Method for preparing nitro compound from aromatic hydrocarbon compound through isothermic tubular reaction
A technology for aromatic hydrocarbon compounds and nitro compounds, which is applied in the field of preparing nitro compounds by a warm-tube reaction, can solve the problems of uneven heating, no zoned temperature control, and increased reaction by-products, etc., and achieves stable and controllable reaction temperature and avoids side effects Product generation, the effect of improving quality stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
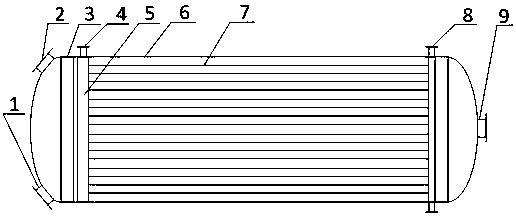
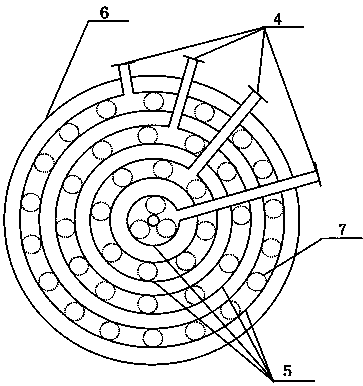
[0029] According to the above specific implementation method, the aromatic hydrocarbon compound is benzene, and HNO in benzene and mixed acid 3 The molar ratio is 1.01:1, and the nitrification reaction is carried out in the tubular reactor. There are 4 coolant inlets connecting the tubular reactor and the coolant distribution pipe (that is, the tubular reactor is divided into 4 diameter areas in the axial direction. temperature control), the nitration control temperature is 60°C, and the nitration reaction product is separated by nitration, washed with alkali, washed with water, and refined to obtain nitro compounds.
[0030] Implementation effect: the actual highest temperature in the axial direction of the tubular reactor with different pipe diameters is 60.2°C, and the lowest temperature is 59.9°C; after the reaction in the tubular reactor, the selectivity of nitrobenzene is 100%; the yield of nitrobenzene product is refined 99.5%.
Embodiment 2
[0032] According to the above specific implementation method, the difference is that the aromatic compound is toluene, and HNO in toluene and mixed acid 3 The molar ratio is 1.10:1, and the nitration reaction is carried out in the tubular reactor. There are 8 coolant inlets connected to the tubular reactor and the coolant distribution pipe (that is, the tubular reactor is divided into 8 diameter areas in the axial direction. temperature control), the nitration control temperature is 40°C, and the nitration reaction products are separated by nitration, washed with alkali, washed with water, and refined to obtain nitro compounds.
[0033] Implementation effect: the actual highest temperature in the axial direction of the tubular reactor with different pipe diameters is 40.1°C, and the lowest temperature is 40.0°C; after the reaction in the tubular reactor, the total selectivity of nitrotoluene (three isomers) is 99.93%; The total yield of refined nitrotoluene (three isomers) is ...
Embodiment 3
[0035] According to the above specific implementation method, embodiment 3 is basically the same as embodiment 1, the difference is that HNO in benzene and mixed acid 3 The molar ratio is 1.03:1, and the nitration reaction is carried out in the tubular reactor. There are 2 coolant inlets connecting the tubular reactor and the coolant distribution pipe (that is, the tubular reactor is divided into 2 diameter areas in the axial direction. temperature control), the nitration control temperature is 58°C, and the nitration reaction products are separated by nitration, washed with alkali, washed with water, and refined to obtain nitro compounds.
[0036] Implementation effect: the actual highest temperature in the tube reactor with different pipe diameters in the axial direction is 58.4°C, and the lowest temperature is 57.8°C; after the reaction in the tubular reactor, the selectivity of nitrobenzene is 99.95%; the yield of nitrobenzene product is refined 99.2%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com