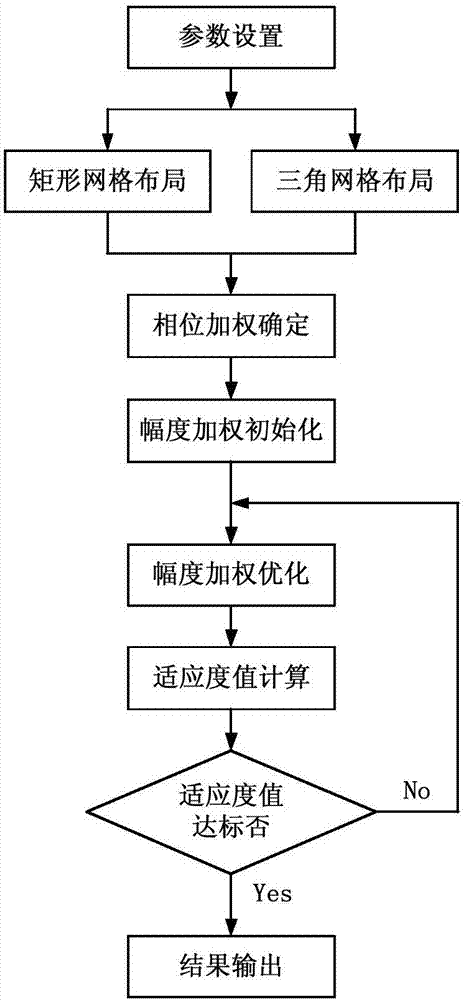
Directional diagram numerical optimization method for round caliber planar-array antenna
A planar array antenna, numerical optimization technology, applied in antennas, antenna arrays, electrical digital data processing and other directions, can solve the problems of increased computational complexity, array directional decomposition, etc., to reduce the computational load and iteration times, reduce memory consumption and The effect of the number of iterations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
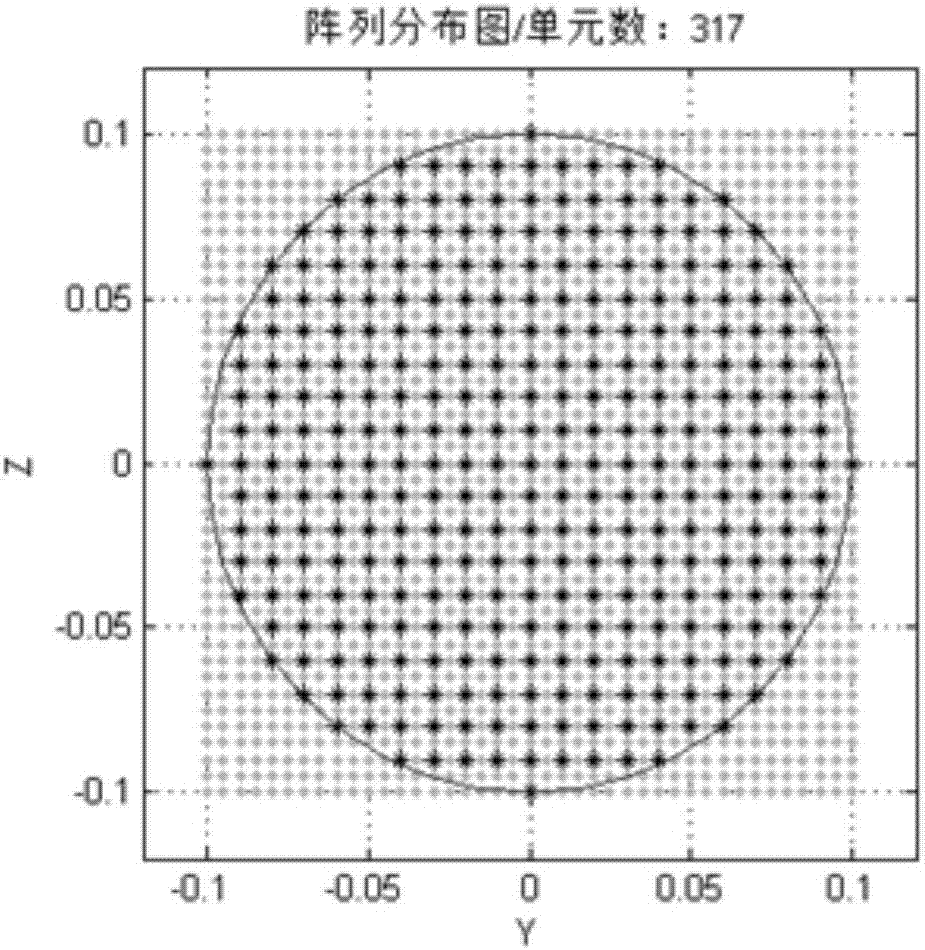
[0093] Embodiment 1: In this example, the numerical optimization of the amplitude weighted matrix of a rectangular grid planar array with a circular aperture is carried out. The parameters are set as follows: the main frequency of transmission is 15 GHz, the diameter of the array aperture is 0.2 meters, the unit spacing is half a wavelength, and the number of units is 317; The pointing angle is set to (80°, 10°); the null angle 1 is (110°, 10°), and the null width is 1; the null angle 2 is (80°, 35°), and the null width is 5; The optimal population size is twice the length of the optimal vector, the variation factor is 0.6, and the crossover probability is 0.9. The optimization index is that the side lobe level reaches -40dB, and the null trap level reaches -60dB.
[0094] The optimization results are shown in Fig. 3(a)-(e). Figure 3(a) is the linear phase required for the main beam pointing to (80°, 10°); Figure 3(b) is the optimized amplitude weighting matrix, it can be see...
Embodiment 2
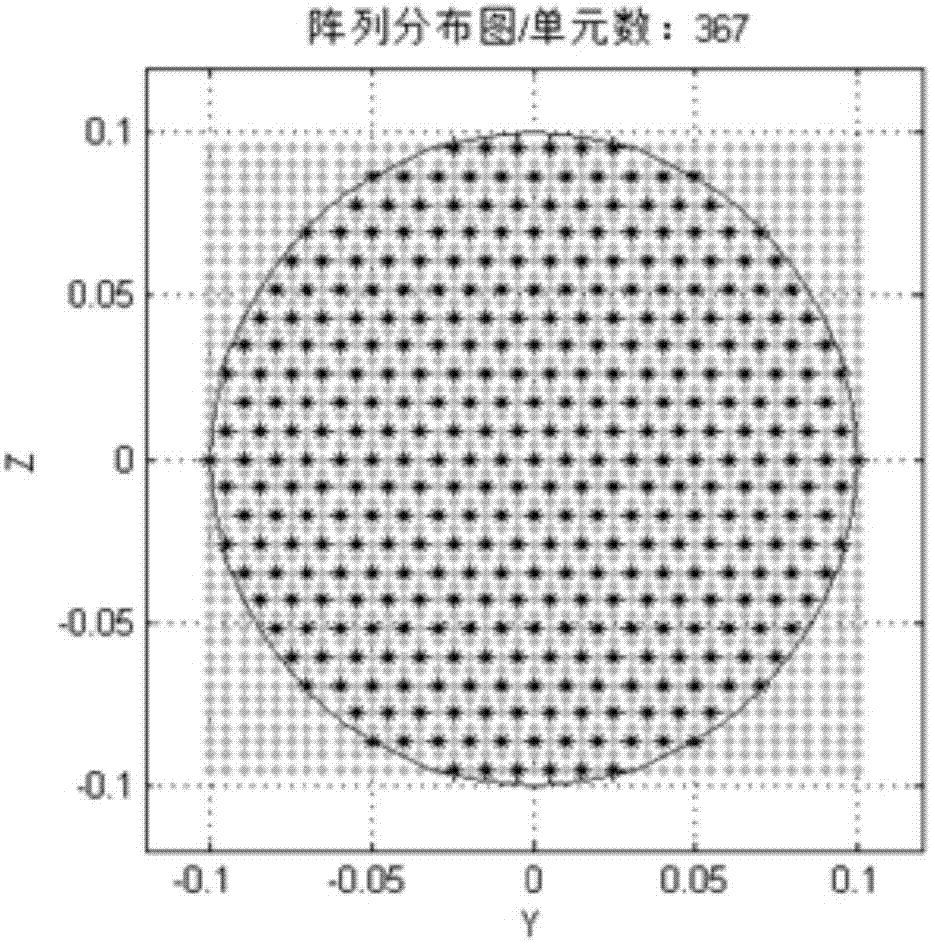
[0095] Embodiment 2: In this example, the numerical optimization of the amplitude weighted matrix of the circular aperture triangular grid planar array is carried out, and the parameters are set as follows: the main frequency of transmission is 15 GHz, the diameter of the array aperture is 0.2 meters, the unit spacing is half a wavelength, and the number of units is 367; The pointing angle is set to (100°, -10°); the null angle 1 is (130°, -10°), and the null width is 1; the null angle 2 is (100°, 20°), and the null width is 5. The optimized population size is twice the length of the optimized vector, the variation factor is 0.6, and the crossover probability is 0.9. The optimization index is that the side lobe level reaches -40dB, and the null trap level reaches -60dB.
[0096] The optimization results are shown in Fig. 4(a)-(e). Figure 4(a) is the linear phase required for the main beam pointing to (100°, -10°); Figure 4(b) is the optimized amplitude weighting matrix. It ca...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com