High-strength and high-conductivity aluminum-based wire and preparation method thereof
A high-conductivity, aluminum-based technology, used in conductive materials, conductive materials, conductors, etc., can solve problems such as strength obstacles, reduce resistivity, improve alloy strength, and reduce the probability of electron scattering.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
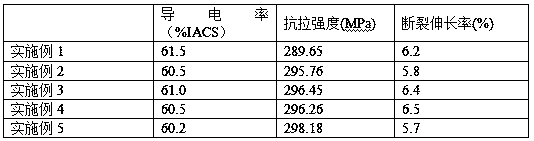
[0017] Embodiment 1: The high-strength and high-conductivity aluminum-based wire of this embodiment is made of the following metal elements and non-metal elements: the mass of aluminum is 1, 0.30% yttrium, 0.50% germanium, 0.20% erbium, and 0.30% copper , magnesium 0.60%, boron 0.40%, silicon 0.50%, iron 0.80%;
[0018] A method for preparing an aluminum-based wire with high strength and high conductivity, the specific steps are as follows:
[0019] (1) Heat and melt aluminum ingots into aluminum water;
[0020] (2) At a temperature higher than the melting point of aluminum (the temperature is 890°C), add an aluminum-germanium master alloy, an aluminum-erbium master alloy, an aluminum-yttrium master alloy, an aluminum-copper master alloy, and an aluminum-boron master alloy to the aluminum water obtained in step (1). Alloy, iron, and silicon are dispersed evenly. After 10 minutes of heat preservation, magnesium is added, and then heat preservation is carried out for 15 minutes...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Embodiment 2: The high-strength and high-conductivity aluminum-based wire of this embodiment is made of the following metal elements and non-metal elements: the mass of aluminum is 1, 0.40% yttrium, 0.20% germanium, 0.40% erbium, and 0.50% copper , magnesium 0.50%, boron 0.20%, silicon 0.80%, iron 0.50%;
[0026] A method for preparing an aluminum-based wire with high strength and high conductivity, the specific steps are as follows:
[0027] (1) Heat and melt aluminum ingots into aluminum water;
[0028] (2) At a temperature higher than the melting point of aluminum (the temperature is 870°C), add an aluminum-germanium master alloy, an aluminum-erbium master alloy, an aluminum-yttrium master alloy, an aluminum-copper master alloy, and an aluminum-boron master alloy to the aluminum water obtained in step (1). Alloy, iron, and silicon are dispersed evenly. After 12 minutes of heat preservation, magnesium is added, and 13 minutes of heat preservation is added. 7g of slag...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Embodiment 3: The aluminum-based wire with high strength and high conductivity of this embodiment is made of the following metal elements and non-metal elements: the mass of aluminum is 1, 0.32% of yttrium, 0.30% of germanium, 0.35% of erbium, and 0.35% of copper , magnesium 0.55%, boron 0.25%, silicon 0.70%, iron 0.70%;
[0034] A method for preparing an aluminum-based wire with high strength and high conductivity, the specific steps are as follows:
[0035] (1) Heat and melt aluminum ingots into aluminum water;
[0036] (2) At a temperature higher than the melting point of aluminum (the temperature is 860°C), add an aluminum-germanium master alloy, an aluminum-erbium master alloy, an aluminum-yttrium master alloy, an aluminum-copper master alloy, and an aluminum-boron master alloy to the aluminum water obtained in step (1). Alloy, iron, and silicon are evenly dispersed. After 15 minutes of heat preservation, magnesium is added, and 10 minutes of heat preservation is ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com