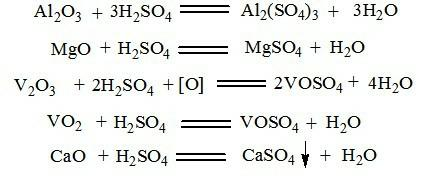Resource recycling method for 80 ferrovanadium slag
A technology of ferrovanadium slag and recycling, applied in the field of metallurgy, can solve the problems of low utilization rate of elements, poor economic benefits, and impossibility of realization, and achieve the effects of quick results, small investment, and simplified production process steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
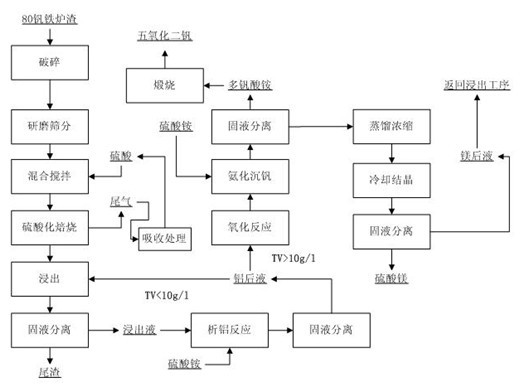
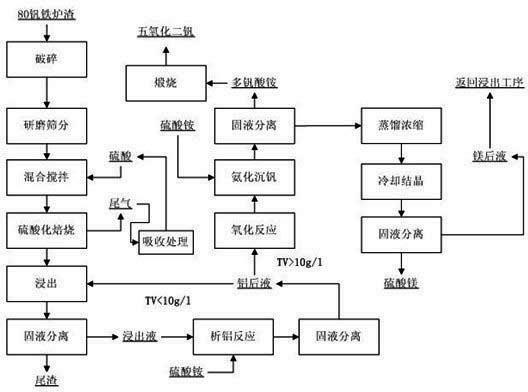
[0027] Embodiment 1: The resource utilization method of the 80 vanadium iron slag adopts the following process steps.
[0028] 1. Raw material pretreatment:
[0029] 1) Crushing: Crushing the poor iron-vanadium slag through a jaw crusher to a particle size of less than 5mm.
[0030] 2) Grinding and screening: Grind the poor ferrovanadium slag after crushing with a ball mill for 20 minutes, and control the particle size of mechanical screening at -80 mesh.
[0031] 2. Mixing and stirring: Mix the poor iron vanadium slag and 80wt% sulfuric acid at a mass ratio of 1:5, and mechanically stir at a speed of 200r / min for 0.6h.
[0032] 3. Sulfation roasting:
[0033] 1) Pre-roasting stage: Pre-roast at 100°C for 24 hours for drying treatment, stirring several times in the middle.
[0034] 2) Roasting stage: Roast at 400°C for 2 hours to make roasted slag, and recover the exhaust gas; the flue gas produced by sulfation roasting is absorbed by sulfuric acid, and the obtained concent...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Embodiment 2: The resource utilization method of the 80 vanadium iron slag adopts the following process steps.
[0044] 1. Raw material pretreatment:
[0045] 1) Crushing: Crushing the poor iron-vanadium slag through a jaw crusher to a particle size of less than 5mm.
[0046] 2) Grinding and screening: Grind the poor ferrovanadium slag after crushing with a ball mill for 2 hours, and control the particle size of mechanical screening at -80 mesh.
[0047] 2. Mixing and stirring: Mix the poor iron vanadium slag and 98wt% sulfuric acid at a mass ratio of 1:3.5, and mechanically stir at a speed of 100r / min for 0.8h.
[0048] 3. Sulfation roasting:
[0049] 1) Pre-roasting stage: Pre-roast at 150°C for 4 hours for drying treatment, stirring several times in the middle.
[0050] 2) Roasting stage: Roast at 500°C for 5 hours to make roasted slag, and recover the exhaust gas; the flue gas produced by sulfation roasting is absorbed by sulfuric acid, and the obtained concentra...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Embodiment 3: The resource utilization method of the 80 vanadium iron slag adopts the following process steps.
[0060] 1. Raw material pretreatment:
[0061] 1) Crushing: Crushing the poor iron-vanadium slag through a jaw crusher to a particle size of less than 5mm.
[0062] 2) Grinding and screening: Grind the poor ferrovanadium slag after crushing with a ball mill for 40 minutes, and control the particle size of mechanical screening at -80 mesh.
[0063] 2. Mixing and stirring: Mix the poor iron vanadium slag and 45wt% sulfuric acid at a mass ratio of 1:10, and mechanically stir at a speed of 150r / min for 0.5h.
[0064] 3. Sulfation roasting:
[0065] 1) Pre-roasting stage: Pre-roast at 200°C for 1 hour for drying treatment, stirring several times in the middle.
[0066] 2) Roasting stage: Roast at 250°C for 6 hours to make roasted slag, and recover the exhaust gas; the flue gas produced by sulfation roasting is absorbed by sulfuric acid, and the obtained concentr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com