Intravascular stent
A vascular stent and blood vessel technology, applied in the field of medical vascular stent and vascular stent, can solve problems such as affecting the normal physiological function of organs/tissues, affecting the blood supply of bifurcated blood vessels, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing the pressure value and improving the effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
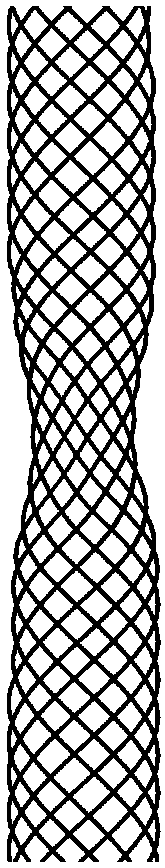
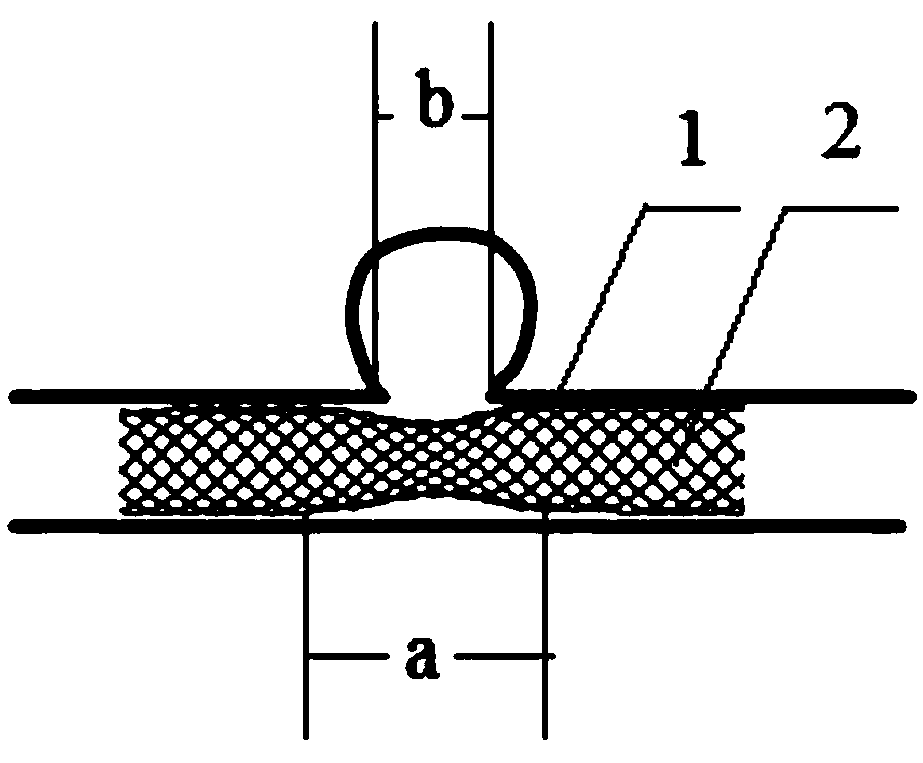
[0029] like figure 2 As shown, through the conventional vascular stent intervention method, the vascular stent 2 provided by the present invention with a local stenosis section is placed on the saccular aneurysm site, the local stenosis section is located at the entrance of the aneurysm, and the outer wall of the conventional section of the vascular stent 2 is in contact with the blood vessel. Wall 1 fits. Ideally, the length a of the local stenosis is equal to the length b of the opening of the aneurysm along the axial direction of the blood vessel, or 0.8b<a<1.2b, and a can also be set as a series of sizes to facilitate clinical selection. The stenotic sectional area of the local stenosis segment is not greater than 30% of the sectional area of the normal blood vessel lumen at this position. Usually, the diameter of the designed stent body is equal to or slightly larger than the inner diameter of the blood vessel at the desired stent site.
Embodiment 2
[0031] like image 3 As shown, by conventional vascular stent intervention methods, the vascular stent provided by the present invention with a local narrow section is placed at the fusiform aneurysm site, and the local narrow section is located at the aneurysm site, and the outer wall of the conventional section of the vascular stent 2 and Vascular wall 1 fit. The ideal state is: the length a of the local stenosis on the vascular stent is equal to the length c of the aneurysm along the vascular axis, or 0.8c<a<1.2c, and a can also be set as a series of sizes for the convenience of clinical selection . The stenotic sectional area of the local stenosis segment is not greater than 30% of the sectional area of the normal blood vessel lumen at this site. Usually, the diameter of the designed stent body is equal to or slightly larger than the inner diameter of the blood vessel at the desired stent site.
Embodiment 3
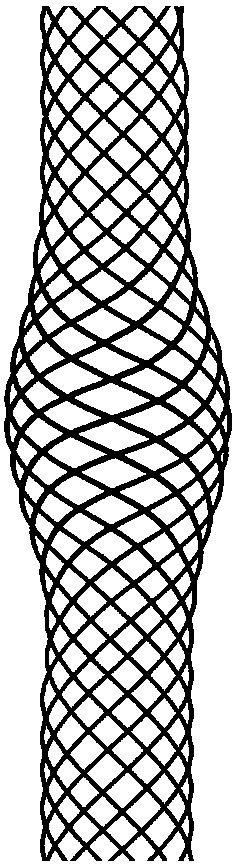
[0033] like Figure 4 As shown, the vascular stent with a partially enlarged section provided by the present invention is placed in a bifurcated vessel through a conventional vascular stent intervention method, and the outer wall of the conventional section of the vascular stent 2 is attached to the vessel wall 1 . The ideal state is: the local enlarged section is placed at the entrance of the bifurcation vessel, the enlarged cross-sectional area of the local enlarged section is not greater than 30% of the cross-sectional area of the main blood vessel at the bifurcation, and the axial length a of the local enlarged section is the bifurcation vessel at the implantation site 0.8-3 times the pipe diameter d, a can also be set as a series of sizes, so as to facilitate clinical selection and use.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com