Method and device for reducing and recycling food waste anaerobic fermentation biogas residue
A technology for anaerobic fermentation and kitchen waste, applied in the field of solid waste resource utilization, can solve the problems of high moisture content of biogas residue, insufficient resource utilization, difficult dehydration, etc. The effect of improving dehydration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
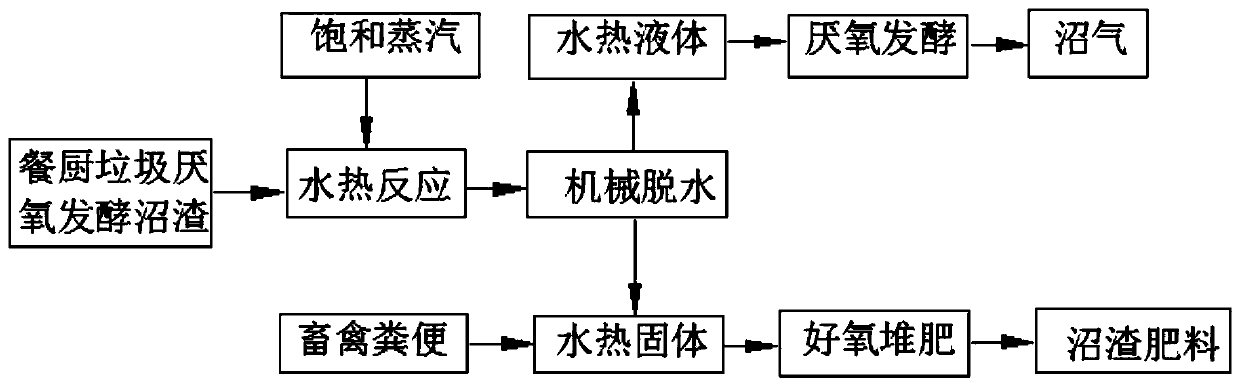
[0031]A method for reducing and recycling food waste anaerobic fermentation biogas residues, such as figure 1 As shown, it includes (1) feeding the anaerobic fermentation biogas residue of food waste into the hydrothermal reaction kettle, feeding saturated steam to contact the biogas residue for heating, so as to increase the temperature and pressure of the hydrothermal reaction kettle, and obtain hydrothermal reaction after the hydrothermal reaction is completed. mixture; (2) sending the hydrothermal mixture in step (1) into a mechanical dehydration device to separate and obtain a hydrothermal solid and a hydrothermal liquid, the mass moisture content of the hydrothermal solid is no more than 40%, and the hydrothermal liquid The concentration of COD in the medium is 10000-40000mg / L; (3) send the hydrothermal liquid separated in step (2) into a high-efficiency anaerobic reactor for anaerobic fermentation to generate biogas, and the hydrothermal liquid obtained in step (2) The ...
Embodiment 2
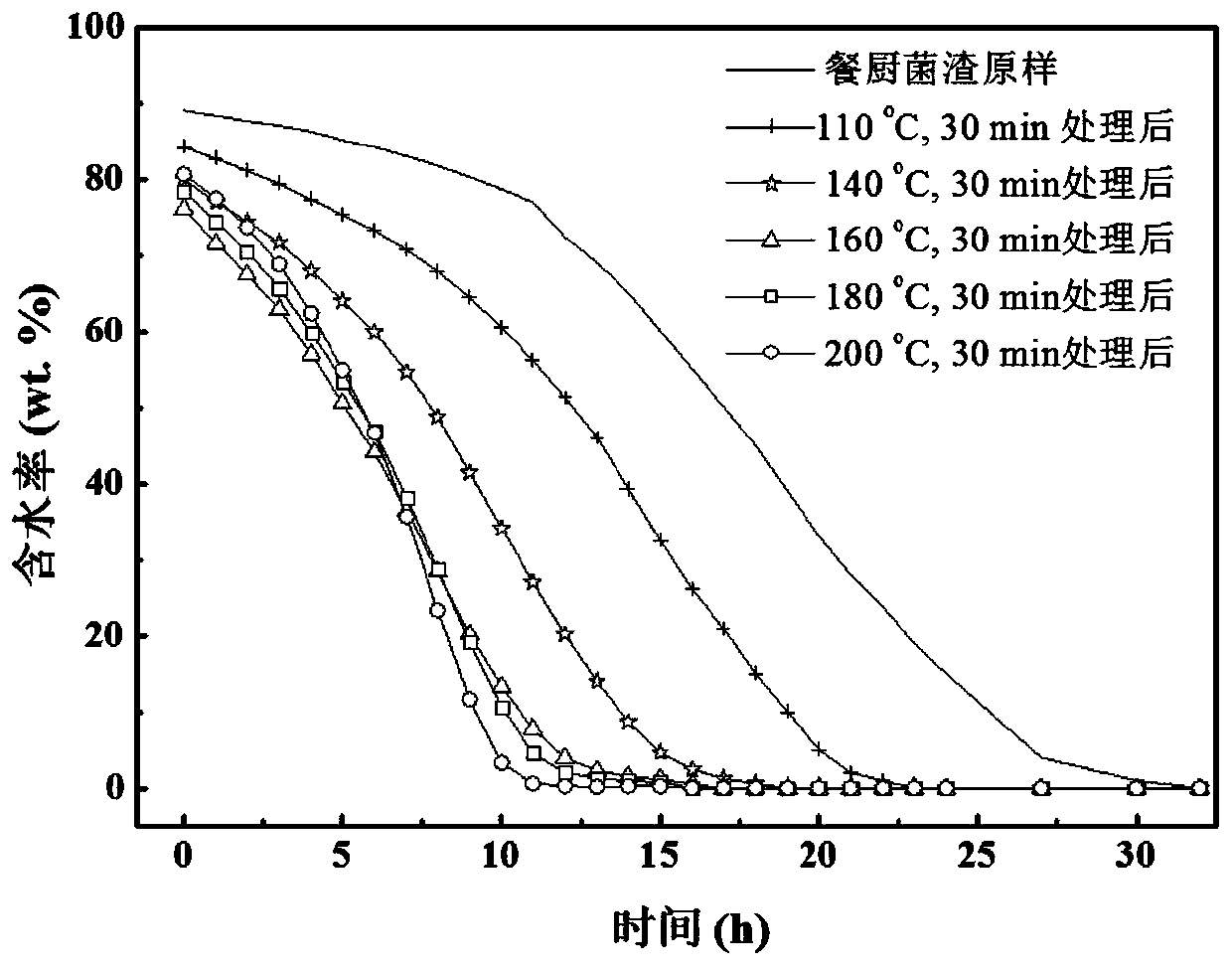
[0034] Take the hydrothermal liquid mixtures of different temperatures (110, 140, 160, 180, 200°C) of the medium mass of Example 1 and put them into a centrifuge, centrifuge for 10 minutes under the centrifugation condition of 7500r / min, and obtain a solid in an oven with a temperature of 75°C, and test the mixture every 1 hour Mass, converted to the water content of the hydrothermal solid when weighing each time, the result is as follows figure 2 As shown, it can be seen that as the hydrothermal temperature increases, the water content in the hydrothermal mixture decreases faster, indicating that the hydrothermal solid is easier to dehydrate.
[0035] Depend on figure 2 The suitable temperature for optimizing the hydrothermal reaction is between 140°C and 180°C. When the water temperature is lower than 140°C, the anaerobic fermentation of food waste is not heated enough, and the cell wall in the body cannot be effectively broken, so that the internal water cannot be easily...
Embodiment 3
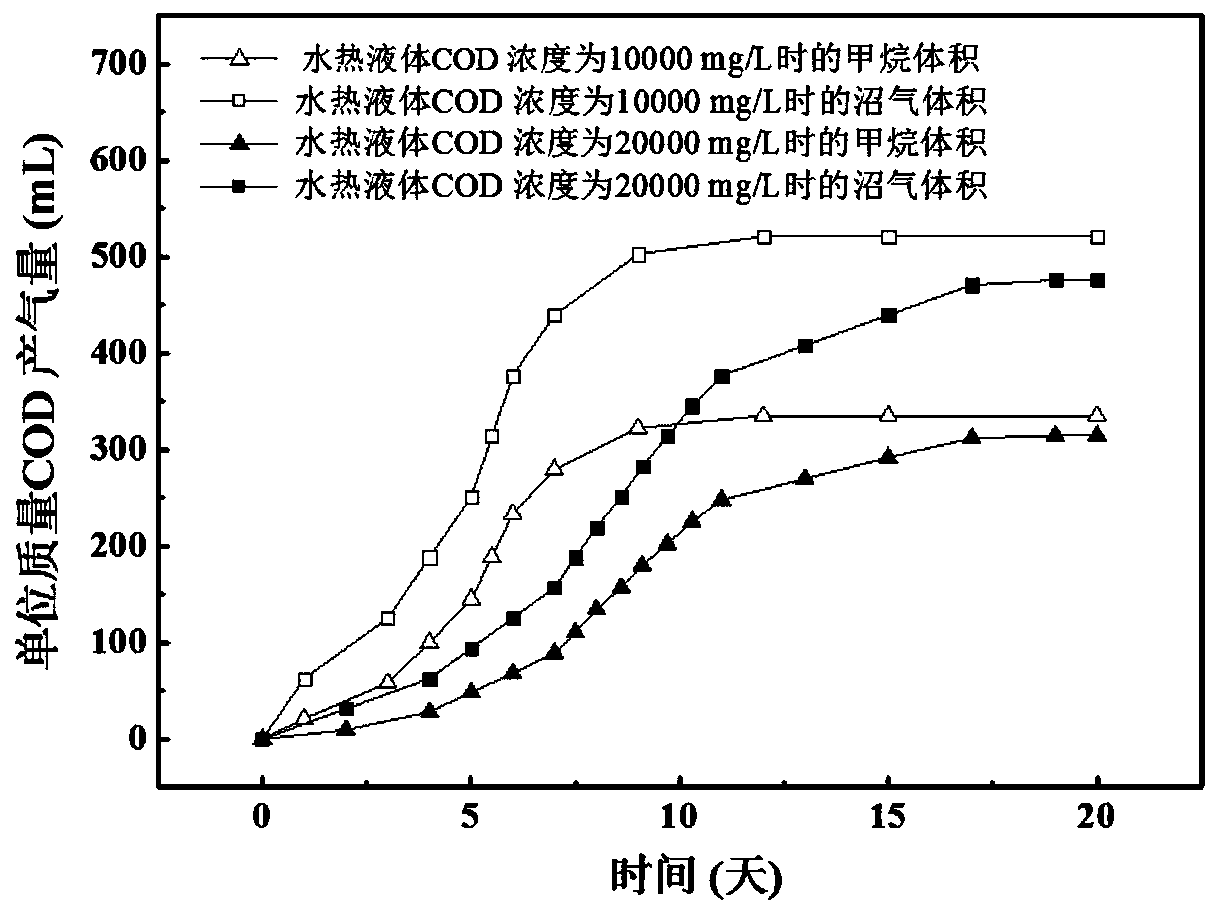
[0037] Send the food waste anaerobic fermentation biogas residue with a moisture content of 85% into the hydrothermal reaction kettle, and feed saturated steam at a temperature of 200°C to contact and heat the food waste anaerobic fermentation biogas residue to increase the temperature and pressure of the hydrothermal reaction kettle , the temperature of the hydrothermal reaction is controlled to be 180°C, and the hydrothermal mixture is obtained after the hydrothermal reaction for 1 hour; the remaining steam after the hydrothermal reaction is mixed with saturated steam and passed into the hydrothermal reaction kettle. The hydrothermal mixture is subjected to solid-liquid separation through a plate and frame filter press to obtain hydrothermal solids and hydrothermal liquids; the moisture content of the hydrothermal solids is 30%, and the COD concentration in the hydrothermal liquids is 30,000 mg / L. Dilute the separated hydrothermal liquid to a COD concentration of 10,000 mg / L ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com