Method used for detecting carbohydrates based on microorganism surface controllable co-display sequential enzyme electrochemical biosensor
A sensor and co-display technology, applied in the field of electrochemical biosensing, can solve the problems of complex fusion protein construction, low sensor sensitivity, and low enzyme expression efficiency, and achieve the effects of fast and sensitive response, sensitive detection, and good reproducibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
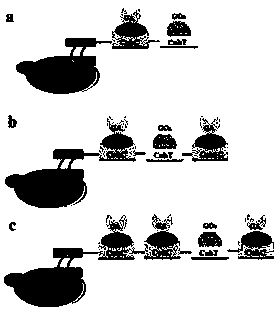
[0045] The sequential enzyme sensor of the present invention is to co-display glucoamylase (GA) and glucose oxidase (GOx) (yeast–GA&GOx (n:1, n=1,2,3) on the yeast surface in proportion and modify them on the electrode (see figure 1 ). The glucoamylase (GA) is derived from the glucoamylase (GA) encoding gene of Saccharomyces fumigatus and the glucose oxidase (GOx) is derived from the glucose oxidase (GOx) encoding gene of Aspergillus niger and the dockerin structure with different specificities Domains DocC and DocT encoding genes were fused.
[0046] Specifically:
[0047] Step 1, constructing a yeast surface display system for scaffold proteins: display cohesin domains CohC and CohT with different specificities on the surface of yeast cells by using a-lectin anchoring protein. Coh-Doc proteins from C.cellulolyticumH10 and C.thermocellum ATCC27405 were cloned, and the gene fragments were cohc / docc and coht / doct, respectively. The gene encoding Coh was fused to the C-termin...
Embodiment 2
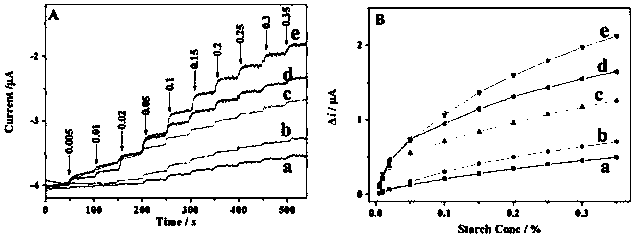
[0058] In 5mL of 0.1M citrate buffer solution (pH 5.0), under the working potential of -0.4V, use the i-t method to measure the current response of the sequential enzyme sensor prepared by the above-mentioned optimal experimental conditions to the soluble starch standard solution ( see image 3 A) and working curve (see image 3 B).
[0059] Depend on image 3 It can be seen that the response time and sensitivity of the whole-cell modified electrode with proportional co-display are better than those of the non-co-display system. After adding the same concentration of starch, the 2:1 co-display GA&GOx modified electrode on the yeast surface had the largest current step value, followed by the 3:1 co-display GA&GOx modified electrode on the yeast surface, and the 1:1 co-display yeast-GA&GOx modification on the yeast surface Electrodes, indicating that the optimal ratio of co-display GA&GOx on the surface is 2:1. Compared with the non-co-display system, the signal response adva...
Embodiment 3
[0061] In 5mL of 0.1M citrate buffer (pH 5.0), apply a potential of –0.4V vs SCE, and use the i–t method to determine the above optimal experimental conditions to prepare yeast–GA&GOx(2:1) / RGO / GCE pair Current response to glucose standard concentration (see Figure 4 A) and working curve (see Figure 4 B).
[0062] It can be seen from the figure that with the addition of glucose, the oxidation current signal increases rapidly and reaches 95% of the stable value within 5s ( Figure 4 A). The linear range of detecting glucose is 0.0002-0.01%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com