An electromagnetic induction linear displacement sensor
A technology of linear displacement and electromagnetic induction, applied in the direction of using electric/magnetic devices to transmit sensing components, using electromagnetic means, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of unfavorable wide application, etc., to increase the degree of induction signal, avoid mechanical errors, width and The effect of small thickness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
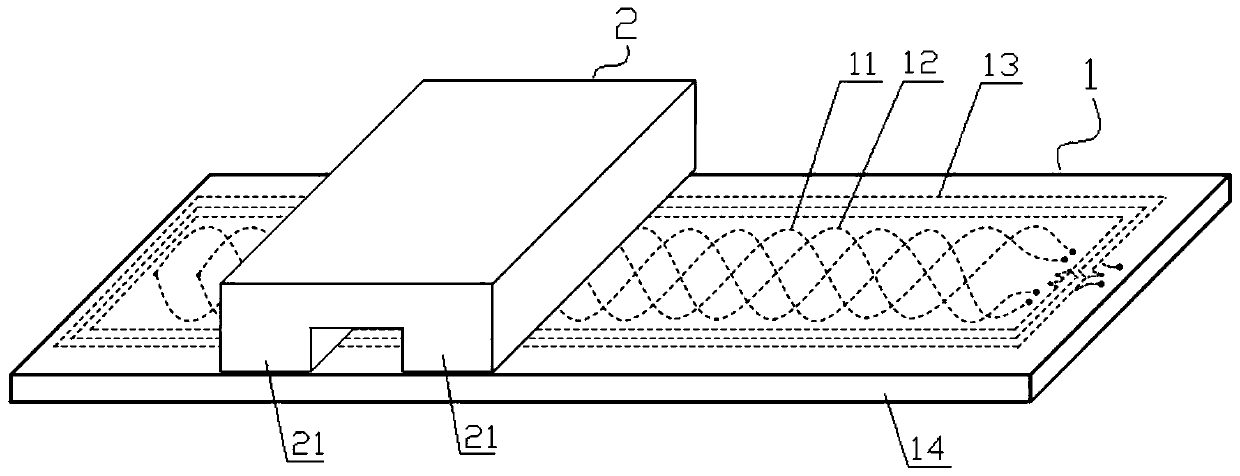
[0027] Embodiment 1: as figure 1 , figure 2 The electromagnetic induction type linear displacement sensor shown includes a fixed ruler 1 and a moving ruler 2 facing and parallel to the fixed ruler 1 with a gap of 0.1 mm to 1 mm.
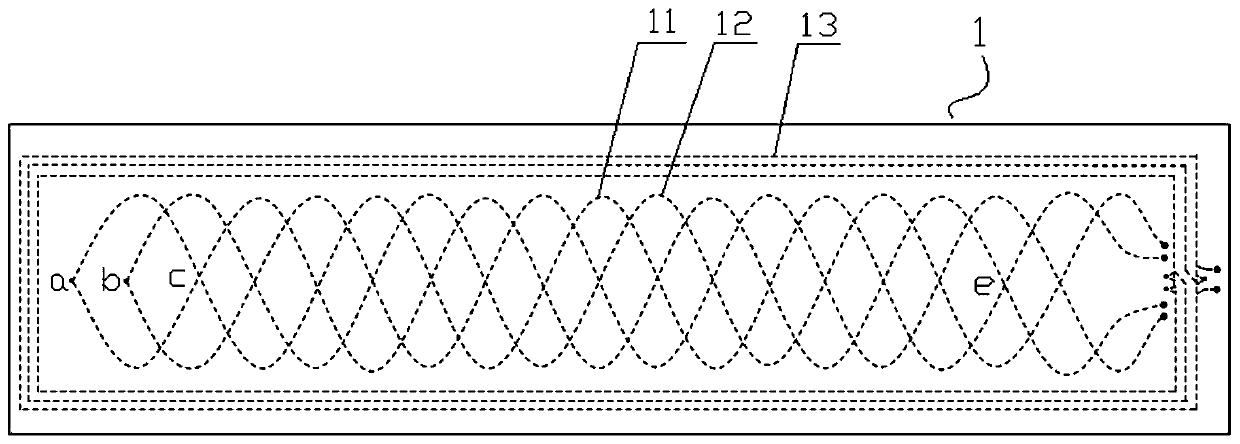
[0028] The fixed length 1 is composed of a magnetically conductive fixed-length base 14 (that is, the fixed-length base 14 is made of a magnetically permeable material) and a sensing unit arranged on the surface of the fixed-length base 14. The sensing unit is equipped with a first coil linear array 11. The second coil array 12 and the printed circuit board of the planar rectangular spiral coil group. The first coil line array 11 and the second coil line array 12 all have the same starting position, the amplitude is 3mm (ie A=3mm), the period is 16mm (ie W=16mm), the number of periods is 4.5, and the initial phase The first sinusoidal coil and the second sinusoidal coil with angles of 0 and π are formed (that is, the winding curve of the first sin...
Embodiment 2
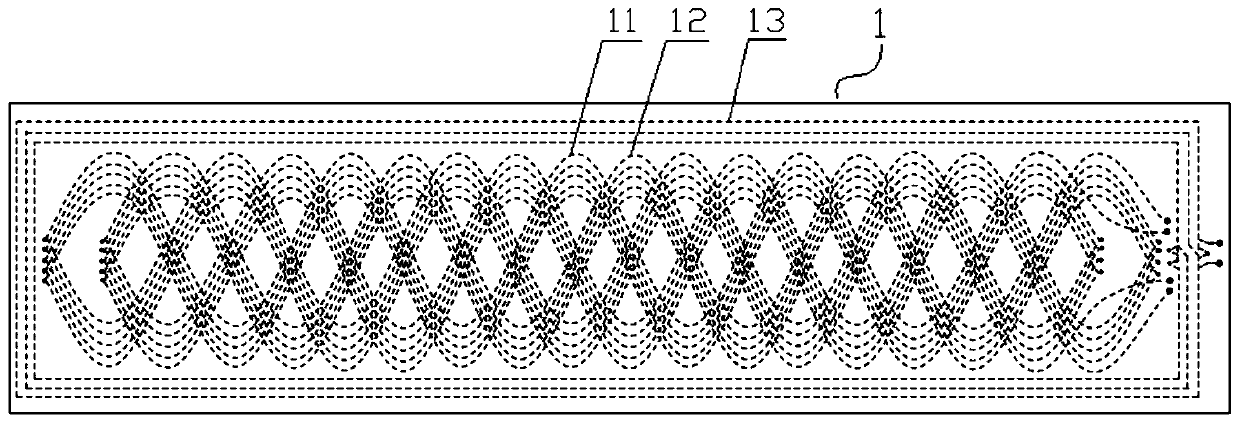
[0034] Embodiment 2: as image 3 As shown, the partial structure of the electromagnetic induction linear displacement sensor of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1, the difference is that: the first coil line array 11 and the second coil line array 12 are composed of five identical and mutually parallel coils The groups are connected in series through holes, and each coil group consists of the first sine coil and the second sine coil with the same starting position, 3mm amplitude, 16mm period, 4.5 periods, and initial phase angles of 0 and π. Coil composition (that is, the winding curve of the first sinusoidal coil is The winding curve of the second sinusoidal coil is The initial positions of the 5 coil groups of the first coil array 11 are aligned along the measurement direction, the distance between two adjacent coil groups perpendicular to the measurement direction is 0.6mm, and the 5 first sinusoidal coils of the first coil array 11 and 5 second sinusoi...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Embodiment 3: The partial structure of the electromagnetic induction linear displacement sensor of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1, except that the moving ruler 2 is a conductive metal and a non-magnetic material. The first coil line array 11 and the second coil line array 12 are as exciting coils, and the planar rectangular spiral coil group is as the induction coil, and the current amplitude of feeding in the first coil line array 11 is 1 m The excitation current i1 = I m sin (ωt), the current amplitude of passing through in the second coil line array 12 is I m The excitation current i 2 = I m cos(ωt), when the moving ruler 2 and the fixed ruler 1 move relative to each other in the measuring direction, the magnetic field coupling between the first coil array 11, the second coil array 12 and the planar rectangular spiral coil group will occur periodically change, the planar rectangular spiral coil group generates and outputs an induction signal e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com