In-situ enriching method and screening method of pullulanase indigenous strains
An in situ enrichment, pullulanase technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, determination/inspection of bacteria, microorganisms, etc. Easy to operate, clear purpose, reliable effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] The in situ enrichment method of the indigenous pullulanase-producing strain in this embodiment includes:
[0028] A. Substrate handling
[0029] Take 5g of sterilized absorbent cotton in the ultra-clean workbench and put it into a sterilized beaker containing 15g of pullulan and 50mL of sterile water, and turn the absorbent cotton to make the pullulan infiltrate and adhere to the absorbent cotton as much as possible. Absorbent cotton blocks are kept sterile.
[0030] B. In-situ enrichment in soil
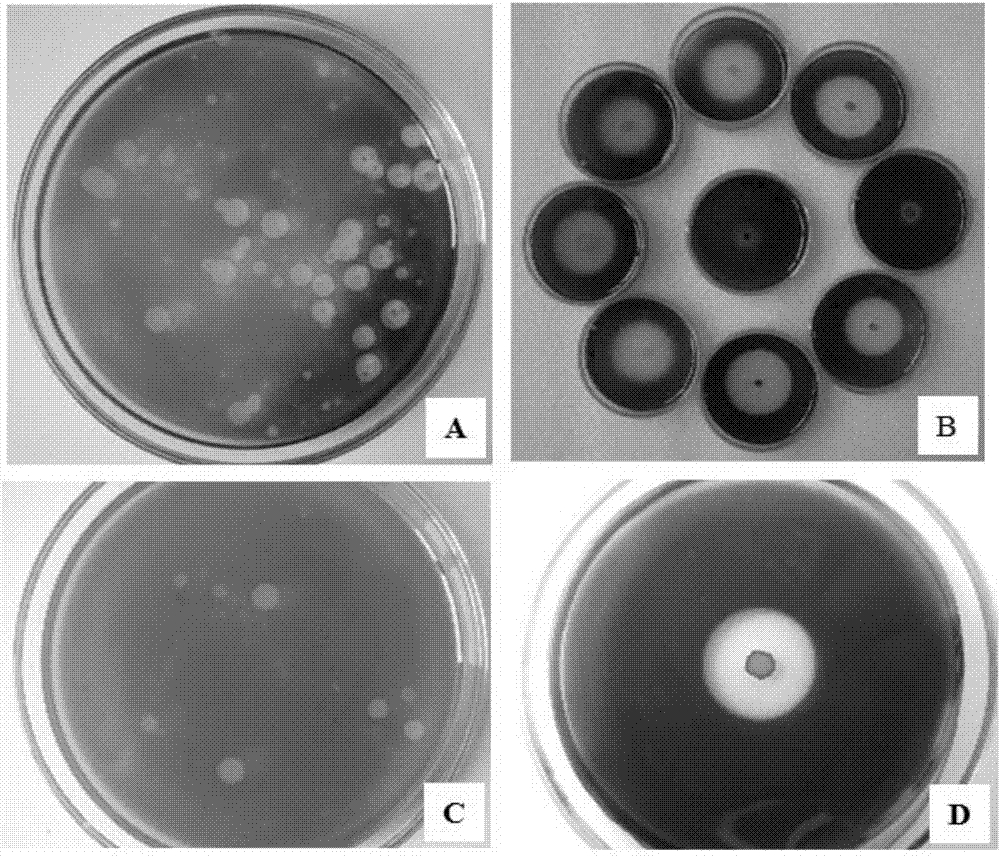
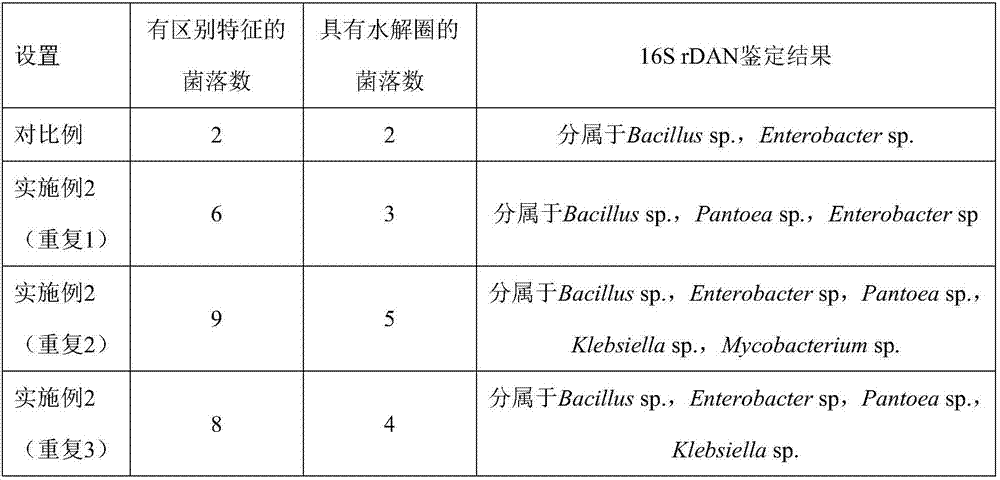
[0031] Dig a 5cm deep pit in the sampling environment soil (the wasteland soil on both sides of the Luohe River in the suburbs of Luoyang), sprinkle 100mL sterile water in the pit, take out the absorbent cotton block processed in step A, and arrange the cotton block into a rectangle ( subject to no breakage), lay flat on the bottom of the hole, and cover the absorbent cotton with the in-situ soil when digging the hole. After 8 days of in-situ enrichment, the absorbent cot...
Embodiment 2
[0036] The in situ enrichment method of the indigenous pullulanase-producing strain in this embodiment includes:
[0037] A. Substrate handling
[0038] Take 5g of sterilized absorbent cotton in the ultra-clean workbench and put it into a sterilized beaker containing 20g of pullulan and 50mL of sterile water, and turn the absorbent cotton to make the pullulan infiltrate and adhere to the absorbent cotton as much as possible. Absorbent cotton blocks are kept sterile.
[0039] B. In-situ enrichment in soil
[0040]Dig a 10cm deep pit in the sampling environment soil (corn field soil in the suburbs of Luoyang), sprinkle 150mL sterile water in the pit, take out the absorbent cotton block processed in step A, and arrange the cotton block into a rectangle ( subject to no breakage), lay flat on the bottom of the hole, and cover the absorbent cotton with the in-situ soil when digging the hole. After 12 days of in-situ enrichment, the absorbent cotton block was carefully taken out, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com