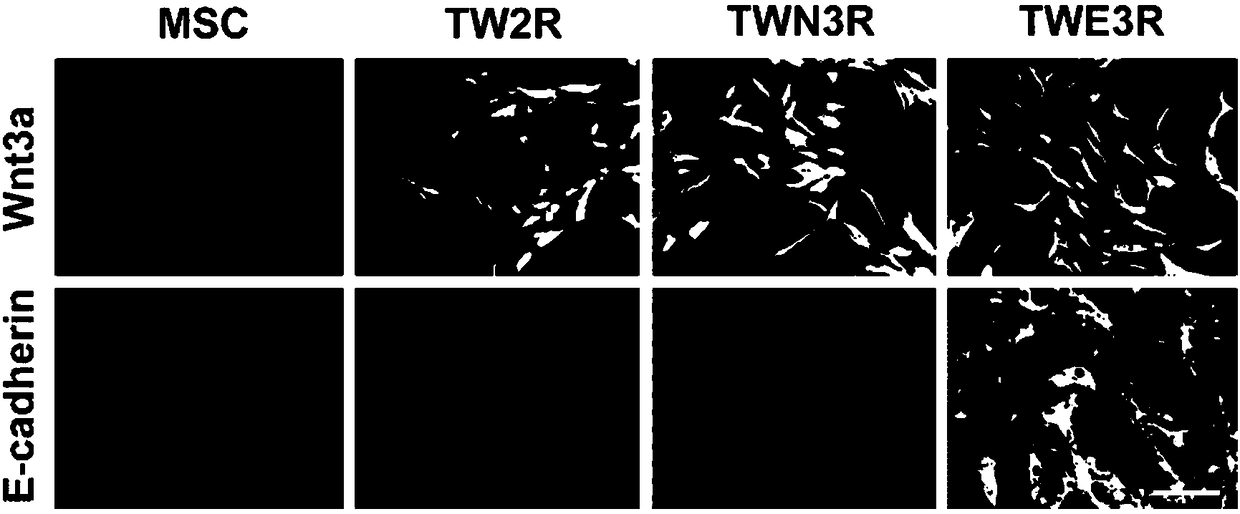
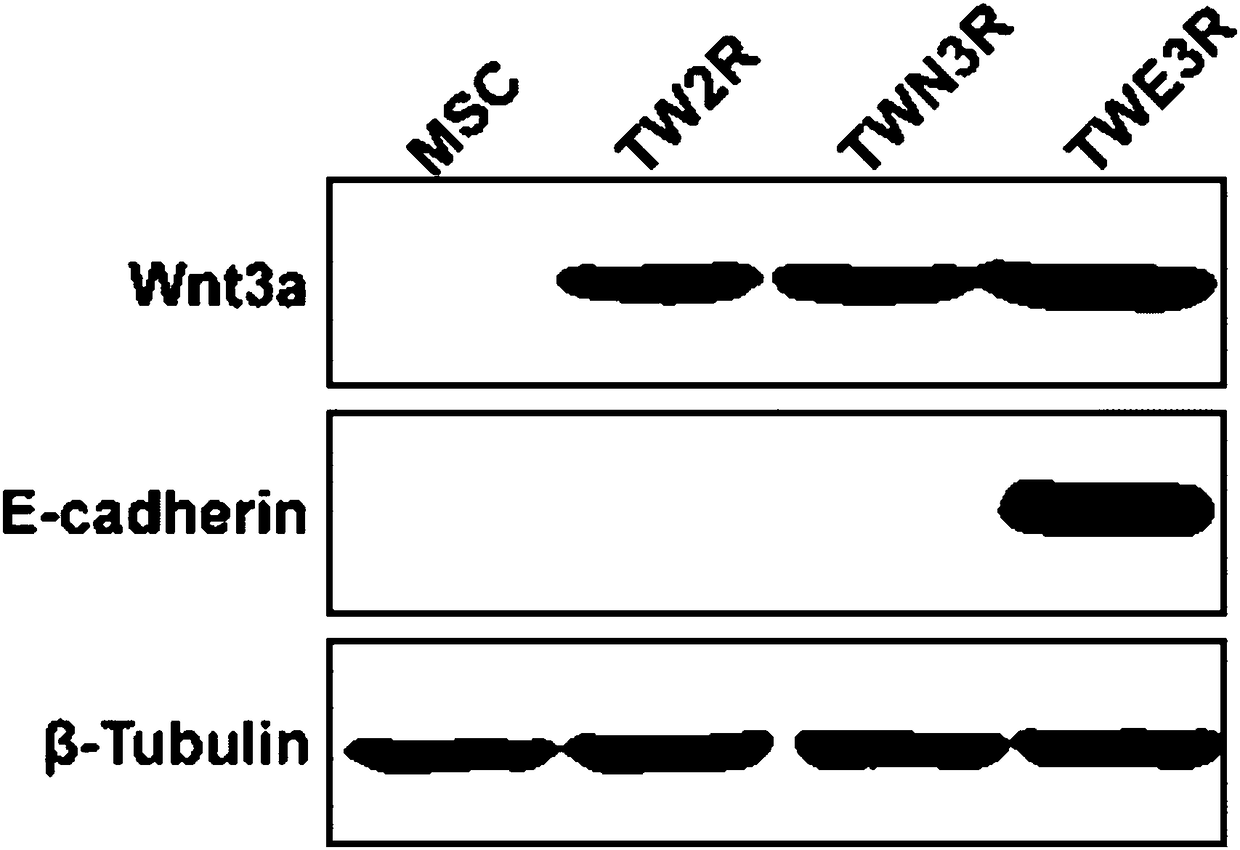
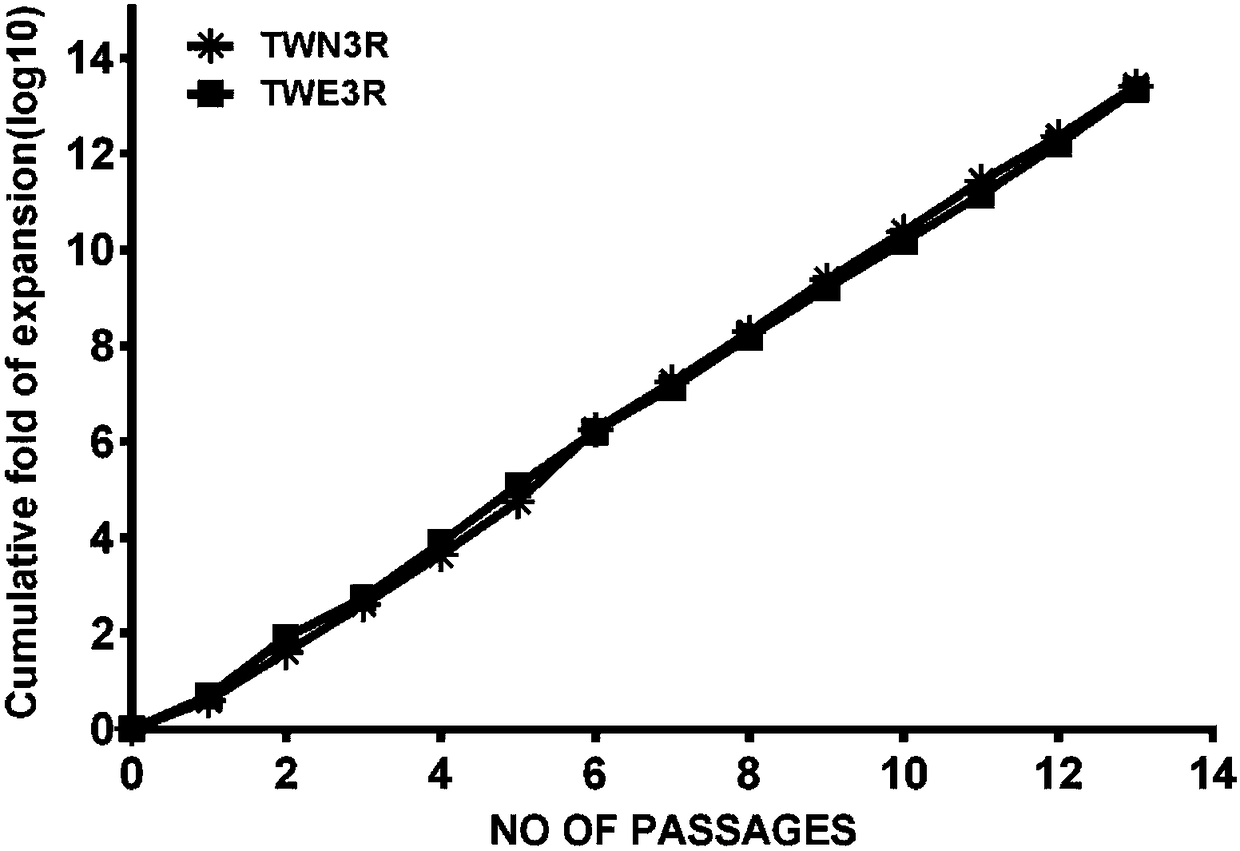
Preparation method of human embryonic stem cell growth-supporting humanized feeder layer cell
A technology of embryonic stem cells and feeder cells, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of biosafety, unstable long-term culture of human embryonic stem cells, unsuitable for routine use, etc., and achieve the effect of improving the clone formation rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] A preparation method of human feeder layer cells that can support the growth of human embryonic stem cells, comprising the following steps:
[0045] S1. Place human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in MSC medium for subculture; human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells are MSC cells;
[0046] S2. Infect the human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells subcultured in S1 with retroviral particles containing hTERT gene and hygromycin B resistance gene, and then add hygromycin B for screening to obtain hTERT gene and hygromycin Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells with protein resistance gene;
[0047] S3. Infect the human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells containing the hTERT gene and the hygromycin resistance gene in S2 with the retroviral particles containing the Wnt3a gene and the neomycin resistance gene, and then add G418 for screening to obtain TW2R cells containing hTERT gene, hygromycin resistance gene, Wnt3a gene, neomycin resistance gene;
[0048] S4. Infect ...
Embodiment 2
[0065] A preparation method of human feeder layer cells that can support the growth of human embryonic stem cells, comprising the following steps:
[0066] S1, placing human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in MSC medium for subculture;
[0067] S2. Infect the human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells subcultured in S1 with retroviral particles containing hTERT gene and hygromycin resistance gene, and then add hygromycin B for screening to obtain hTERT gene and hygromycin resistance gene human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells;
[0068] S3. Infect the human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells containing the hTERT gene and the hygromycin resistance gene in S2 with the retroviral particles containing the Wnt3a gene and the neomycin resistance gene, and then add G418 for screening to obtain hTERT gene , TW2R cells with hygromycin resistance gene, Wnt3a gene and neomycin resistance gene;
[0069] S4. Infect TW2R cells in S3 with lentiviral particles containing E-cadherin gene a...
Embodiment 3
[0086] A preparation method of human feeder layer cells that can support the growth of human embryonic stem cells, comprising the following steps:
[0087] S1, placing human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in MSC medium for subculture;
[0088] S2. Infect the human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells subcultured in S1 with retroviral particles containing hTERT gene and hygromycin resistance gene, and then add hygromycin B for screening to obtain hTERT gene and hygromycin resistance gene human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; the retroviral particles containing hTERT gene and hygromycin resistance gene will be infected into the subcultured human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in S1;
[0089] S3. Infect the human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells containing the hTERT gene and the hygromycin resistance gene in S2 with the retroviral particles containing the Wnt3a gene and the neomycin resistance gene, and then add G418 for screening to obtain hTERT gene , TW2R cells wi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com