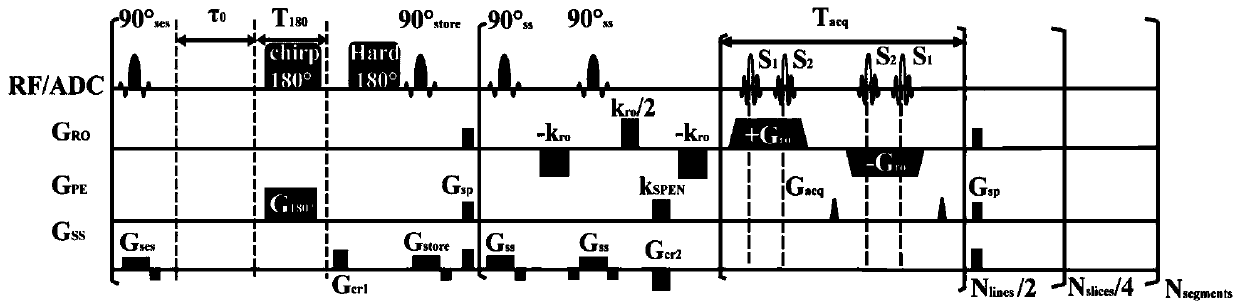
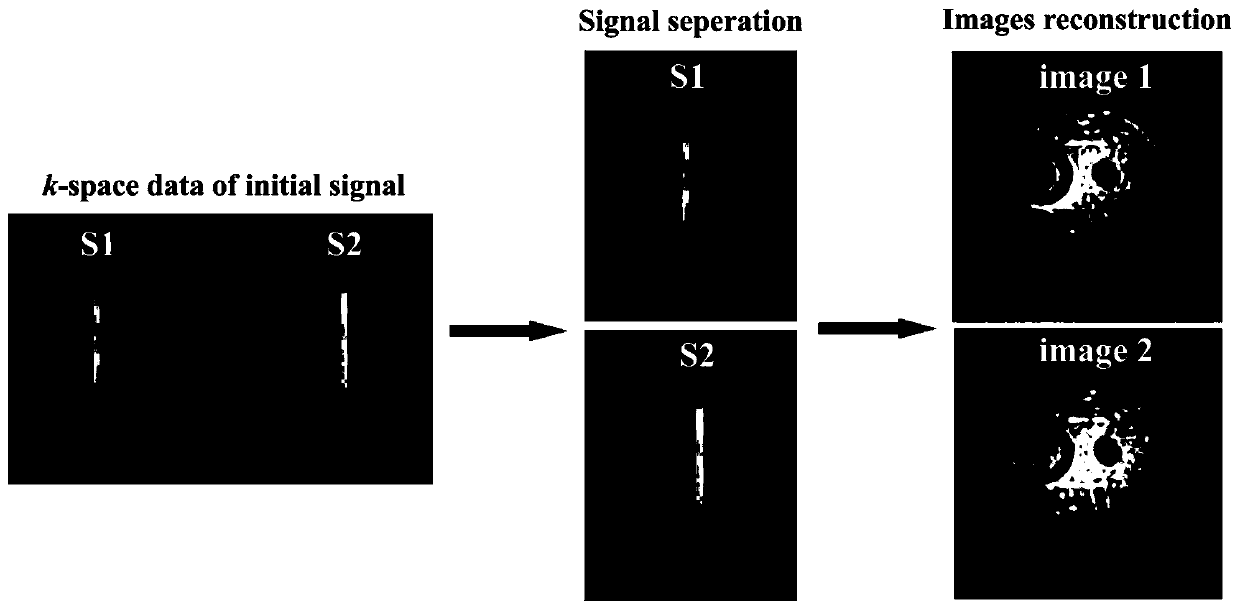
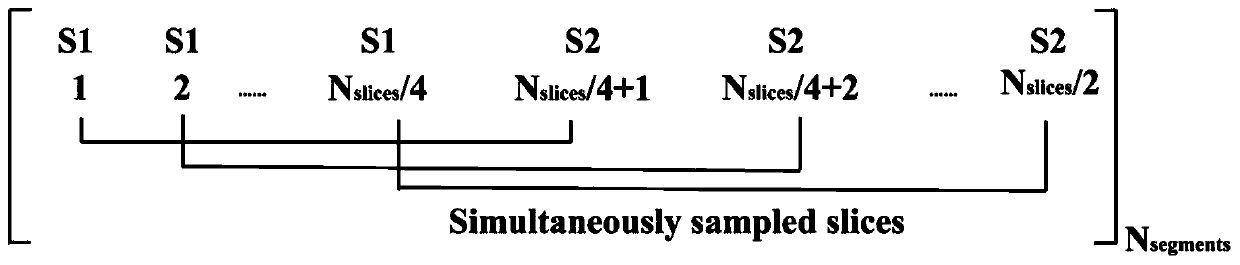
Multi-echo multi-slice spatio-temporal encoding magnetic resonance imaging method based on segmented excitation
A technology of magnetic resonance imaging and spatio-temporal coding, which is used in the measurement of magnetic variables, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of images being easily affected by eddy current effects, high absorption rate of linear sweep pulses, and limited applications, and achieves enhanced resistance to Capability of inhomogeneous magnetic fields and chemical shift effects, reduced sampling time, effect of slowing down effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment
[0084] The experiments in this example were performed on a Varian 7T imager (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA), and the samples were rats. The steps are as follows: Prepare live rats, first use isoflurane mixed with oxygen to quickly anesthetize the rats, then place the rats on the experimental bed and fix them, and continue to use low-concentration isoflurane mixed with oxygen to maintain the anesthetized state of the rats. The test bed is sent into the detection chamber of the magnetic resonance imaging machine. Open the operating software on the operating table of the magnetic resonance imager, first locate the region of interest of the sample to be tested, and then perform tuning, frequency correction, power correction and automatic shimming on the imager. In order to evaluate this method, multi-scan gradient echo imaging, multi-layer spin echo EPI, multi-layer double-echo EPI, and multi-layer segmental space-time coding imaging experiments were carried out in th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com