Gene capable of increasing nitrogen fertilizer utilization efficiency and yield of rice and application thereof
A high-nitrogen fertilizer, high-yield technology, applied in application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve problems such as limited understanding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
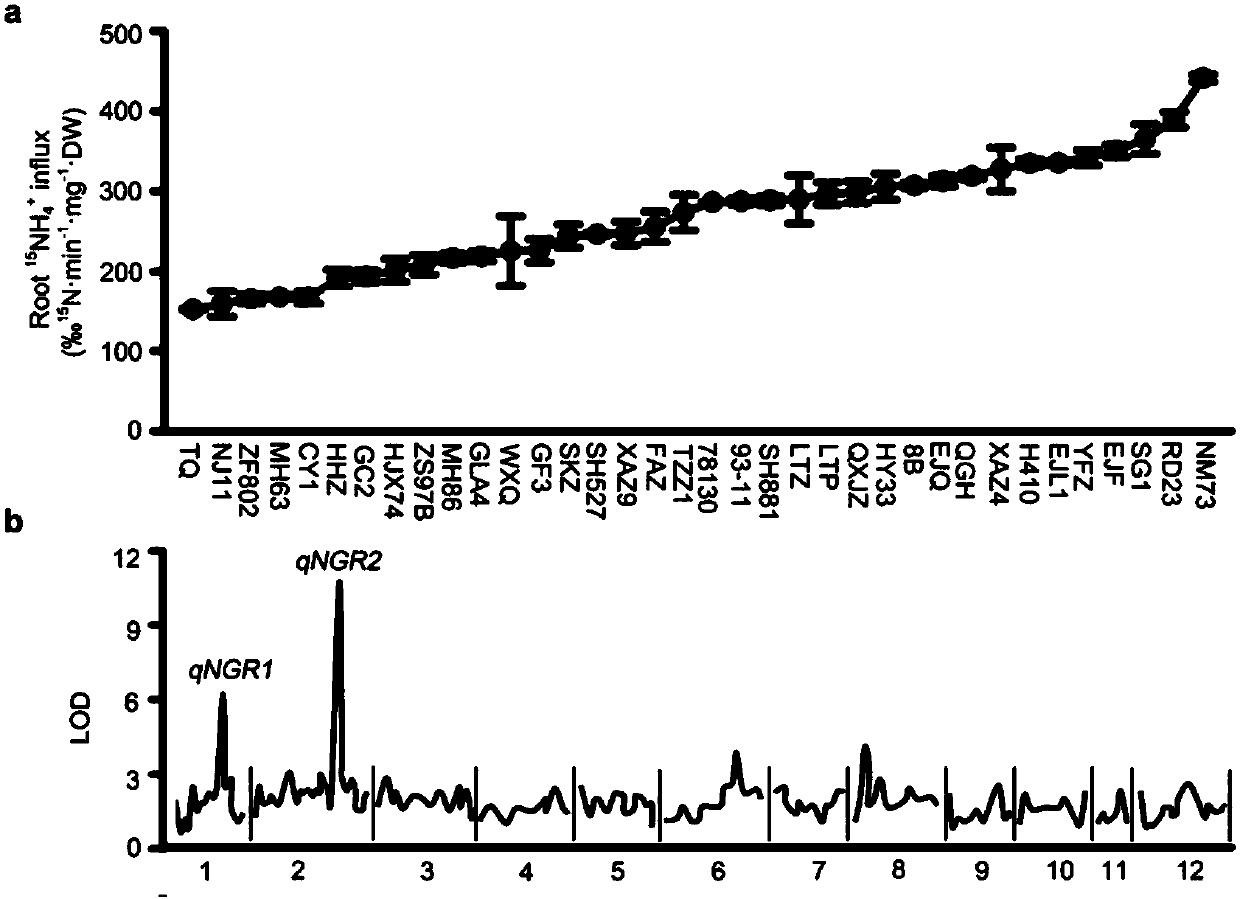
[0132] Example 1: Identification of the main QTL-qNGR2 controlling the nitrogen absorption efficiency of rice
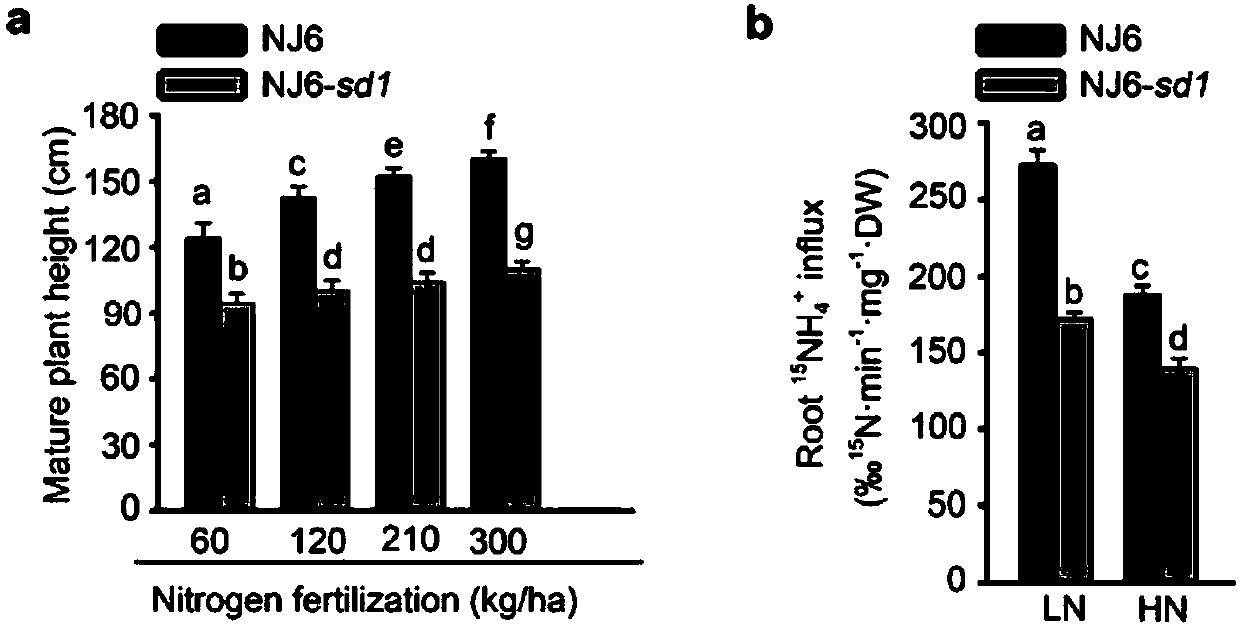
[0133] The inventors carried out hydroponic cultivation on 36 different rice resource materials carrying the "green revolution" gene sd1 for 4 weeks; after that, the pair of different varieties of materials was measured 15 The absorption rate of N-labeled ammonium nitrogen was screened and obtained a rice strain NM73 ( figure 1 a). NM73 is an intermediate breeding material selected by Anhui Quanyin Hi-Tech Seed Industry Co., Ltd.
[0134] Studies have shown that the plant height of NM73 is not sensitive to external application of nitrogen fertilizer: after two different fertilization treatments of low nitrogen and high nitrogen, its plant height does not change significantly. On the contrary, the plant height and yield of the indica rice variety Nanjing 6 (NJ6) are sensitive to exogenous nitrogen fertilizer application: under low-nitrogen treatments, Nanjing 6 exhibits a...
Embodiment 2
[0144] Example 2: Fine mapping and map-based cloning of qNGR2
[0145] The inventors used NM73 and NJ6 hybrid F 1 Materials, and NJ6 as the reincarnation parent, backcrossed continuously for multiple generations to construct BC 4 F 2 group. On this basis, we carried out fine mapping and map-based cloning, and successfully isolated and cloned the candidate gene NGR2. The sequences of the polymorphic marker primers used for fine mapping and map-based cloning are shown in Table 3, and the method for detecting polymorphic markers is as described in Example 1.
[0146] Table 3. Primers and sequences used for fine mapping and map-based cloning
[0147]
[0148]
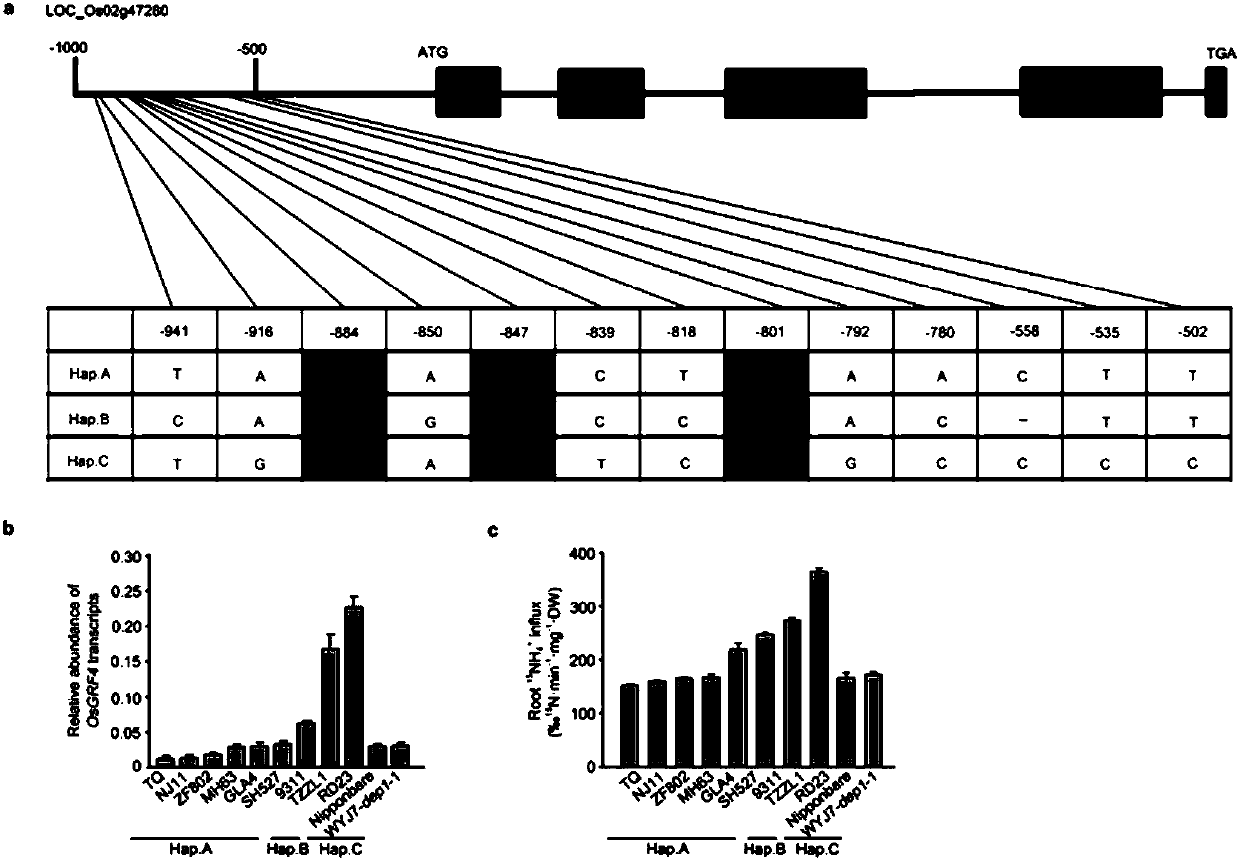
[0149] In the following examples, it is confirmed that the NGR2 candidate gene is OsGRF4 through the comparative analysis of the candidate gene sequencing in the card position segment and the genetic complementation verification experiment.
[0150] In addition, the inventors found through sequence comparison and analysis that the...
Embodiment 3
[0151] Example 3: Excellent allele OsGRF4 ngr2 SNPs analysis of the promoter region
[0152] Compared with the 1kb promoter (SEQ ID NO: 1) of the OsGRF4 gene in the NJ6 variety, the allele OsGRF4 ngr2 There are 8 SNPs differences in its 1kb promoter (SEQ ID NO: 4). The inventors sequenced and analyzed the promoter region within 1 kb of the OsGRF4 gene in the different rice resource varieties described in Example 1, and the results showed that the allele OsGRF4 ngr2 There are 3 specific SNPs (c.-884T>A, c.-847C>T, c.-801C>T) in the 1kb promoter region. Further studies have shown that these SNP changes are related to increasing the expression level of OsGRF4 gene and the rate of ammonia nitrogen uptake by rice roots.
[0153] On this basis, the inventors performed haplotype analysis on the SNPs in the promoter region of the OsGRF4 gene within 1 kb in 225 cultivated rice varieties. The results of the study showed that there are 3 different haplotypes, namely Hap.A (such as high-yield...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com