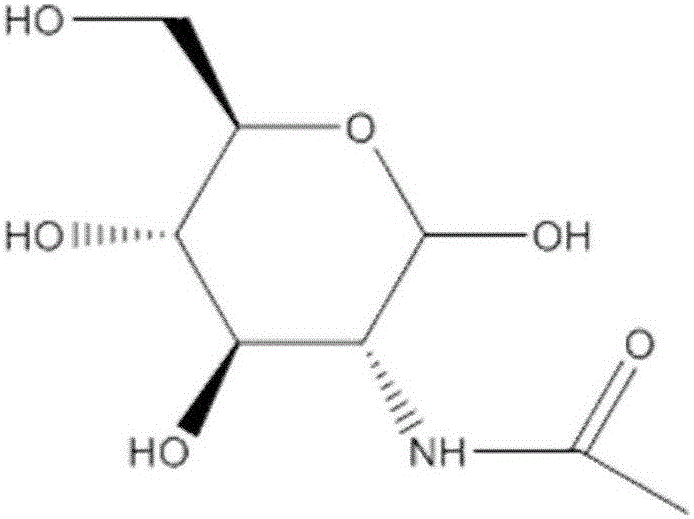
Method for separating and extracting N-acetyl-D-glucosamine and D-glucosamine from ammonia sugar fermentation liquor
A technology of glucosamine and acetyl group, applied in amino sugar, chemical instruments and methods, sugar derivatives, etc., can solve problems such as long process route, and achieve the effects of simple operation process, few separation steps, and low production energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Take 10L of fermentation broth, wherein the content ratio of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine to glucosamine is 6:4, filter through a polypropylene microfiltration membrane with a pore size of 1 μm to remove impurity particles and some microbial cells in the fermentation broth, A crude extract is obtained; the operating pressure is 0.5Mpa, and the operating temperature is 30°C. The filtered crude extract is passed through a polyolefin ultrafiltration membrane with a pore size of 0.05 μm to remove residual protein, nucleic acid, and colloidal particle macromolecular impurities in the fermentation broth. The operating pressure is 0.25 MPa, the temperature is 30 ° C, and the concentration factor is 4. times. The filtrate obtained by microfiltration and ultrafiltration is then subjected to reverse osmosis to remove water or small molecular impurities. The filtrate was stirred and heated to 60°C in a water bath, and the fermentation broth was further concentrated to 2L, with a final ...
Embodiment 2
[0024]Take 50L of fermentation broth, wherein the content ratio of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine to glucosamine is 7:3, filter through a polypropylene microfiltration membrane with a pore size of 1 μm to remove impurity particles and some microbial cells in the fermentation broth, A crude extract is obtained; the operating pressure is 0.2 MPa, and the operating temperature is 30°C. The filtered crude extract is passed through a polyolefin ultrafiltration membrane with a pore size of 0.02 μm to remove residual protein, nucleic acid, and colloidal particle macromolecular impurities in the fermentation broth. The operating pressure is 0.25MPa, the temperature is 30°C, and the concentration factor is 4 times. The filtrate obtained by microfiltration and ultrafiltration is then subjected to reverse osmosis to remove water or small molecular impurities. The filtrate was stirred and heated to 70°C in a water bath, and the fermentation broth was further concentrated to 10L, so that the fina...
Embodiment 3
[0026] Take 50L of fermentation broth, wherein the content ratio of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine to glucosamine is 8:2, filter through a polypropylene microfiltration membrane with a pore size of 0.5 μm to remove impurity particles and some microbial cells in the fermentation broth , to obtain a crude extract; the operating pressure is 0.2MPa, and the operating temperature is 30°C. The filtered crude extract is passed through a polyolefin ultrafiltration membrane with a pore size of 0.02 μm to remove residual protein, nucleic acid, and colloidal particle macromolecular impurities in the fermentation broth. The operating pressure is 0.25 MPa and the temperature is 30°C. The filtrate obtained by microfiltration and ultrafiltration is then subjected to reverse osmosis to remove water or small molecular impurities. The filtrate was stirred and heated to 70°C in a water bath, and the fermentation broth was further concentrated to 10L, so that the final concentration of acetylglucosamine ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com