Method for Trace Detection of Mercury Ions
A mercury ion and trace technology, applied in the field of detection, can solve the problems of weak anti-interference ability, inability to detect mercury ions, and many chemicals, and achieve the effect of simple detection method, good consistency and repeatability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] The specific steps for trace detection of mercury ions are:
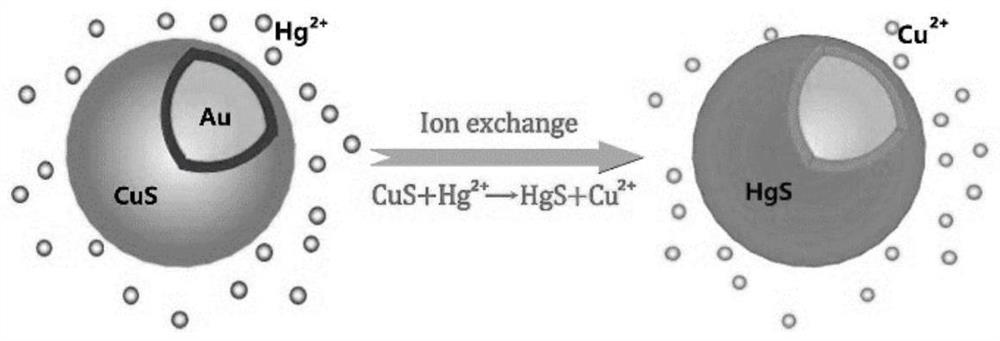
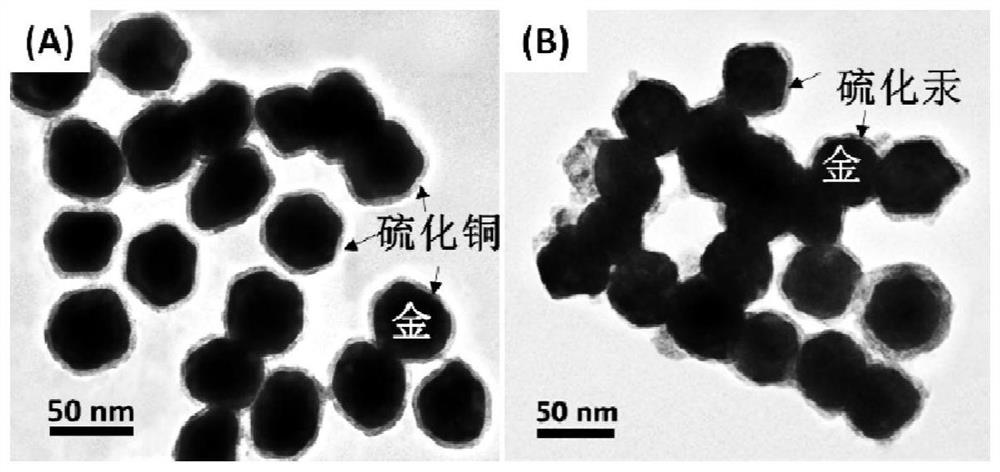
[0027] Step 1, first place the gold nanoparticles coated with copper sulfide shells in mercury ion solution and soak for 5 minutes; wherein, the particle diameter of gold nanoparticles is 10nm, and the shell thickness of the copper sulfide shells coated outside 0.6nm. Then it is subjected to solid-liquid separation treatment; wherein, the solid-liquid separation treatment is centrifugation (or filtration separation), the rotating speed of centrifugation is 3000r / min, and the time is 7min to obtain the product.
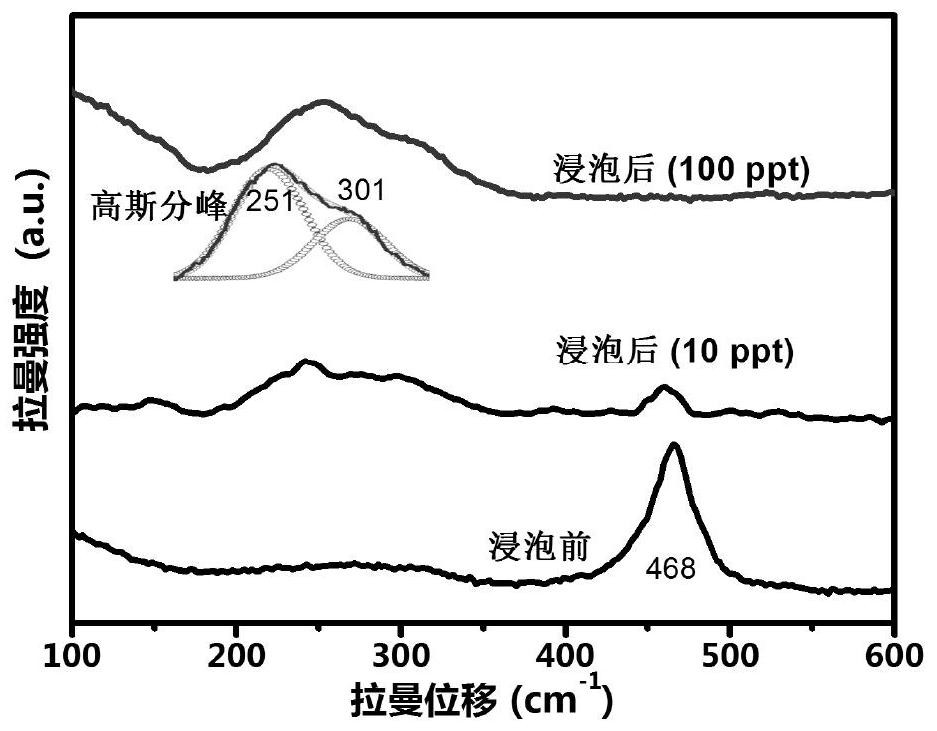
[0028] Step 2, using the product as an active substrate for surface-enhanced Raman scattering, and using a laser Raman spectrometer to measure the reaction-enriched mercury on it; wherein, the excitation wavelength of the laser Raman spectrometer is 532nm, and the output power is 0.1mW / μm 2 , the integration time is 20s, and the obtained image 3 , Figure 4 The detection results are shown in the c...
Embodiment 2
[0030] The specific steps for trace detection of mercury ions are:
[0031] Step 1, first place the gold nanoparticles coated with the copper sulfide shell layer in the mercury ion solution and soak for 35min; wherein the particle diameter of the gold nanoparticles is 58nm, and the shell thickness of the copper sulfide shell layer coated outside 6nm. Then it is subjected to solid-liquid separation treatment; wherein, the solid-liquid separation treatment is centrifugation (or filtration separation), the rotating speed of centrifugation is 4000r / min, and the time is 6min to obtain the product.
[0032] Step 2, using the product as an active substrate for surface-enhanced Raman scattering, and using a laser Raman spectrometer to measure the reaction-enriched mercury on it; wherein, the excitation wavelength of the laser Raman spectrometer is 532nm, and the output power is 1mW / μm 2 , the integration time is 15s, and the obtained image 3 , Figure 4 The detection results are s...
Embodiment 3
[0034] The specific steps for trace detection of mercury ions are:
[0035] Step 1, first place the gold nanoparticles covered with copper sulfide shells in mercury ion solution and soak for 63min; 12nm. Then it is subjected to solid-liquid separation treatment; wherein, the solid-liquid separation treatment is centrifugation (or filtration separation), the rotating speed of centrifugation is 5000r / min, and the time is 5min to obtain the product.
[0036] Step 2, using the product as an active substrate for surface-enhanced Raman scattering, and using a laser Raman spectrometer to measure the reaction-enriched mercury on it; wherein, the excitation wavelength of the laser Raman spectrometer is 532nm, and the output power is 9mW / μm 2 , the integration time is 10s, and the obtained image 3 , Figure 4 The detection results are shown in the curves in .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com