Novel gamma-photon high spatial resolution detection device
A technology of high spatial resolution and detection device, which is applied in the direction of measuring device, radiation measurement, X/γ/cosmic radiation measurement, etc., can solve the problem of reducing the photon receiving efficiency of the photoelectric conversion part, improving the photoelectric conversion element, and improving the spatial resolution. and other issues, to achieve the effect of reducing crosstalk, reducing coupling process, and reducing detector resolution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
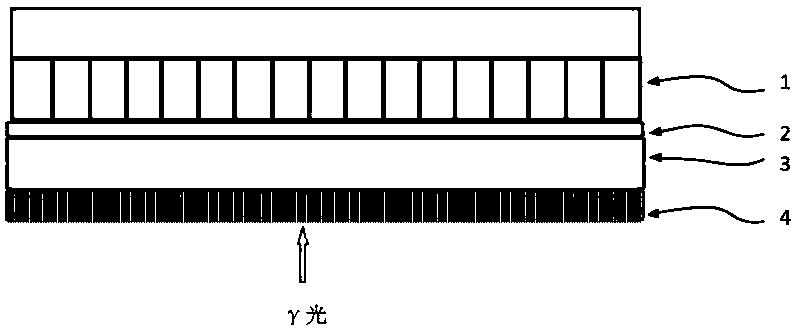
[0034] like image 3 As shown, a novel gamma photon high spatial resolution detection device includes a collimator 1, a scintillator 4, a light guide layer 3, an X-axis fiber layer 2, and a Y-axis fiber layer 5 attached in sequence, and also includes multiple SiPM 6. One end of the X-axis fiber layer 2 and the Y-axis fiber layer 5 are respectively coupled to the light guide layer 3, and the other ends are respectively coupled to the line array SiPM 6 (not shown in the figure); another plurality of SiPM 6 are attached to the side of the scintillator 4 Provides a trigger signal for photon counting.
[0035] to combine Figure 4 Shown, the use principle of the present invention is:
[0036] After the γ photons enter the scintillator 4 from the collimator 1 (not shown), fluorescent photons are generated in the scintillator 4, and the X-axis fiber layer 2 and the Y-axis fiber layer 5 respectively couple the fluorescent photons to the X-axis line array SiPM 6 (as shown in the ho...
Embodiment 2
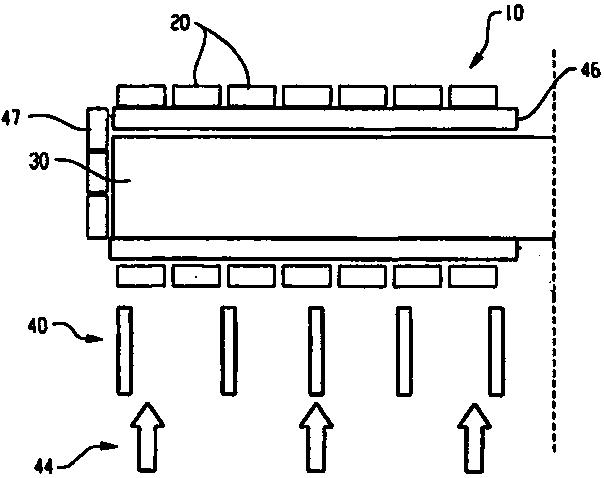
[0039] like Figure 5 As shown, a novel gamma photon detection device with high spatial resolution includes a collimator 1, an X-axis optical fiber layer 2, a first light-guiding layer 3, a scintillator 4, a second light-guiding layer 7, and a Y The axial fiber layer 5 also includes a plurality of SiPMs 6 . One end of the X-axis optical fiber layer 2 is coupled to the first optical guide layer 3, and the other end is coupled to the SiPM 6 (not shown in the figure) of the line array; one end of the Y-axis optical fiber layer 5 is respectively coupled to the second optical guide layer 7, The other end is coupled to a line array SiPM 6 (not shown in the figure); another plurality of SiPMs 6 are attached to the side of the scintillator 4 to provide a trigger signal for photon counting.
Embodiment 3
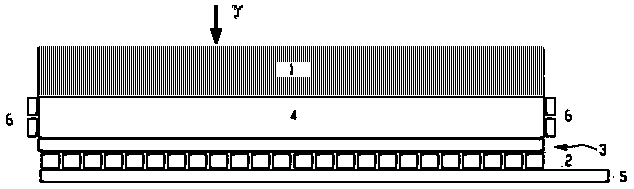
[0041] like Figure 6 As shown, a novel gamma photon high spatial resolution detection device includes a collimator 1, an X-axis fiber layer 2, a Y-axis fiber layer 5, a light guide layer 3 and a scintillator 4 attached in sequence, and also includes multiple SiPM 6. One end of the X-axis fiber layer 2 and the Y-axis fiber layer 5 are respectively coupled to the light guide layer 3, and the other ends are respectively coupled to the line array SiPM 6 (not shown in the figure); another plurality of SiPM 6 are attached to the side of the scintillator 4 Provides a trigger signal for photon counting.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com