density lipoprotein, in-sample technology, which is applied in the field of measuring small and dense low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in samples, can solve the problems of many operation steps, unsuitable for routine detection, and low resolution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0085] Reagents containing different ion selective agents have different reactivity to sdLDL-C and LLDL-C.
[0086] First, use ultracentrifugation to separate and purify sdLDL and LLDL. The specifics are as follows: Take the serum without turbidity and mix, add EDTA to a final concentration of 0.04%, and add NaN 3 The final concentration is 0.05%, and the density is adjusted to 1.019 with KBr. Centrifuge for 28h at 40,000 rpm and 20°C (centrifuge: Beckman Optima XE; rotor: Type 70Ti). After centrifugation, carefully discard the upper lipoprotein, including chyle. VLDL and IDL. The density of the lower layer was adjusted to 1.040 with KBr and centrifuged at 40,000 rpm and 20°C for 28 h. After centrifugation, the upper lipoprotein was carefully collected, that is, LLDL with a density of 1.019-1.040. Then adjust the density of the lower lipoprotein to 1.063 with KBr, and centrifuge at 40,000 rpm, 20°C for 28 hours. After centrifugation, carefully collect the upper lipoprotein, that ...
Embodiment 2
[0099] Through the above examples, it is found that as long as the conditions are suitable, a detection method for sdLDL-C can be established. Therefore, the following reagents are specially formulated for the detection of sdLDL-C.
[0100] R1
[0101]
[0102] R2
[0103] PIPES buffer (pH7.0) 50mM
[0104] Triton X-100 1.0%
[0105] TOOS 2mM.
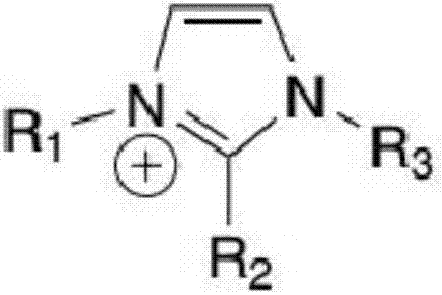
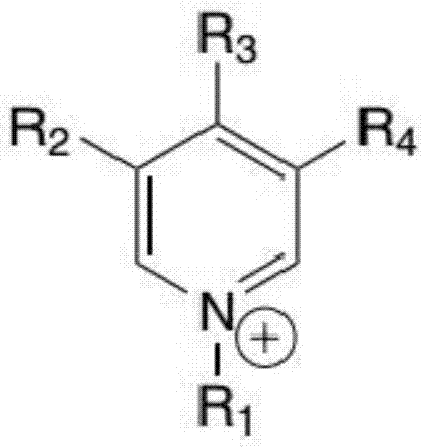
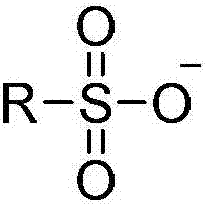
[0106] Among them, the sample reagent ratio, sample: reagent R1: reagent R2 = 3:150:50. After incubating the sample with reagent R1 for 5 min, add R2, react for 5 min, and then measure the absorbance at 600 nm. Ion selective agents in R1 include ionic liquids and ionic polymers, wherein the cationic part of the ion selective agent is selected from the following types: imidazolium salt, pyridine, pyrrolidinium, quaternary phosphonium salt, ammonium base, sulfonium salt, anionic part It is selected from the following types: alkyl sulfate, tosylate, methanesulfonate, bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide, hexafluorophosphate, tetrafluoroborate, hali...
Embodiment 3
[0113] Influence of cholesterol esterase and cholesterol oxidase
[0114] It consists of the following R1 and R2 reagents, and uses the cholesterol oxidase (COO), cholesterol esterase (COE) and peroxidase (POD) in Table 3.
[0115] R1
[0116]
[0117] R2
[0118] PIPES buffer (pH7.0) 50mM
[0119] Triton X-100 1.0%
[0120] TOOS 2mM
[0121] table 3
[0122]
[0123]
[0124] It can be seen from Table 3 that as long as the content of cholesterol oxidase, cholesterol esterase, and peroxidase is sufficient, this method can effectively detect sdLDL-C. Therefore, cholesterol oxidase and cholesterol esterase can effectively detect sdLDL-C in the range of 0.1-50KU / L, preferably 1-5KU / L, while peroxidase is in the range of 0.1-10KU / L The sdLDL-C can be effectively detected within, preferably 1-5KU / L.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com