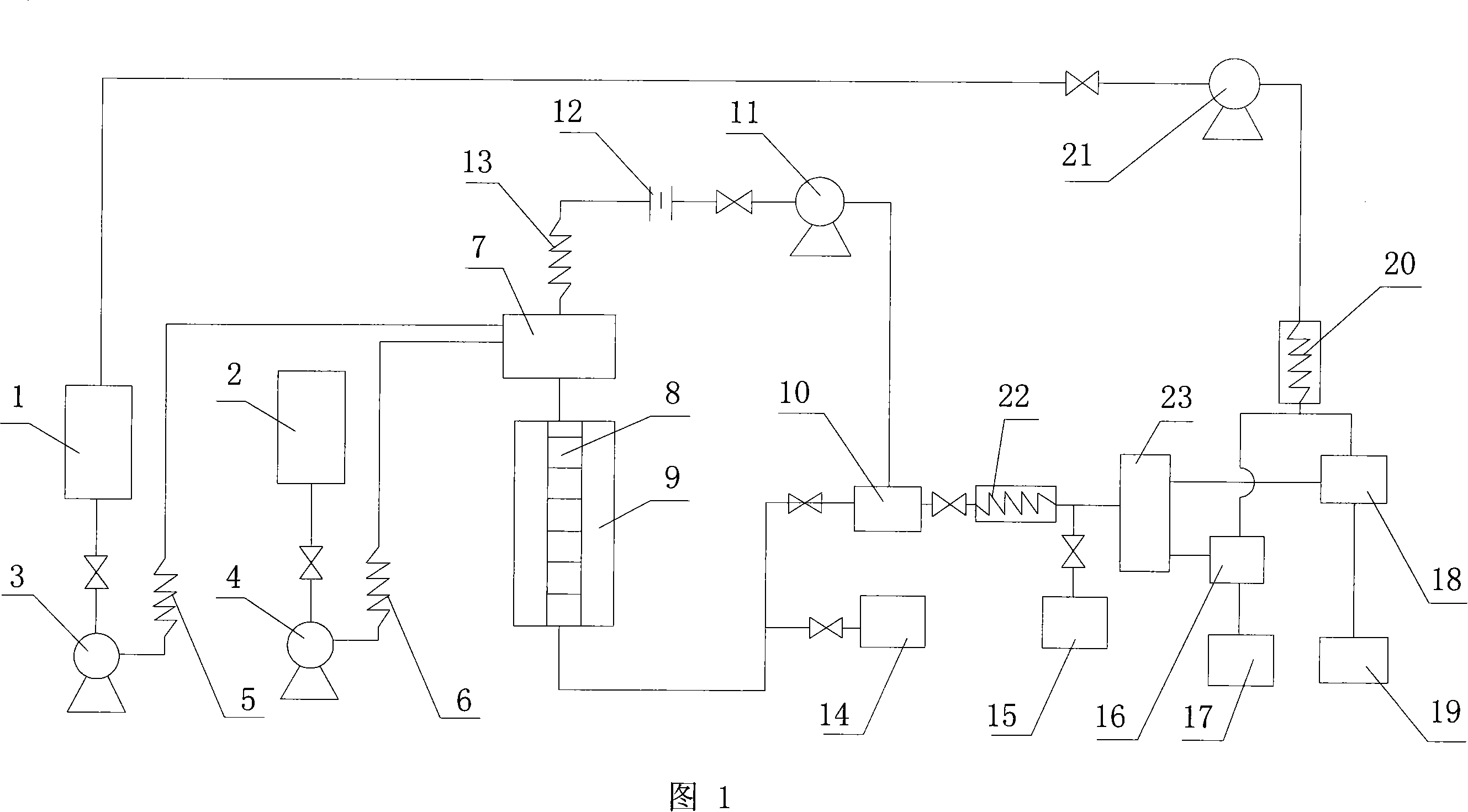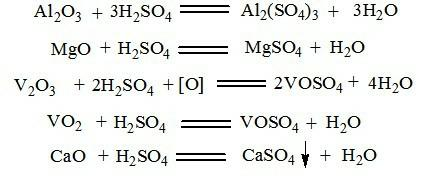Patents
Literature
224results about How to "Fewer separation steps" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
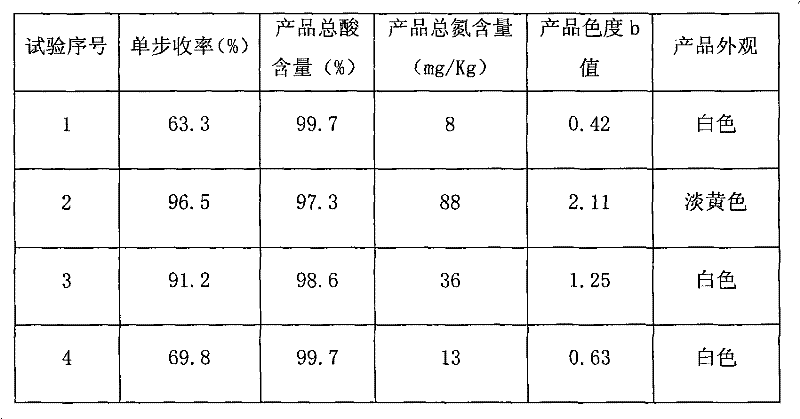
Method of preparing aluminum oxide from fly ash
ActiveCN1923695AHigh dissolution rateFewer separation stepsAluminium oxide/hydroxide preparationAluminium oxides/hydroxidesAluminium sulfateSlag
The invention discloses a preparing method of alumina through fly ash, which comprises the following steps: grinding fly ash; sintering; activating; stirring with H2SO4 evenly to sinter into dried slag; immersing through hot water; stripping aluminum sulfate; condensing; cooling to evolve aluminum sulfate; crystallizing; heating; dehydrating to obtain anhydrous aluminum sulfate; heating; decomposing to obtain gamma-Al2O3.
Owner:PINGSHUO INDAL
Process for decomposing bactnaesite by hydrochloric acid method
The present invention belongs to the field of wet RE metallurgical technology, and especially bastnaesite decomposing process. Bastnaesite is treated through oxidation roasting, alkali transfer and eliminating fluorine with sodium hydroxide, washing, and dissolving with hydrochloric acid to obtain RE chloride material solution with less cerium. The slag is washed, dissolved in hydrochloric acid, precipitated and baked to obtain CeO2 product with purity over 95 %. The said technological process has no waste gas produced, slag with low RE content, less waste water exhausted, environment friendship and high RE yield.
Owner:北京方正稀土科技研究所有限公司
Preparation method of integrated TS-1 catalyst for chloro propylene epoxidation
InactiveCN1830564AEasy to prepareEasy to installOrganic chemistryMolecular sieve catalystsPre treatmentEpichlorohydrin
An integral catalyst TS-1 used for epoxidizing chloropropene to obtain epoxy chloropropane is prepared through calcining the multi-channel cylindrical porous ceramic in fuffle furnace, natural cooling, adding it to the synthetic liquid prepared from tert-butyl titanate, ethyl silicate, deionized water, ammonium tetrapropyl hydroxide and isopropanol, crystallizing reaction in crystallizer, and activating.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
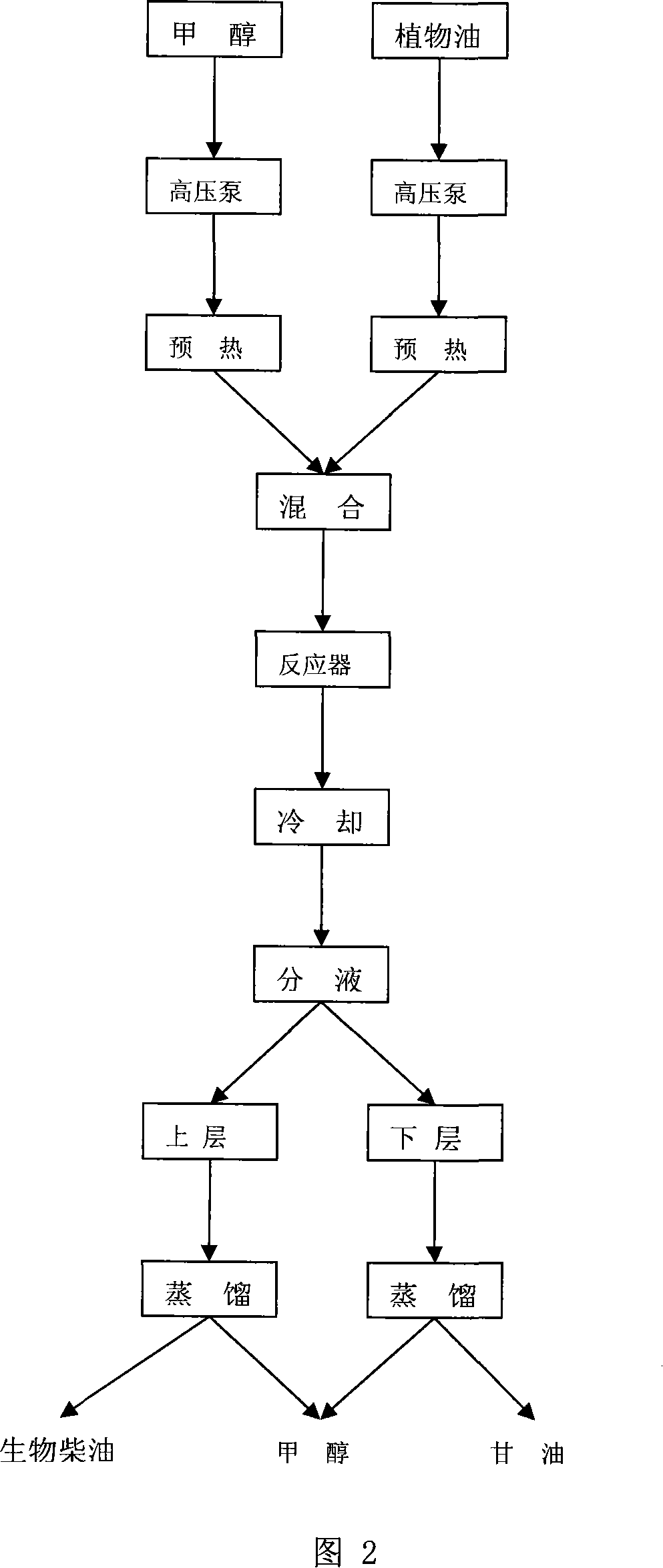
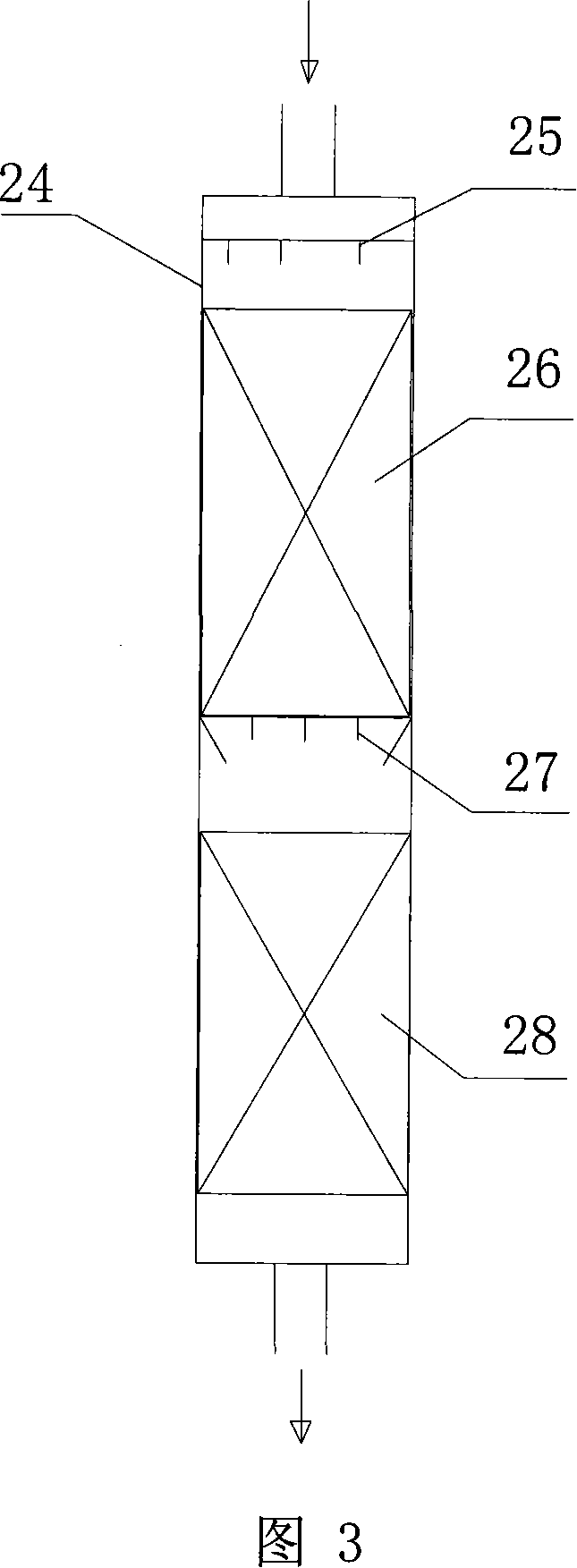
Technique for hypercritical continuous preparation of biological diesel oil and equipment thereof
InactiveCN101104812AFewer separation stepsReduce processBiofuelsLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionVegetable oilBiodiesel
The invention relates to preparation technology for bio-diesel and the producing equipments. The technology for supercritical continuously producing of bio-diesel comprises the following steps: preparing a reserve of methanol and vegetable oil in a mole ratio of 30-50 to one; mixing methanol with vegetable oil in a mixer after preheating the methanol and vegetable oil at a constant temperature respectively of 200DEG C and 250 DEG C which are pumped by high pressure pump into two independent preheaters; sending the fully-mixed methanol and vegetable oil into the tubular reactor at a temperature of 300-350 DEG C, a pressure of 18-20MPa and letting the reaction last for eight to ten minutes; 4.putting the reaction products into a preliminary separator after a complete reaction, wherein the methanol is separated for recycling use and the head product is decompressed and cooled; taking the cooled substance out and keeping the cooled substance still for separation; distilling the upper and lower layers respectively, wherein the bio-diesel is obtained by steaming the methanol out of the upper layer and the by-product of glycerol is obtained by steaming out methanol out of the lower layer; putting the steamed methanol into a tank for recycling use. The invention is characterized by simple technology, environment protection, rapid preparation and high yield.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
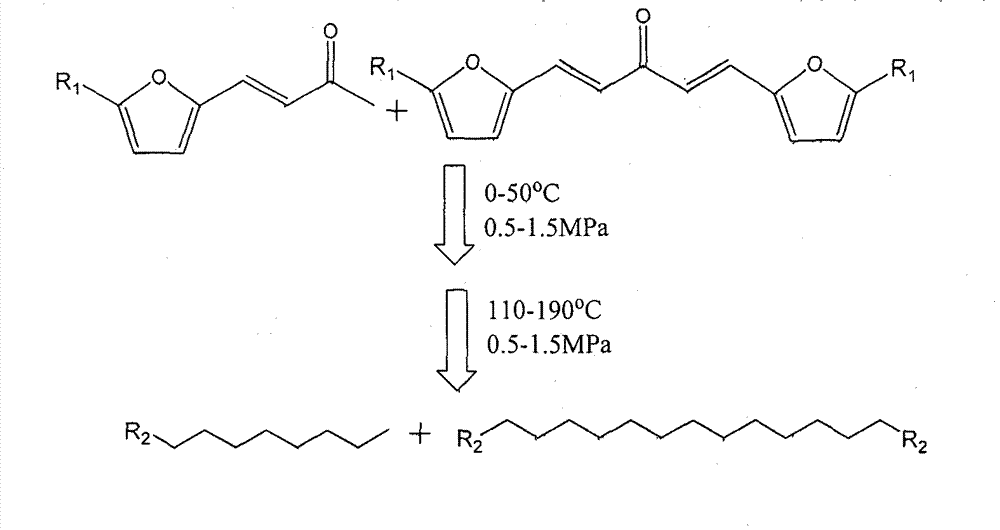
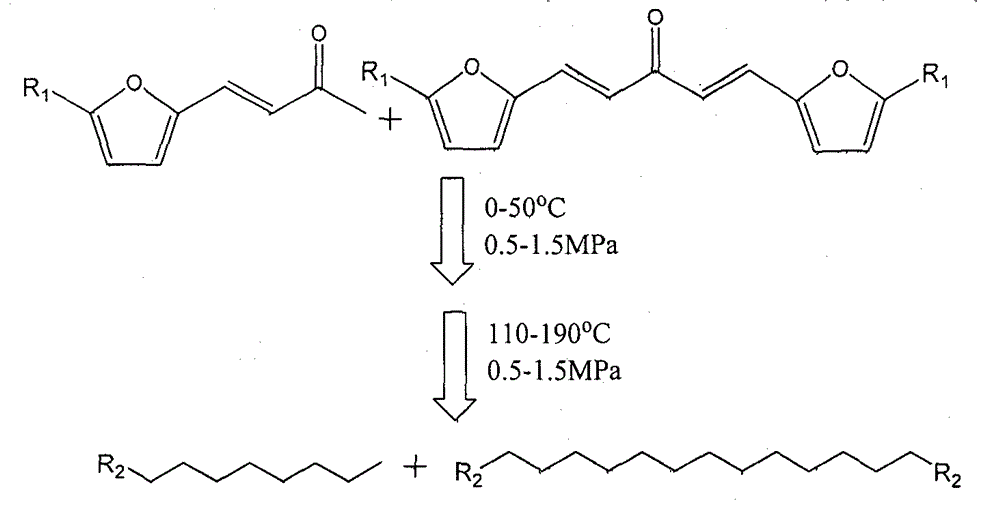
Novel technique for preparing long-chain alkane efficiently through multifunctional catalyst in one-step method
ActiveCN102850157ARedox activeExtend your lifeLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionHydrocarbonsMetal metalPerylene derivatives
The invention relates to a novel technique for preparing long-chain alkane efficiently through a multifunctional catalyst in a one-step method. The novel technique can be used for producing the long-chain alkane in one step with high selectively under a relative mild condition, and solve the problems of strict reaction condition, low energy efficiency and low alkane selectivity in a process of preparing the long-chain alkane by biomass derivatives. According to the technique, condensation products (C8, C9, C13 and C15) of a biomass derivative, namely furfural or HMF (Hydroxy Methyl Furfural), and acetone are taken as the raw materials, and by designing the three-center multifunctional catalyst of metal (I)-metal (II)-acid, the original two steps of independent reactions which require strict reaction conditions and need different catalysts to join in are combined into an one-step reaction which requires tender reaction conditions, so that the selectivity on corresponding alkane (octane, nonane, tridecane and pentadecane) is improved greatly, the highest yield can be 97%, and meanwhile, a step of separating the product from the catalyst is omitted, therefore, the energy efficiency of the while process is improved by a great step.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for refining long chain binary acid by combining ultrafiltration and liquid-liquid extraction
ActiveCN102476987AShort processLow equipment requirementsCarboxylic compound separation/purificationUltrafiltrationSolid particle
The invention provides a method for refining long chain binary acid by combining ultrafiltration and liquid-liquid extraction, which comprises the following steps: a broth in a fermentation section is filtered through a microfiltration membrane to remove the solid particles, filtered through an organic ultrafilter membrane with 3000-50000 Dalton molecular flux, partial protein and pigment in a filtrate are removed, an ultrafiltrate and an extractant (monohydric alcohol with one or more C4-C12) are mixed, heated and acidified, certain pH value and temperature are controlled, the extractant and the ultrafiltrate are mixed and stirred for certain time, a process of liquid-liquid extraction is carried out, the extract phase is taken and cooled to obtain the crystallisate, the solvent is removed to obtain the purified product. The method of the invention has the characteristics of short process flow, low equipment requirement, less separation step, easy process control and the like.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
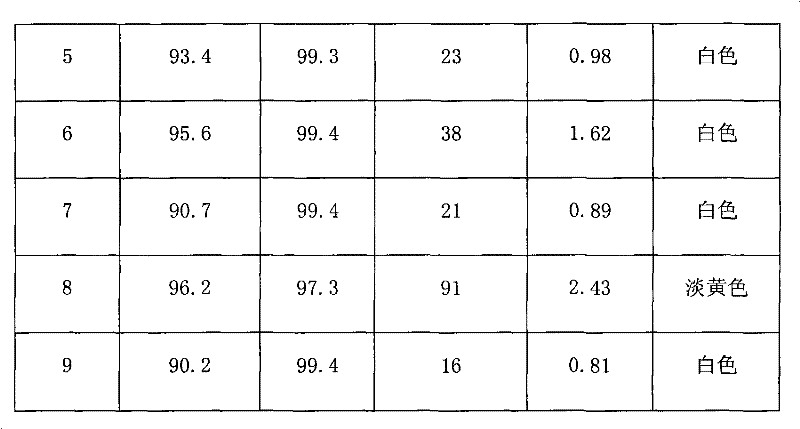
Method for preparing nuclear-shell-structured rutile monocrystal titanium dioxide nanowire array with surface-cladding carbon layer
InactiveCN102107850AControl thicknessSave energyDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingCarbon layerQuantum yield
The invention discloses a method for preparing a nuclear-shell-structured rutile monocrystal titanium dioxide nanowire array with a surface-cladding carbon layer, and the method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (a) immersing a rutile monocrystal titanium dioxide nanowire array into a phenol aqueous solution or an aqueous solution of phenol and a precious metal salt, preparing arutile monocrystal titanium dioxide nanowire array with a surface-cladding polyphenol compound by using a photochemical reaction method, then taking out the rutile monocrystal titanium dioxide nanowire array with the surface-cladding polyphenol compound, washing with water, and drying; and (b) carrying out high-temperature pyrolysis on the rutile monocrystal titanium dioxide nanowire array with the surface-cladding polyphenol compound in the presence of inert gas to obtain the nuclear-shell-structured rutile monocrystal titanium dioxide nanowire array with the surface-cladding carbon layer. By means of the preparation method disclosed by the invention, clean and pollution-free solar energy can be fully utilized so as to effectively reduce the energy consumption for production and the production cost. The prepared nuclear-shell-structured rutile monocrystal titanium dioxide nanowire array with the surface-cladding carbon layer not only has stable and efficient photocatalytic activity, but also can achieve wide-spectrum response to visible light so as to obviously improve the photo quantum yield of the titanium dioxide nanowire array and improve the solar utilization rate, and can be widely applied to the fields of hydrogen production through photodecomposition of water, pollutant degradation through photocatalysis and the like.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
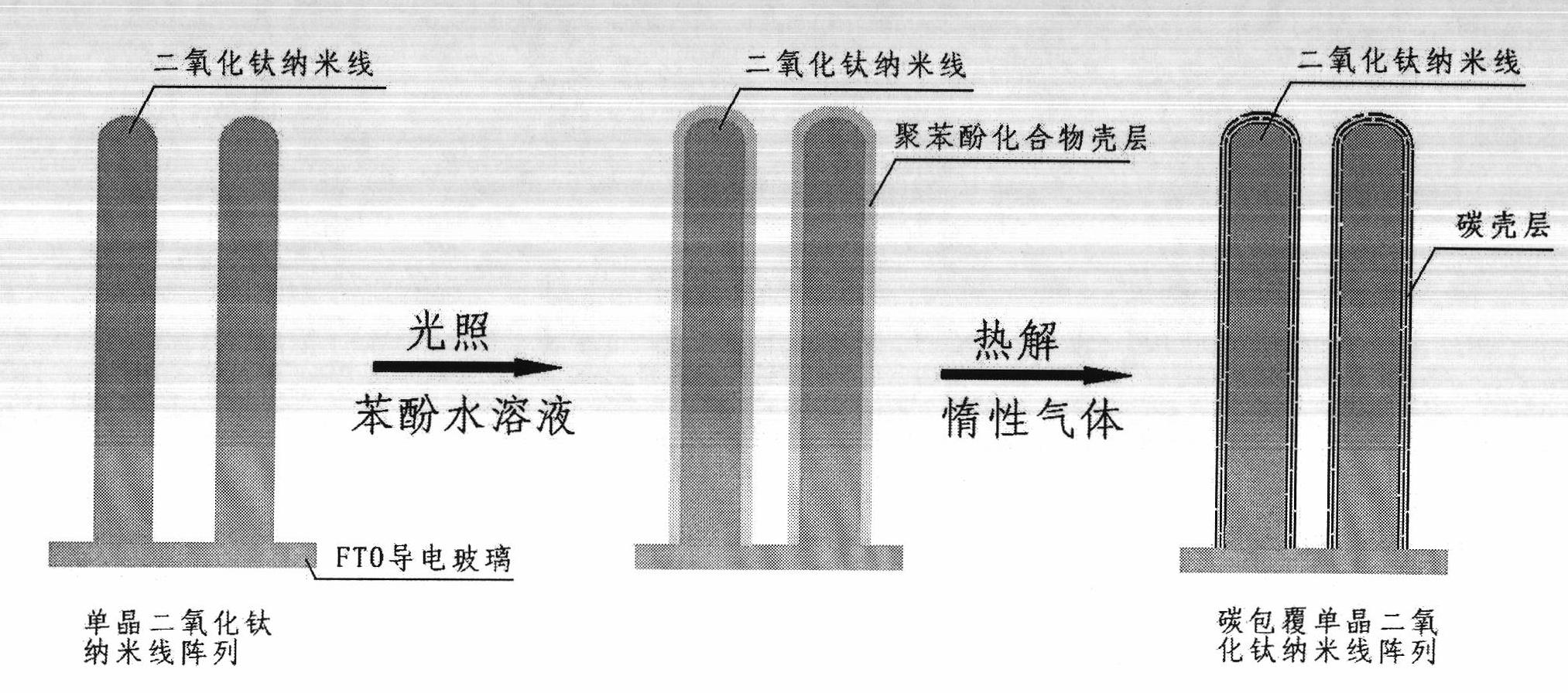
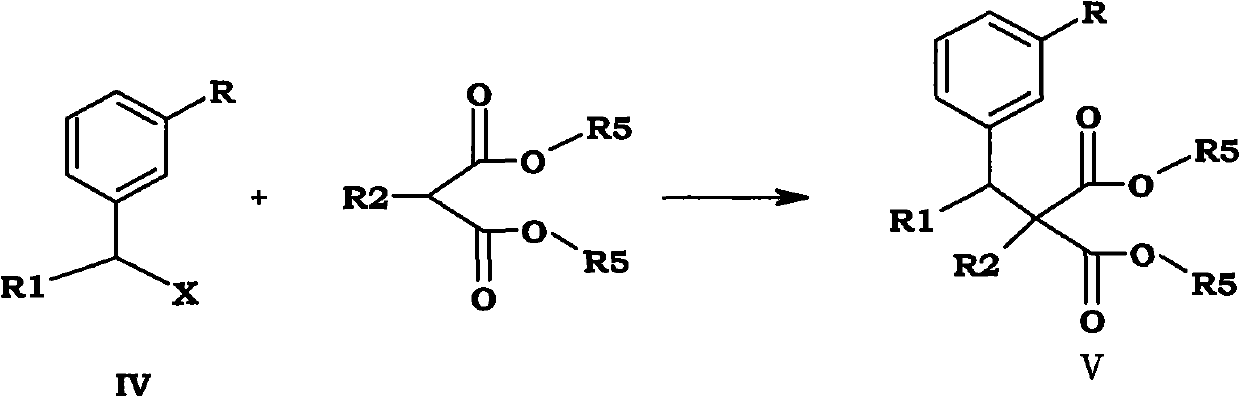
New method for synthesizing tapentadol hydrochloride and analogue of tapentadol hydrochloride
ActiveCN102557851AReduce processing costsEasy to industrializeOrganic compound preparationOptically-active compound separationKetoneChemistry
The invention provides a new method for synthesizing tapentadol hydrochloride and analogue of the tapentadol hydrochloride, and particularly provides a method for synthesizing a compound with the formula shown as a formula (1). Groups of the compound are defined in the specification. The invention also particularly provides a method for synthesizing the tapentadol hydrochloride and the analogue compound of the tapentadol hydrochloride by using 1-(3-substituted phenyl)-1-ketone compound as an initial raw material. According to the method, the raw materials are easy to obtain, and reaction conditions are mild; and the method is easy to control and operate, reduces production cost and is particularly suitable for industrial production.
Owner:ANHUI NEW STAR PHARMA DEV
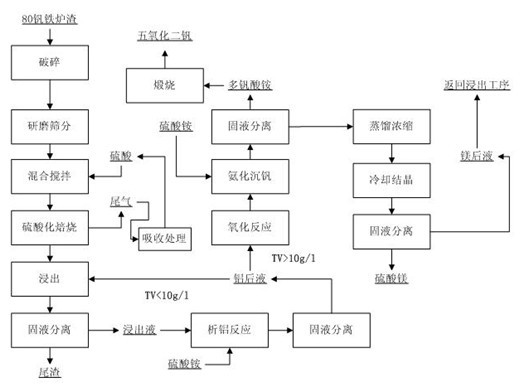
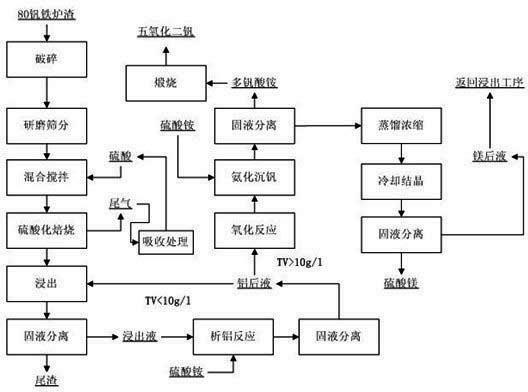
Resource recycling method for 80 ferrovanadium slag
ActiveCN102616851AFewer separation stepsEfficient recyclingSolid waste disposalMagnesium sulfatesSlagAluminum ammonium sulfate
The invention discloses a resource recycling method for 80 ferrovanadium slag, which adopts the following steps: (1) sulfating roasting: mixing the ferrovanadium slag and sulfuric acid, stirring, and then conducting sulfating roasting to obtain roasting slag; (2) leaching: mixing the roasting slag and deionized water or diluted acid, stirring and leaching, and then filtering to obtain leaching liquid; (3) enriching vanadium: adding ammonium sulfate into the leaching liquid, heating and dissolving, and then cooling, crystallizing, and filtering to obtain aluminum ammonium sulfate crystal and crystallization post liquid; (4) oxidizing and sinking vanadium: adding oxidant into the crystallizing post liquid to conduct oxidizing, converting all V3+ and V4+ in the crystallizing post liquid into V5+, then dropwise adding ammonia water, stirring and filtering to obtain ammonium polyvanadate sediment and filtrate, and roasting ammonium polyvanadate to obtain vanadium pentoxide; and (5) magnesium separating reacting: distilling and concentrating the filtrate, cooling, and filtering to obtain magnesium sulfate crystal. The method has the advantages of being simple in technology process, low in energy consumption and friendly in environment.
Owner:HEBEI IRON AND STEEL
Recovery method of positive electrode material of waste ternary lithium ion battery
InactiveCN111252814AEfficient recyclingImprove electrochemical performanceWaste accumulators reclaimingNickel compoundsPhysical chemistryManganate
The invention discloses a recovery method of a positive electrode material of a waste ternary lithium ion battery. The method specifically comprises the steps: leaching the ternary material in the waste ternary lithium ion battery by adopting acid and a reducing agent, adding a precipitant and a complexing agent into the leachate to obtain a nickel-cobalt-manganese-lithium coprecipitation precursor, and calcining the precursor at high temperature to obtain the nickel-cobalt-lithium manganate ternary material. According to the method, nickel, cobalt, manganese and lithium in the positive electrode material of the waste ternary battery are recycled at the same time through a one-step coprecipitation method, valuable metals in the positive electrode material of the waste ternary lithium ion battery are efficiently recycled, meanwhile, the regenerated ternary positive electrode material can be obtained, and the obtained regenerated ternary positive electrode material has good electrochemical performance. According to the recycling process, the step of separating lithium from nickel, cobalt and manganese and the step of preparing lithium salt and nickel, cobalt and manganese precursorsare omitted, the process is greatly simplified, and the recycling cost is remarkably reduced.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
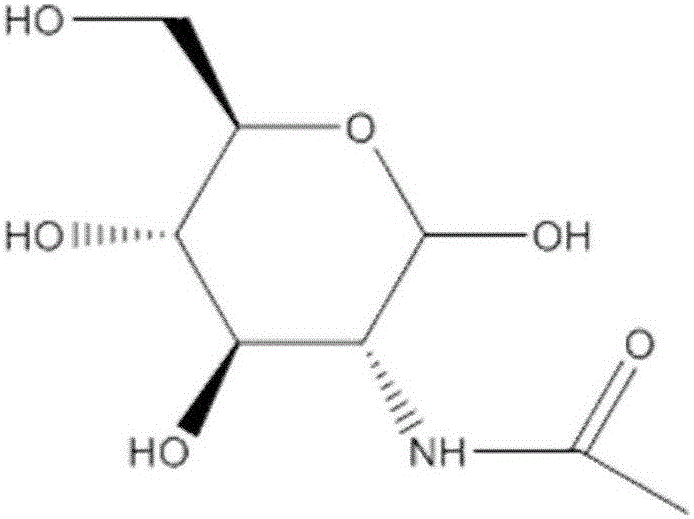
Method for separating and extracting N-acetyl-D-glucosamine and D-glucosamine from ammonia sugar fermentation liquor
ActiveCN106188167ASimple operation processFewer separation stepsSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationNucleotideReverse osmosis
The invention discloses a method for separating and extracting N-acetyl-D-glucosamine and D-glucosamine from ammonia sugar fermentation liquor. The method includes the steps of microfiltration, ultrafiltration, nanofiltration and the like, the fermentation liquor is filtered through a microfiltration membrane with the aperture of 0.1-10 micrometers to remove impurity particles and microbial thalli, protein, nucleic acid, colloidal particle large molecules and other impurities are removed through filtering by means of an ultrafiltration membrane with the aperture of 0.001-0.1 micrometer, and pigment, polypeptide, nucleotide and other small-molecular impurities are removed through a reverse osmosis system; N-acetyl-D-glucosamine is crystallized and separated from the fermentation filtrate containing N-acetyl-D-glucosamine and glucosamine. The method includes the steps of fermentation filtrate heating and concentration, seed crystal addition, temperature-control crystallization, N-acetyl-D-glucosamine crystal collection, residual glucosamine recycling and the like. The method is low in cost and does not influence the structure of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine, and the obtained N-acetyl-D-glucosamine is high in purity.
Owner:YANGZHOU RIXING BIO TECH +1
Green synthesis method of methyl phosphorus dichloride
InactiveCN106117267AImprove conversion rateImprove protectionGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsPhosphorus pentachloridePhosphorus trichloride
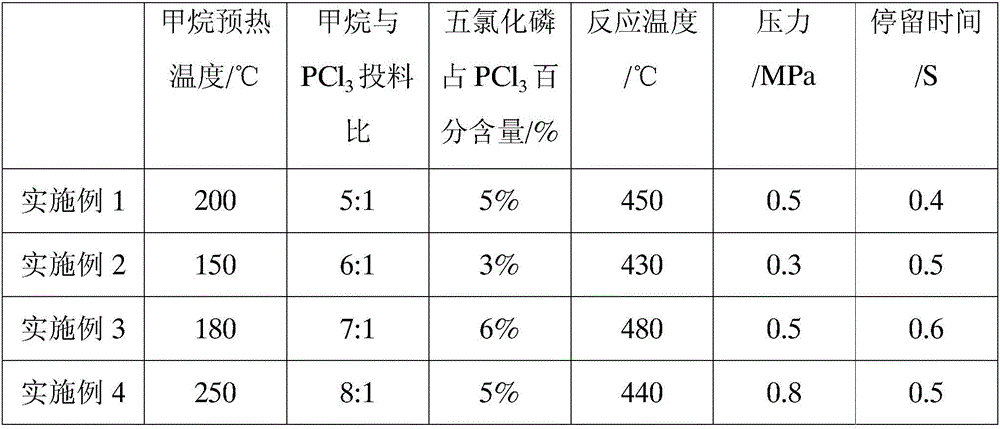
The invention discloses a green synthesis method of methyl phosphorus dichloride. The method comprises the following steps: by taking phosphorus pentachloride as a catalyst, heating phosphorus trichloride and phosphorus pentachloride into vapor, and preheating to 150-250 DEG C and mixing with methane and then entering a tubular reactor, and reacting for 0.1-1.0s under the conditions that the temperature is at 400-500 DEG C and the pressure is 0.3-1.2MPa, to obtain methyl phosphorus dichloride. After the catalyst is applied to methane and phosphorus trichloride to synthesize methyl phosphorus dichloride, the conversion rate of the phosphorus trichloride is effectively improved to 40%-50%, and the yield is 90%-95%; the adopted catalyst phosphorus pentachloride is decomposed into phosphorus trichloride and chlorine gas, the catalyst and the product is not required for separation, three wastes are not generated during the whole preparation, and all the materials are recycled, so that the resources are saved, the environment is beneficially protected, and the synthesis method is green.
Owner:ANHUI COSTAR BIOCHEM CO LTD
Rare-earth permanent magnet material mixed with bayan obo co-existence and associated crude ores and method for manufacturing rare-earth permanent magnet material
InactiveCN104637643ALow priceReduce pollutionInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureThermal deformationAlloy
The invention relates to a rare-earth permanent magnet mixed with bayan obo co-existence and associated crude ores and a method for manufacturing the rare-earth permanent magnet. Compositions of the rare-earth permanent magnet are shown as a following formula of MM<x>Fe<y>A<z>B, the x is larger than or equal to 2 and is smaller than or equal to 2.5, the y is larger than or equal to 11 and is smaller than or equal to 14, the z is larger than or equal to 0 and is smaller than or equal to 0.6, the MM represents rare-earth mixed with the bayan obo co-existence and associated crude ores, and the A represents nanometer auxiliary alloy which includes one type of Nd elements, Pr elements, Al elements and Cu elements or a plurality of types of the Nd elements, the Pr elements, the Al elements and Cu elements. The rare-earth permanent magnet can be manufactured by the aid of a powder metallurgy technology and rapid quenching and thermal pressure and thermal deformation technologies. The rare-earth permanent magnet and the method have the advantages that the novel resource-saving rare-earth permanent magnet which is developed from the rare-earth mixed with the bayan obo co-existence and associated crude ores can replace the traditional rare-earth permanent magnet and is low in cost, and environmental pollution can be reduced; the magnetic energy product scope of the magnet ranges from 20MGOe to 40MGOe, and applicable scope gaps of ferrites and SmCo rare-earth permanent magnets can be effectively filled.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for separating purified protamine using reverse micelle method
InactiveCN101357935AHigh recovery rate of enzyme activityContinuous operationPeptide preparation methodsIonic strengthOrganic solvent
The invention belongs to the technical field of separation and purification of bio-active substances, more particularly relates to a method for directly separating and purifying the protamine from crude protamine extract with a reverse micelle method. The invention aims at solving the problems of complex process, multiple steps and long cycle of present protamine purification. The invention directly separates, purifies the protamine from the crude protamine extract by adopting the reverse micelle solution which consists of a surfactant and an organic solvent and can realize the high-efficient extraction and back extraction of the protamine by adjusting the conditions of extraction processes such as pH of water phases, ionic strength, phase ratio, contact time of two phases; the highest enzyme recovery rate can reach more than 96 percent and the purification factor reaches more than 2.1. The process has the effects of both concentration and decoloration. In addition, the separation and purification of the protamine with the reverse protamine technology have the advantages of short cycle, convenient continuous operation and being easily amplified.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
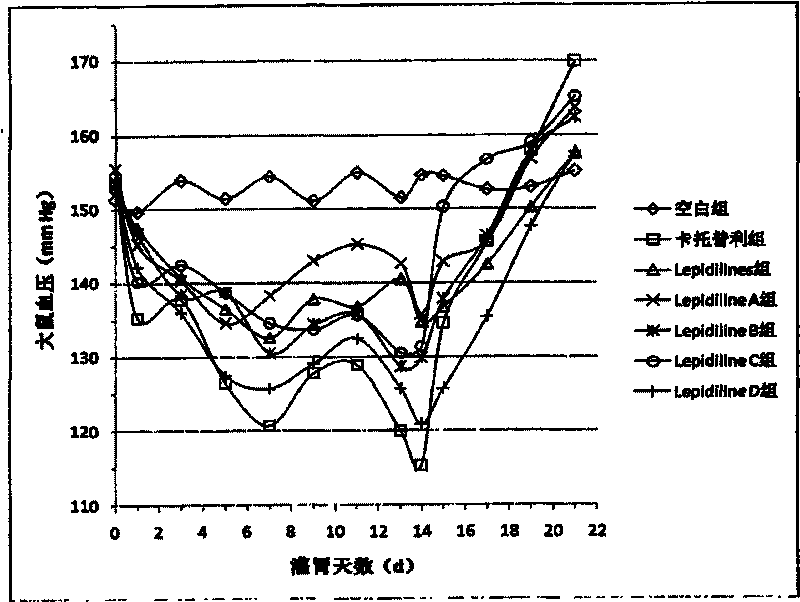
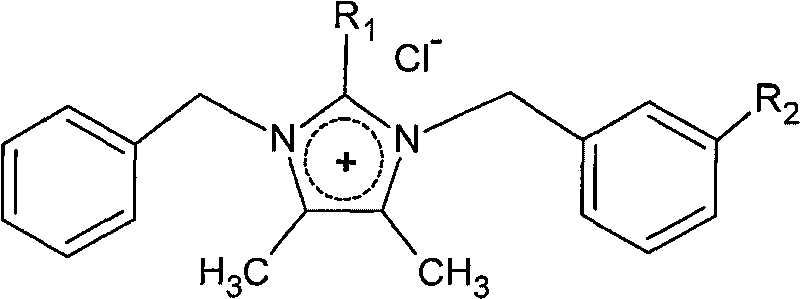
Application of maca imidazole alkaloid in preparation of cardiovascular drugs
InactiveCN101756965ABiologically activeFewer separation stepsOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderCardiovascular drugStructural formula
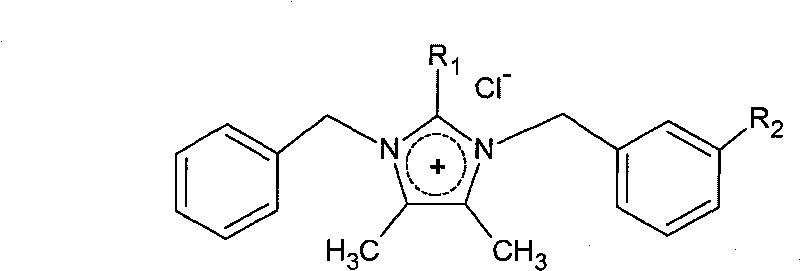
The invention discloses an application of maca imidazole alkaloid, in particular to an application to the preparation of cardiovascular drugs. All or part of the components are prepared from one or mixture of compounds having the following chemical structural formula as shown in formula (I), wherein R1 can be H or CH3, and R2 is H or OCH3. The invention first discovers the remarkable pharmaceutical activity of the compounds on blood pressure drop and arrhythmia resistance. Therefore, the maca imidazole alkaloid prepared by the new process can be used for developing antineoplastic drugs and can be expected to act as drugs for treating corresponding cardiovascular diseases. Formula (I).
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for separating and extracting L-arginine from fermentation liquor
InactiveCN102001972AExtended service lifeEmission reductionOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationWater dischargeArginine
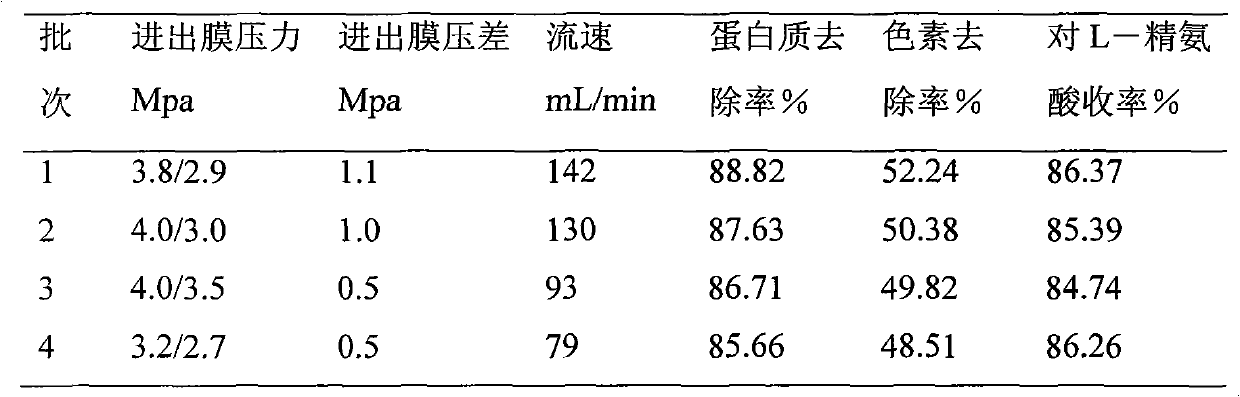
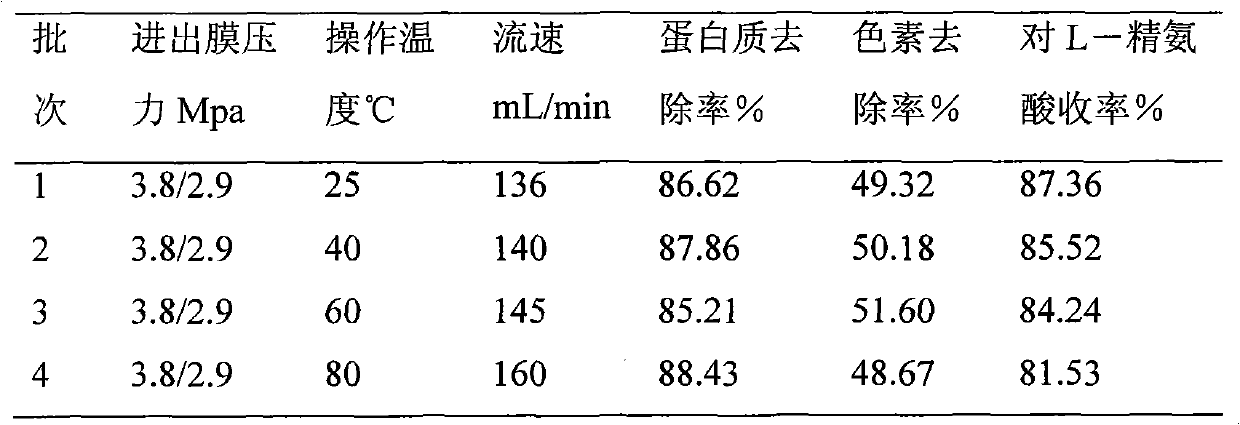
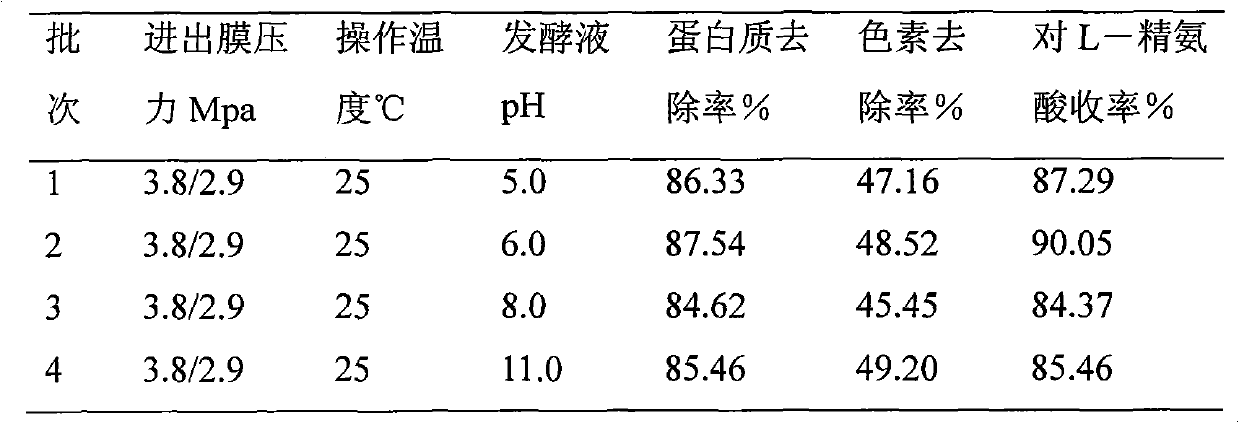
The invention discloses a method for separating and extracting L-arginine from fermentation liquor, which comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out microfiltration on L-arginine fermentation liquor by a metal microfiltration membrane; and then, decoloring the obtained product; finally, sequentially carrying out reduced pressure evaporation, crystallization and refining on the decolored product. The method of the invention is simple and easy to operate, convenient in device maintenance and less in investment, and the adopted metal membrane is long in service time, has heat-resistance, acid-resistance, alkali-resistance and is easy to clean; the whole extraction process is performed by using a physical separation method, therefore, less acid, alkali and steam are consumed in the extraction process, and the extraction cost is greatly reduced; meanwhile, the method is mild in condition, is simple in operation, is few in separation steps, is less in waste water discharge, is high in yield, is good in product quality, and the like; and through analysis, the purity of the L-arginine product obtained through alcohol-precipitation and crystallization reaches over 99 percent.
Owner:STAR LAKE BIOSCI CO INC ZHAOQING GUANGDONG
Optimized karyote in-vitro separation kit and application method thereof
ActiveCN102643781ASimple processReduce energy consumptionBlood/immune system cellsFermentationSucroseCentrifugation
An optimized karyote in-vitro separation kit comprises two reagents. The reagent 1 is composed of erythrocyte precipitant, sodium chloride or potassium chloride. The reagent 2 is composed of natrii diatrizoas and polysucrose No.400, natrii diatrizoas and polysucrose dextranum, or percoll, and has density of 1.076-1.090. An application method of the optimized karyote in-vitro separation kit includes directly adding 100ml of human marrow blood, umbilical cord blood or peripheral blood into 200ml of solution of the reagent 1, allowing for standing for 10-30 minutes, collecting supernate, centrifuging at 2000rpm (1100xg) for 5 minutes, discarding the supernate, adding remnant a centrifugal tube containing solution of the reagent 2, performing density gradient centrifugation for 30 minutes, controlling the rotation speed at 1500rpm, absorbing a karyote layer, performing centrifugal cleaning for once to three times, using 50ml of cell preservative solution for diluting, and taking 100 microliters for testing or self-testing.
Owner:NINGXIA ZHONGLIANDA BIOPHYSICS
Method for synthesizing 2,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene through multi-step successive reaction of hexafluoropropylene
ActiveCN103449963ASimple processFewer separation stepsPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offHydrogen fluorideOrganic solvent
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing 2,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene through multi-step successive reaction of hexafluoropropylene, which comprises the following steps: (1) performing hydrogenation reaction on hexafluoropropylene and hydrogen gas to generate a product containing 1,1,1,2,3,3-hexafluoropropane; (2) directly introducing the product containing the 1,1,1,2,3,3-hexafluoropropane into a mixture of an alkaline solution and organic solvent, and performing dehydrofluorination to generate a product containing 1,1,1,2,3-pentafluoropropene; (3) dehydrating the product containing the 1,1,1,2,3-pentafluoropropene, and performing hydrogenation reaction to generate a product containing 1,1,1,2,3-pentafluoropropane; and (4) directly introducing the product containing the 1,1,1,2,3-pentafluoropropane into a mixture of an alkaline solution and organic solvent, and performing dehydrofluorination to generate the 2,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene. The method has the advantages of simple process, less equipment investment, low energy consumption and less discharge of three wastes.
Owner:JUHUA GROUP TECH CENT +1
Method for producing Gamma-aminobutyric acid through centrifugal mother liquid of glutamic acid
ActiveCN102978250AIncrease added valueReduce pollutionOrganic compound preparationMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMonosodium glutamate
The invention relates to a production method of Gamma-aminobutyric acid. The method comprises the following steps: (1) fermentation of monosodium glutamate isoelectric mother liquor: inoculating lactic acid bacteria strain to the monosodium glutamate mother liquor which is subjected to isoelectric crystallization, and fermenting to obtain the fermentation liquor of Gamma-aminobutyric acid; (2) removal of impurities: processing the fermentation liquor of the Gamma-aminobutyric acid through a ceramic membrane filter so as to remove larger particulate impurities and thallus, and concentrating, then adding dialysis water for dialyzing, so as to obtain the clear liquid of the ceramic membrane; (3) decolorizing and removing of micromolecular impurities: filtering the clear liquid of the ceramic membrane obtained in step (2) through a nanofiltration membrane, and then carrying out dialysis to obtain the clear liquid of the nanofiltration membrane; and (4) concentrating: concentrating the clear liquid subjected to the nanofiltration and dialyzing and obtained in step (3) through a reverse osmosis membrance, thus obtaining the concentrate of the reverse osmosis membrance, and finally drying to obtain the Gamma-aminobutyric acid. According to the method, the supernate obtained after the isoelectric extraction of glutamic acid in the monosodium glutamate production technology is recycled to produce the Gamma-aminobutyric acid; and the method is easy for industrial continuity, low in energy consumption, and high in purity of the Gamma-aminobutyric acid.
Owner:JIANGSU JIUWU HITECH
Preparation method and application of SAPO-34 molecular sieves with flaky morphology
ActiveCN106477595AHigh selectivityIncreased diffusion rateMaterial nanotechnologyEthylene productionSynthesis methodsSolvent
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of molecular sieves and particularly relates to synthesis of SAPO-34 molecular sieves with flaky morphology and an application of the SAPO-34 molecular sieves in preparation of methanol to olefin. The molecular sieves are subjected to one-step hydrothermal synthesis, a double-template agent is mixed with an aluminum source, a silicon source and a phosphorus source, hydrothermal crystallization is performed, and the SAPO-34 molecular sieves are prepared. The synthesized SAPO-34 product adopts the flaky morphology, the crystal size ranges from 0.5 mu m to 2 mu m, and the thickness ranges from 50 nm to 200 nm. The synthesis method is simple, other solvents, surfactants and the like do not need to be added. The prepared product has high low-carbon olefin selectivity, especially high ethylene selectivity in a methanol-to-olefin reaction.
Owner:陕西煤化工技术工程中心有限公司
Test method for detection of tea polyphenol and flavonoid constituents of golden camellia
The invention relates to the technical field of solid-phase extraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrum coupling, and provides a test method for detection of tea polyphenol and flavonoid constituents of golden camellia. The test method comprises solid-phase extraction adsorption-gas chromatography-mass spectrum coupling detection, wherein the solid-phase extraction is carried out by a stirring rod in a direct stirring manner; the stirring rod is coated with a graphene-polymer coating on the basis of two-dimension or three-dimension; the materials of thegraphene-polymer coating comprise graphene and a graphene modified material; thegraphene modified material comprises graphene oxide, graphene-polyethylene glycol dimethyl acrylic ester, graphene-polypyrrole, graphene-polymethyl trimethoxy silane and a graphene nanomaterial. The test method for detection of tea polyphenol and flavonoid constituents of golden camellia has the characteristics of correct detection, high sensitivity, good preferential adsorption effect and long service life.
Owner:程金生
Novel technique for preparing long-chain alkane efficiently through multifunctional catalyst in one-step method
ActiveCN102850157BRedox activeExtend your lifeLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionHydrocarbonsAlkaneNonane
The invention relates to a novel technique for preparing long-chain alkane efficiently through a multifunctional catalyst in a one-step method. The novel technique can be used for producing the long-chain alkane in one step with high selectively under a relative mild condition, and solve the problems of strict reaction condition, low energy efficiency and low alkane selectivity in a process of preparing the long-chain alkane by biomass derivatives. According to the technique, condensation products (C8, C9, C13 and C15) of a biomass derivative, namely furfural or HMF (Hydroxy Methyl Furfural), and acetone are taken as the raw materials, and by designing the three-center multifunctional catalyst of metal (I)-metal (II)-acid, the original two steps of independent reactions which require strict reaction conditions and need different catalysts to join in are combined into an one-step reaction which requires tender reaction conditions, so that the selectivity on corresponding alkane (octane, nonane, tridecane and pentadecane) is improved greatly, the highest yield can be 97%, and meanwhile, a step of separating the product from the catalyst is omitted, therefore, the energy efficiency of the while process is improved by a great step.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Hierarchical pore SAPO-34 molecular sieve synthesis method
InactiveCN107697925AExtended service lifeLow costMolecular-sieve and base-exchange phosphatesMolecular-sieve silicoaluminophosphatesMolecular sieveSynthesis methods
The invention provides a hierarchical pore SAPO-34 molecular sieve synthesis method which is characterized in that an aluminum source, a silicon source, a phosphorus source, an organic template agentand water are mixed and added into a hydrothermal reactor, and in-situ synthesis is performed to form an SAPO-34 molecular sieve with hierarchical pores. According to the hierarchical pore SAPO-34 molecular sieve synthesis method, a hierarchical pore structure can be formed without acid or alkali post-treatment process or addition of other components, raw material cost and subsequent separation steps are reduced, industrial amplifying production is facilitated, substance diffusion and heat conduction in methanol-to-olefin reaction are facilitated by formation of the hierarchical pores, and theservice life of the molecular sieve is greatly prolonged.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for rapid induction of homogenous polyploids of Chinese jujube
InactiveCN101926283AFewer separation stepsEliminate multiple purification stepsPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsColchicineSomatic cell
The invention relates to a method for rapid induction of homogenous polyploids of Chinese jujube, that is the method can double and further develop chromosomes of a single-cell embryo into homogenous tetraploids by simultaneously carrying out induction with colchicine during the somatic embryogenesis process of in vitro leaf blades of the Chinese jujube. The method comprises the steps of somatic embryo induction, doubling of the chromosomes, development of embryoids till nature and detection and screening of the homogenous tetraploids. The specific steps are as follows: selecting tissue culture seedling leaf blades of the Chinese jujube with robust growth and seedling age of 20-30d, and using a pair of scissors after sterilization to shear 5-8 times by being vertical to nervures; then inoculating the leaf blades in an induction culture medium MS plus 15-25g / L of maltose plus 3.0-5.0g / L of agar plus 5.0-10.0mg / L of TDZ plus 1.0-2.0mg / L of AgNO3 by leading the front surfaces to face upwards, and simultaneously adding 15-20mg / L of the colchicine into the culture medium, and carrying out dark culture for 40-50 days; transferring embryoids differentiated from calli of the leaf blades of the Chinese jujube into a hormone-free culture medium of the MS plus 40g / L of sucrose plus 500mg / L of caseinhydrolysate for lighting culture and further developing the embryoids into somatic embryo seedlings; and screening out the homogenous tetraploids from the somatic embryo seedlings through chromosome detection or the detection by a flow cytometer, wherein the pH of the culture medium is 5.0-6.0, and the culture temperature is 25-30 DEG C. The method can avoid the appearance of chimeras, omit the steps of separation and purification, rapidly obtain the homogenous polyploids and have important application value for accelerating the breeding process of the polyploids of the Chinese jujube.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
A method for synthesizing 2,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene by multi-step continuous reaction of hexafluoropropene
ActiveCN103449963BSimple processFewer separation stepsPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offHydrogen fluorideOrganic solvent
Owner:JUHUA GROUP TECH CENT +1
Preparation method of high-purity halogenated hydrocarbon used for liquid chromatogram
ActiveCN101781163AEasy to recycleReduce process stepsHalogenated hydrocarbon separation/purificationMolecular sieveAlcohol
The invention relates to a method for producing high-purity halogenated hydrocarbon used for liquid chromatogram by primarily rectified industrial halogenated hydrocarbon. The method comprises the following steps: eliminating unsaturated compounds by sulphuric acid, using water for extractive distillation to remove oxidizable substances, alcohols and high-hydrophilicity impurities with the similar boiling point to the halogenated hydrocarbon; using molecular sieves for water removal through absorption; and using toluene for extractive distillation to remove hydrocarbon with the similar boiling point to the halogenated hydrocarbon.
Owner:ANQING FULLTIME CHEM INDAL
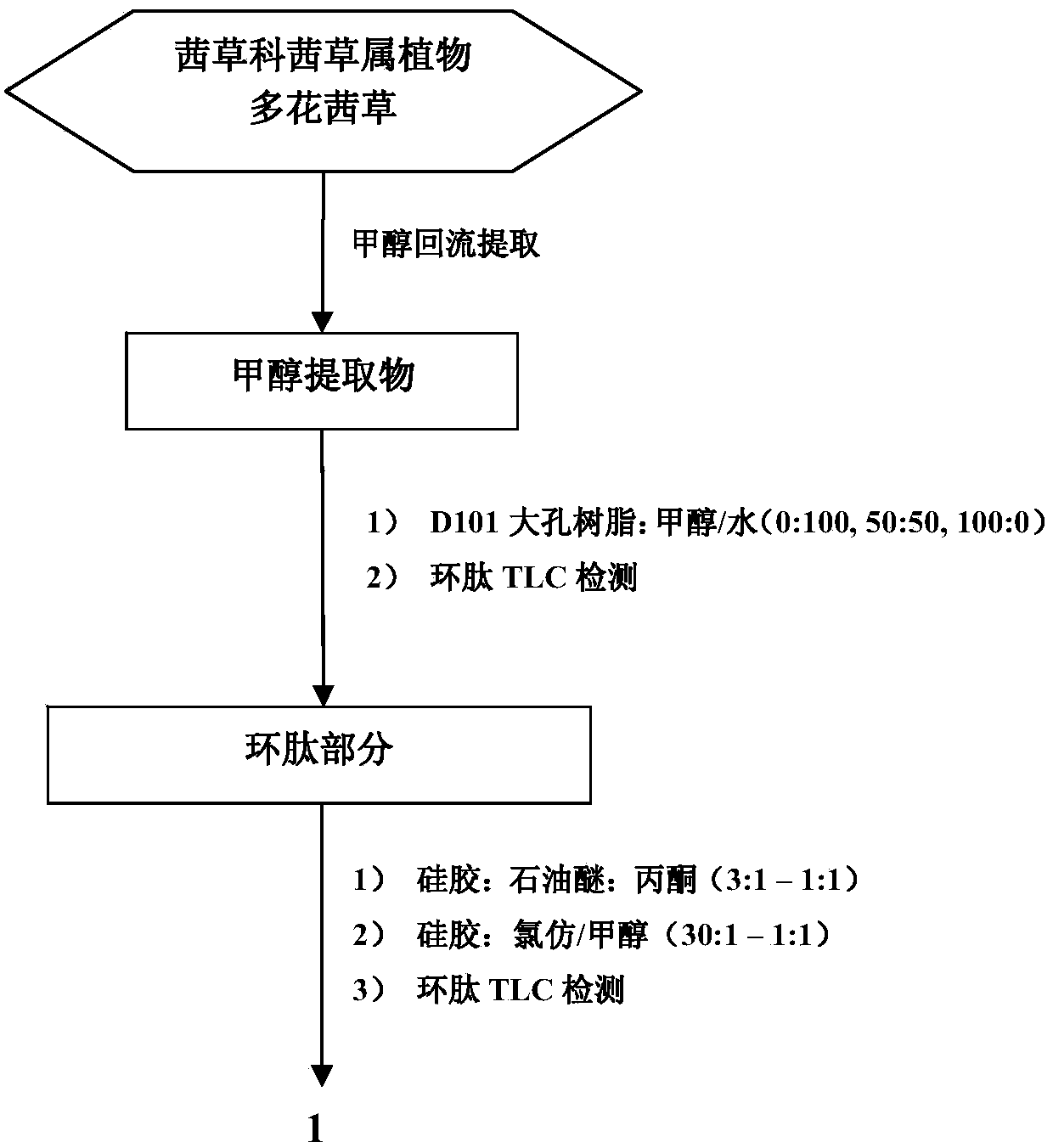
Preparation method of rubiaceous cyclopeptide and application of rubiaceous cyclopeptide as Hippo-YAP signal pathway inhibitor
InactiveCN104193808AEasy to separateImprove efficiencyPeptide preparation methodsCyclic peptide ingredientsCyclic peptideMethyltyrosines
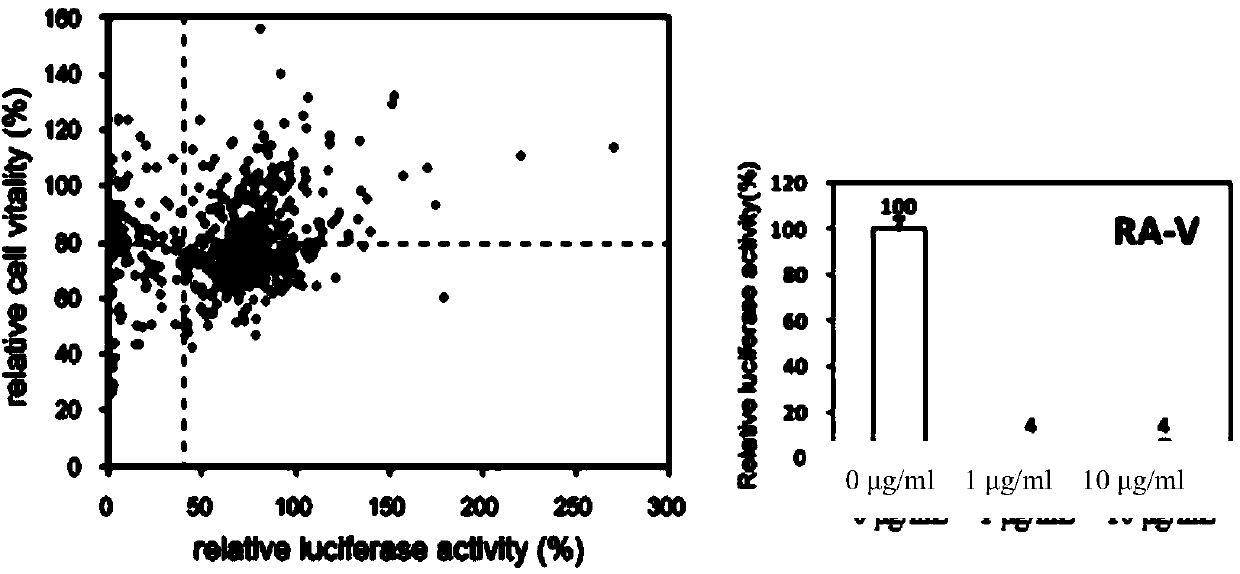
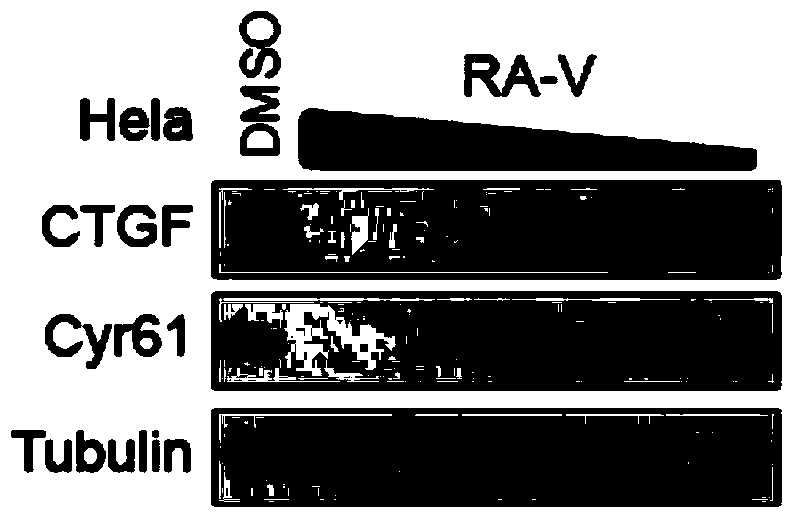
The invention provides an application of rubiaceous cyclopeptide RA-V (1) as a Hippo-YAP signal pathway inhibitor, a preparation method of the rubiaceous cyclopeptide and an application of the rubiaceous cyclopeptide to preparation of drugs for treating and preventing YAP abnormal activation related cancers. The rubiaceous cyclopeptide provided by the invention is formed by condensation of peptide bonds of one alpha-D-alanine, one alpha-L-alanine, three substituted N-methyl-alpha-L-tyrosine and one alpha-L-amino acid of other types, and six amino acids are condensed to form an eighteen-membered ring, wherein a benzene ring between two vicinal tyrosines is connected through an oxygen bridge to form a fourteen-membered ring. Compared with the prior art, the preparation method provided by the invention can be used for rapidly separating and purifying the target compound RA-V (1) and has the advantages of high efficiency, strong purposiveness, few separation step, convenience in operation, good controllability and repeatability, recyclable solvent, low cost and suitability for industrial production.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +2
Polyimide (PI) composite membrane for pervaporation separation of amide/water and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108126538AEfficient separationFewer separation stepsSemi-permeable membranesChain structurePolyamic acid
The invention discloses a polyimide composite membrane for pervaporation separation of amide / water and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of pervaporation separation. An inorganic porous base membrane is coated with a compact polyimide separated layer through a dipping and pulling process so that the polyimide pervaporation composite membrane is obtained. In order to prepare the polyimide pervaporation composite membrane with high separation performances, the main chain structure of a precursor polyamic acid resin of the separated layer polyimide membrane has symmetry groups with rigid chains (such as benzene rings) and the main chain structure contains the symmetry rigid chains. The membrane satisfies the requirements on the amide / water mixed pervaporation separation membrane in solvent resistance and selective separation and is suitable for the preparation of the pervaporation membranes.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
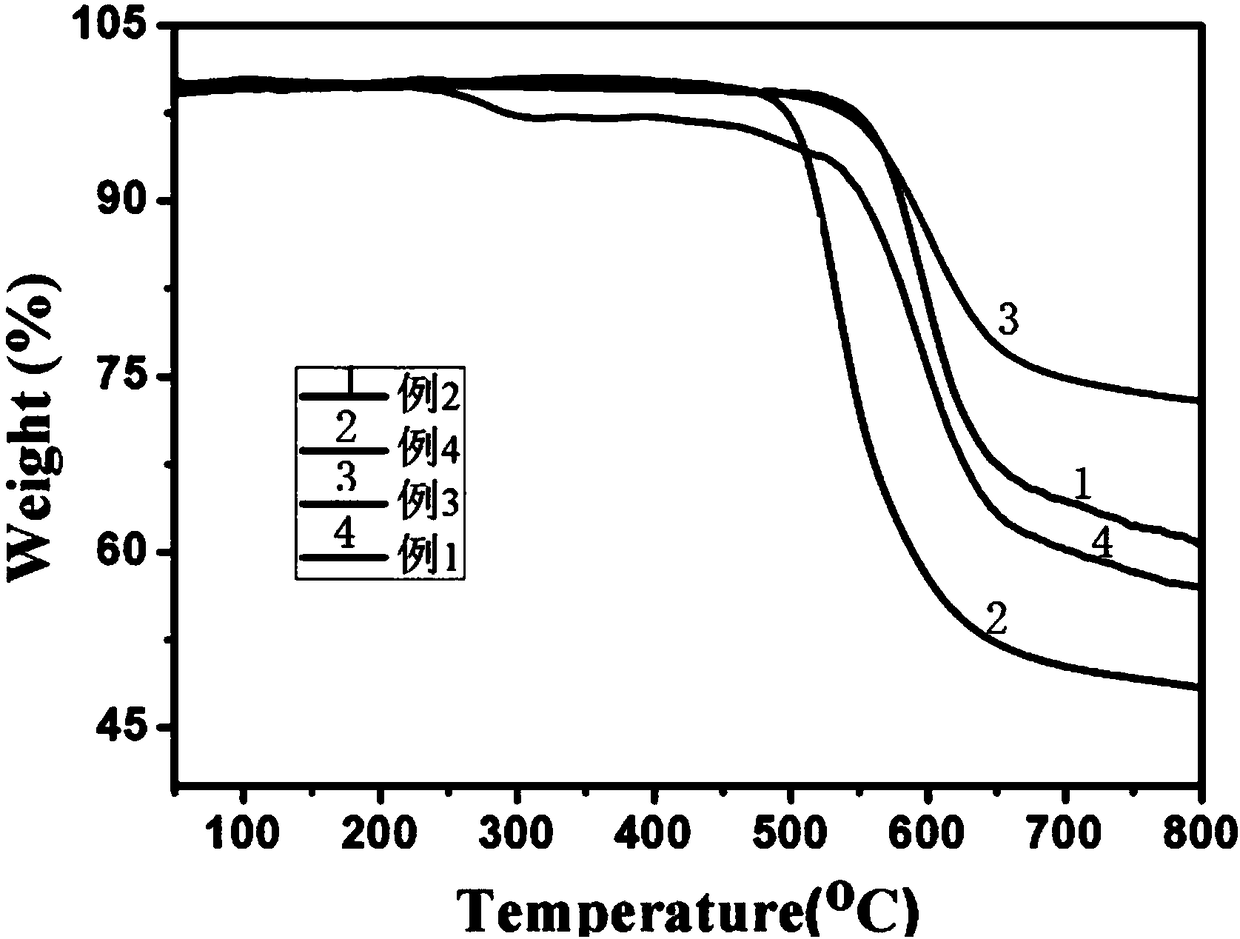
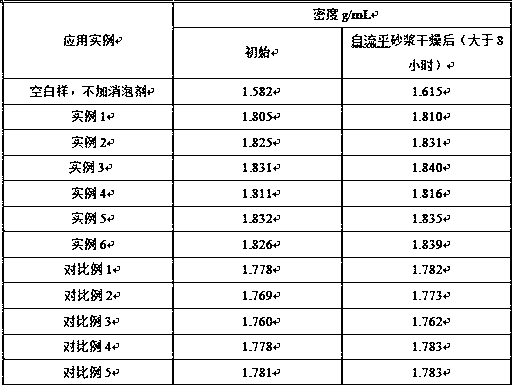
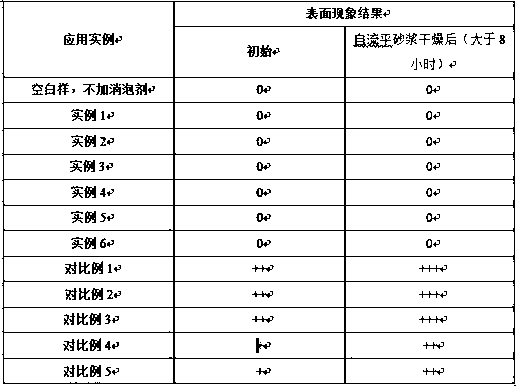
Defoaming agent applied to thin-layer self-leveling mortar and preparation method of defoaming agent
The invention provides a defoaming agent applied to thin-layer self-leveling mortar and a preparation method of the defoaming agent. The defoaming agent comprises the components: white carbon black, polyether, fatty alcohol and alkynol silicon polyether. The preparation method comprises the steps: (1) firstly, mixing and stirring fatty alcohol and part of white carbon black to form a dispersoid M1; (2) preparing alkynol silicon polyether, then adding the dispersoid M1 and polyether, and mixing to obtain a dispersoid M2; and (3) slowly spraying the dispersoid M2 onto A2 through a metering pumpunder certain temperature and rotating speed conditions, and mixing to obtain M3; and finally, screening the M3 to obtain the solid defoaming agent. The solid defoamer prepared by the method is specially used for solving the problems of surface cracking and hollowing of thin-layer self-leveling mortar, and compared with a traditional defoaming agent, the defoaming agent disclosed by the inventionhas the advantages of simple preparation method, good defoaming and foam inhibition performances, no influence on the stability of a self-leveling mortar system and capability of remarkably improvingthe surface performance of the self-leveling mortar.
Owner:JIANGSU SIXIN SCI-TECH APPL RES INST CO LTD +1
Method of separation and extraction of D-lactic acid from sodium D-lactate fermentation liquid
ActiveCN104974032AStrong continuityShort acidification timeCarboxylic compound separation/purificationIonIon exchange
The invention discloses a method of separation and extraction of D-lactic acid from sodium D-lactate fermentation liquid, belongs to the technical field of bio-engineering and particularly relates to the method of separation and extraction of D-lactic acid from the fermentation liquid. The method includes the steps of (1) performing solid-liquid separation to the sodium D-lactate fermentation liquid, removing proteins and pigments to obtain a clarified fermentation liquid; (2) decoloring the clarified fermentation liquid obtained in the step (1); (3) performing ion exchange to the fermentation liquid obtained in the step (2); and (4) concentrating the fermentation liquid after the ion exchange to obtain the D-lactic acid. In the method, only is normal-temperature acidification required so that the method is short in acidification time. The method is effectively reduced in the content of protein and a part of the pigments in the fermentation liquid and is free of generation of calcium sulfate which is low in additional value and is difficult to treat. The method is optimized in operation and is less in separation steps.
Owner:SINOPEC YANGZI PETROCHEM +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com