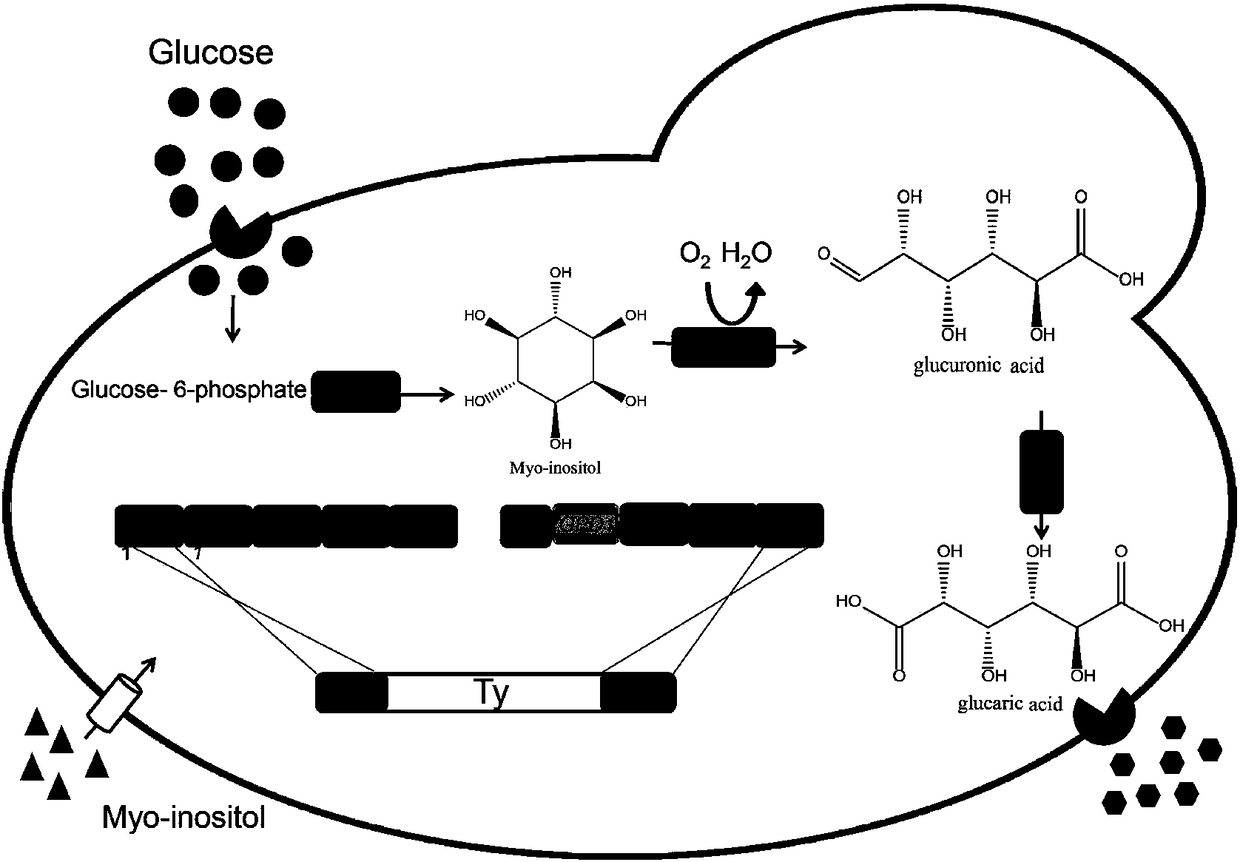
Method for producing glucaric acid by improving saccharomyces cerevisiae engineered strain fermentation
A technology of glucaric acid and Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which is applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, fermentation, etc., can solve the problems of easy loss, unstable plasmid expression, and unsuitable for industrial production.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
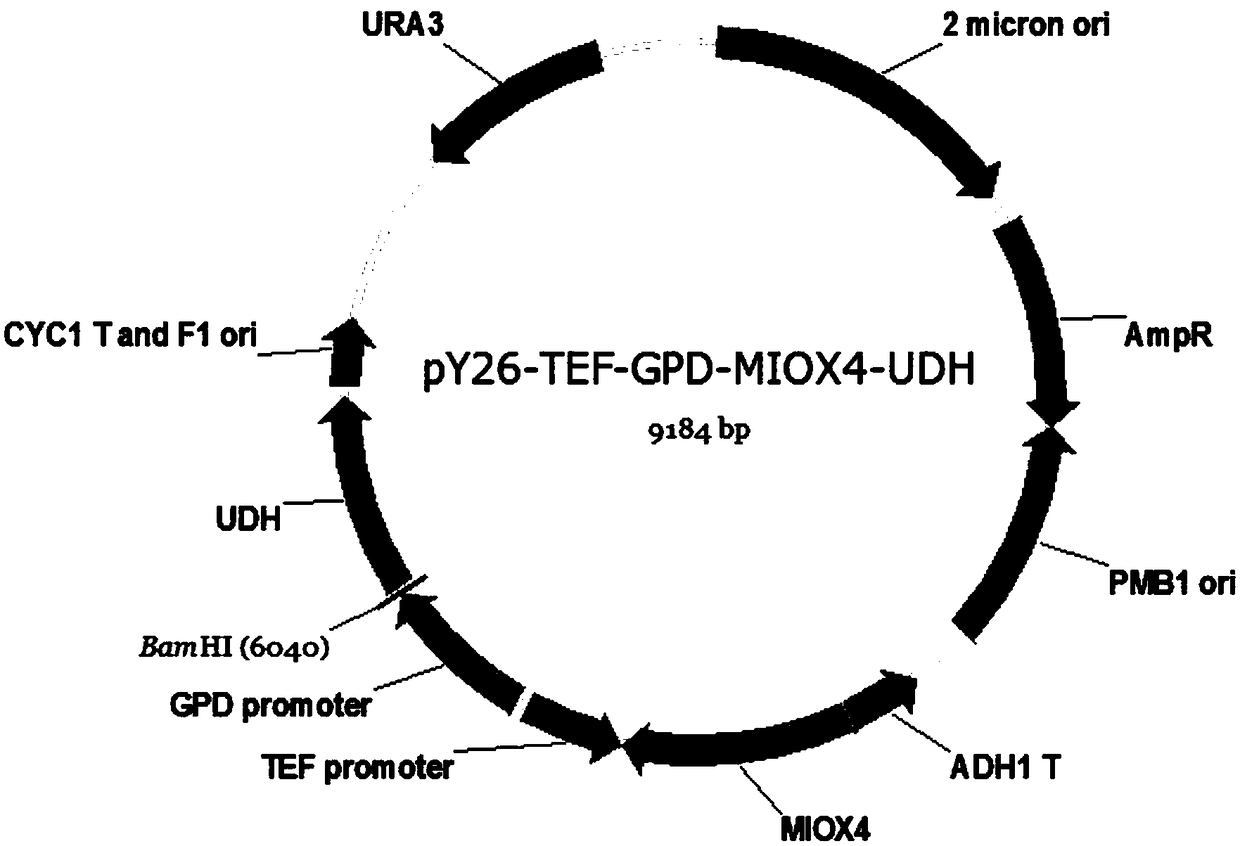
[0042] Example 1 Construction of plasmid pY26-TEF-GPD-MIOX4-UDH
[0043] PUC57-MIOX4-UDH was used as template, and pY26-MIOX4F / pY26-MIOX4R and pY26-UDHF / pY26-UDHR were used as primers to amplify MIOX4 and UDH genes respectively. The recovered product of MIOX4 and the plasmid pY26-TEF-GPD were digested with BglII / NotI respectively to obtain the pY26-MIOX4 plasmid, which was purified and recovered by overnight ligation with T4 ligase to construct the plasmid pY26-TEF-GPD-MIOX4. The pY26-MIOX4-UDH plasmid will be constructed using Gibson Assembly, and then the plasmid pY26-TEF-GPD-UDH plasmid will be digested with EcoRI, and the pY26-TEF-GPD–MIOX4-UDH plasmid will be constructed using Gibson Assembly, and the primers will be veri- pYF and veri-pYR. After colony PCR verification, the plasmid was constructed successfully.
Embodiment 2
[0044] Example 2 Obtaining of integrated fragments DMH-001 and DUH-001 fragments.
[0045] Using the Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4741 genome as a template, using Delta1F / Delta1R and Delta2F / Delta2R as primers to amplify Delta1 and Delta2 fragments respectively; ID NO.1) is a template, U-GPDF / U-GPDR and M-TEFF / M-TEFR are primers to amplify fragments U-TEF (including promoter GPD, gene UDH, terminator CYC1) and M-TEF respectively TEF (including promoter TEF, gene MIOX4, terminator ADH1); with plasmid pRS313 (preserved in this experiment, its nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2) as a template, primers His1F / His1F and His2F / His2R were respectively amplified Add fragments His1 and His2. The three fragments of Delta1, M-TEF and His1 were subjected to drop-down PCR, using the PCR product as a template and Delta1F / His1R as primers to amplify to obtain DMH-001. His2, U-GPD, and Delta2 were subjected to drop-down PCR, using the PCR product as a template and His2F / Delta2R as primer...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Example 3 High-yield glucaric acid integrated strain Bga-001 obtained
[0047] The above two integrated fragments DMH-001 and DUH-001 were respectively transformed into Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4741ΔOPI (preserved in our laboratory) by lithium acetate transformation method, coated with SD-His-deficient medium, and the transformants were picked after 2-3 days. In order to integrate successfully recombinant bacteria, insert positive transformants into 10ml YPD liquid medium as seeds, cultivate overnight, transfer 50mlYPD (adding 60mM inositol in the medium) liquid medium with 2% inoculum, shake at 30°C at 250rpm Bed culture 7d. Samples were taken every 12 hours, centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 5 minutes to obtain the supernatant, and filtered through a 0.22 μm filter membrane. The production of glucaric acid was detected by Hitachi high performance liquid chromatography with a differential detector, the column temperature was 30°C, and the injection volume was 30ul. Thu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com