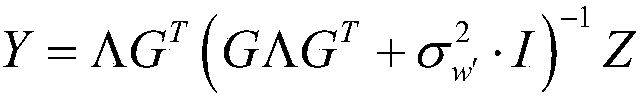Decoding method based on maximum posterior probability in analog coding
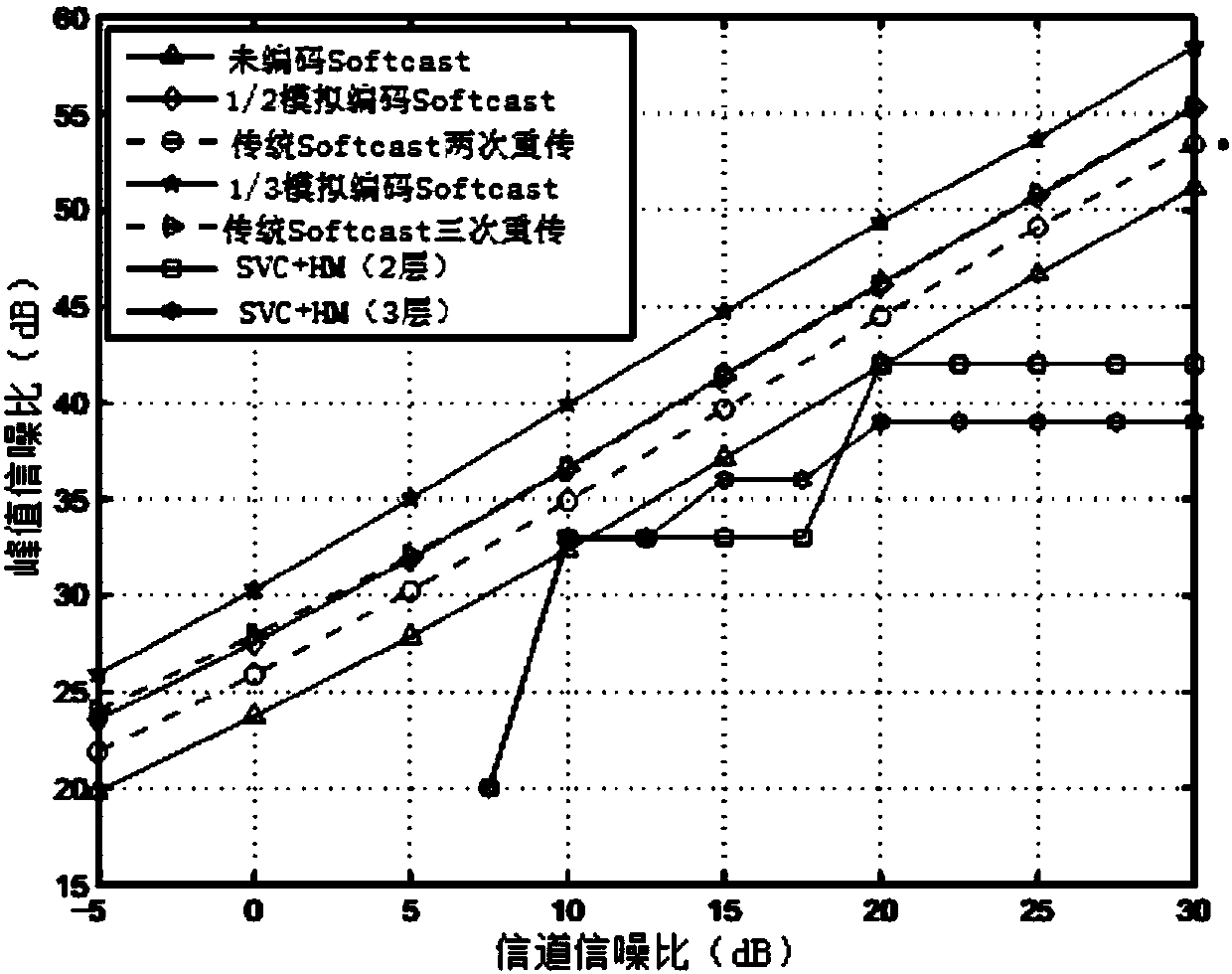
A technology of maximum a posteriori probability and analog coding, applied in digital transmission systems, electrical components, error prevention, etc., can solve problems such as high algorithm complexity and difficulty in implementation, and achieve reduced power penalties, reduced computational complexity, and channel noise Improved effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0048] A decoding method based on maximum a posteriori probability in analog coding, comprising the following steps:
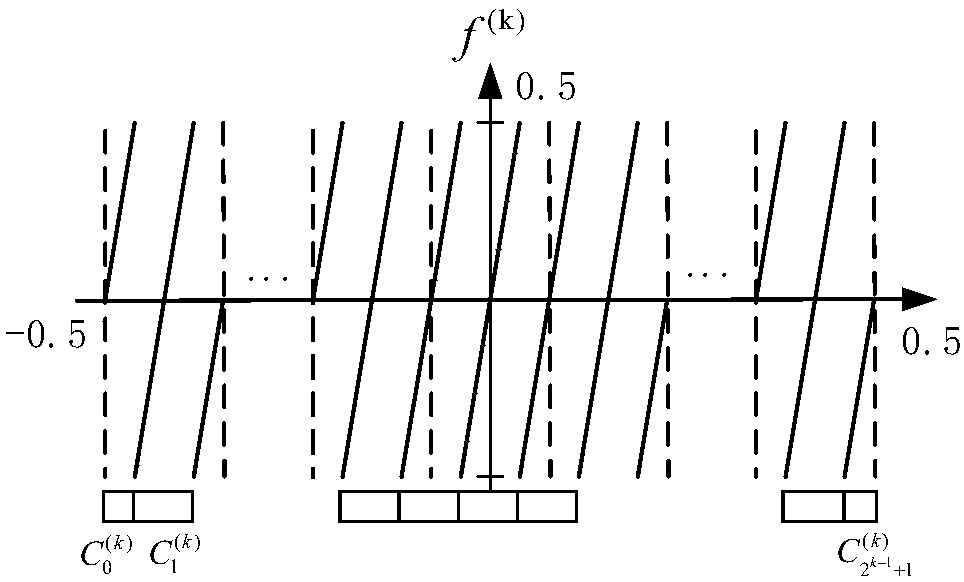
[0049] S1. The sending end sends the simulated coded signal and the group of pictures (GOP) block variance in the form of metadata to the receiving end through the introduction of a pseudo-analog transmission SoftCast that sets a chaotic function;
[0050] S2. Modeling the noise of the received analog signal as Gaussian noise to obtain an equivalently modeled signal to be decoded;
[0051] S3. Calculate the coding gain;
[0052] S4. Using the closed expression of the set chaotic function and the Gaussian distribution function of the MAP decoder, the closed expression of MAP decoding of 1 / 2 analog encoding and 1 / 3 analog encoding is obtained;
[0053] S5. Obtain the DCT coefficient matrix by decoding the closed expression through MAP, and obtain the decoded output of the noisy coded symbols through IDCT reconstruction.
[0054] Step S1 introduces a chaotic fu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com