M-phase stator winding switch reluctance motor, driving method and pole-changing method
A technology of switched reluctance motor and stator winding, which is applied in the direction of AC motor control, connection with control/drive circuit, electrical components, etc., and can solve problems such as increased control complexity, easy slipping of conductors in the slot, and reduced motor performance , to achieve the effect of easy driving mode, high slot full rate, and fewer outlets
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
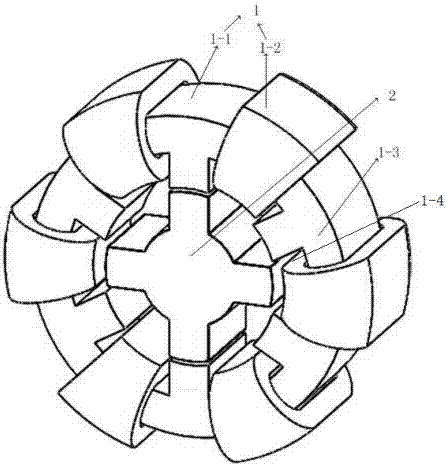
[0032] Such as figure 1 figure 2 image 3 A three-phase stator winding switched reluctance motor, including a stator 1 and a rotor 2, and a drive unit, the stator 1 includes a stator core 1-1 and a stator winding, the rotor 2 is arranged inside the stator 1; the stator core 1- The inner surface of 1 is evenly opened with 6 coil slots 1-4; the stator winding is composed of 6 coils 1-2, which are respectively wound on the stator yoke 1-3 of the stator 1, and each of the coils 1-2 2 is set in a coil slot 1-4, and the second coil side is set outside the stator yoke 1-3 on the same radial direction as the coil slot 1-4; each coil 1-2 leads The wires are respectively connected to the output end of a drive unit, and the drive unit can provide forward or reverse current to supply power to each coil 1-2 of the stator winding individually.
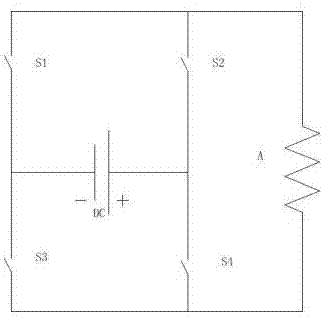
[0033] Each drive unit is composed of four switching tubes S1, S2, S3, S4 and DC power supply; the DC power supply is connected with the four s...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Such as Figure 1-3 A three-phase toroidal winding switched reluctance motor driving method is shown, taking the three-phase 6 / 4 mechanism as an example,
[0037] The motor clockwise rotation drive steps are as follows:
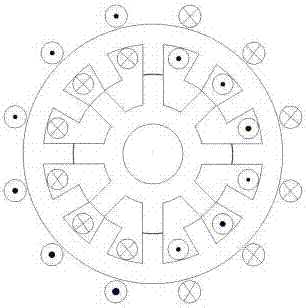
[0038] A1: Turn on the S2 and S3 switches at the same time, pass the forward current to the a1, b1, c1 windings respectively, pass the reverse current to the a2, b2, c2 windings respectively, generate a magnetic field in the stator, and pass through the stator teeth 101 into the rotor.
[0039] A2: Pass forward current to b1, c1, a2 windings respectively, and pass reverse current to b2, c2, a1 windings respectively, the magnetic field in the stator passes through the stator teeth 102 and enters the rotor.
[0040] A3: Pass forward current to c1, a2 and b2 windings respectively, and pass reverse current to c2, a1 and b1 windings respectively, and the magnetic field in the stator passes through the stator teeth 103 and flows into the rotor.
[0041] T...
Embodiment 3
[0046] A pole-changing method for an m-phase toroidal winding switched reluctance motor. When n connected drive units pass forward or reverse current at the same time, the magnetic circuit of the motor is 2km / n poles, where n is a positive integer, 2km / n is a positive integer.
[0047] Take the 12-phase toroidal winding switched reluctance motor as an example: Figure 4 As shown, when there are 6 connected drive units passing forward current at the same time, the motor magnetic circuit is two poles;
[0048] Such as Figure 5 As shown, when there are 3 connected drive units passing forward or reverse current at the same time, the motor has 4 poles; with this rule, the number of poles of the motor can be changed.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com