Electroluminescent device
An electroluminescent device and device technology, applied in the direction of electric solid-state devices, electrical components, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of low luminous efficiency and achieve the effect of improving luminous efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
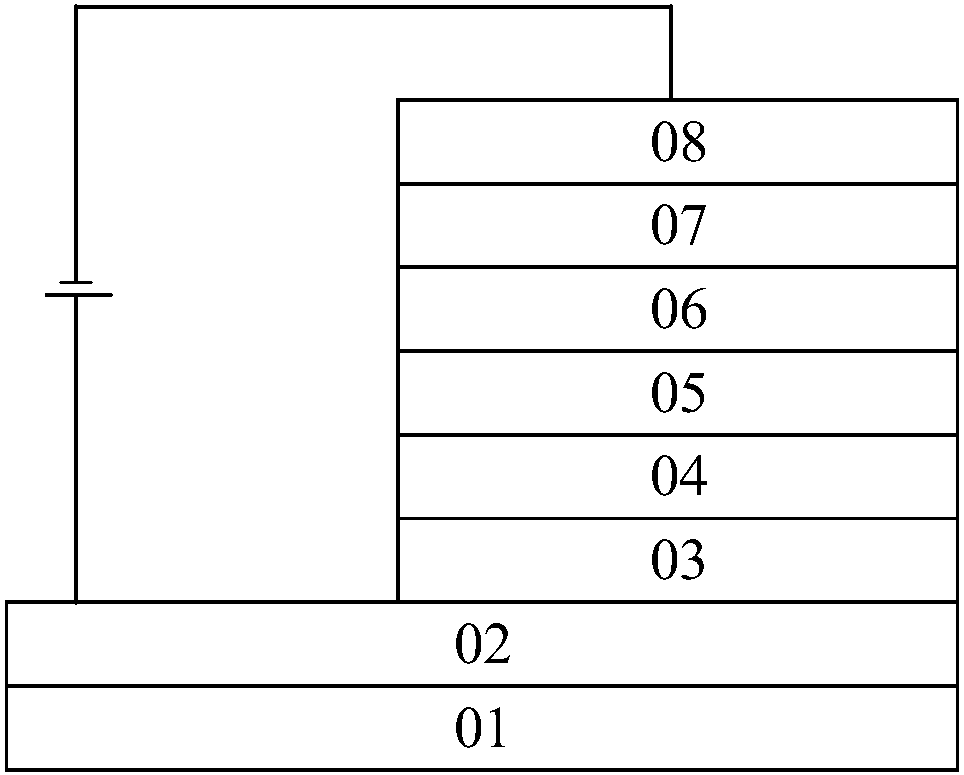
[0041] figure 1 It is a schematic structural diagram of an electroluminescent device provided in Example 1 of the present application. see figure 1 , the electroluminescent device may specifically include: a substrate 01, an anode 02, a hole transport layer 03, an inorganic light-emitting layer 06, an electron transport layer 07, and a cathode 08, and further includes:
[0042] An electron donor layer 04 located between the phosphorescent layer 06 and the hole transport layer 03 and an electron acceptor layer 05 located between the electron donor layer 04 and the phosphorescent layer 06;
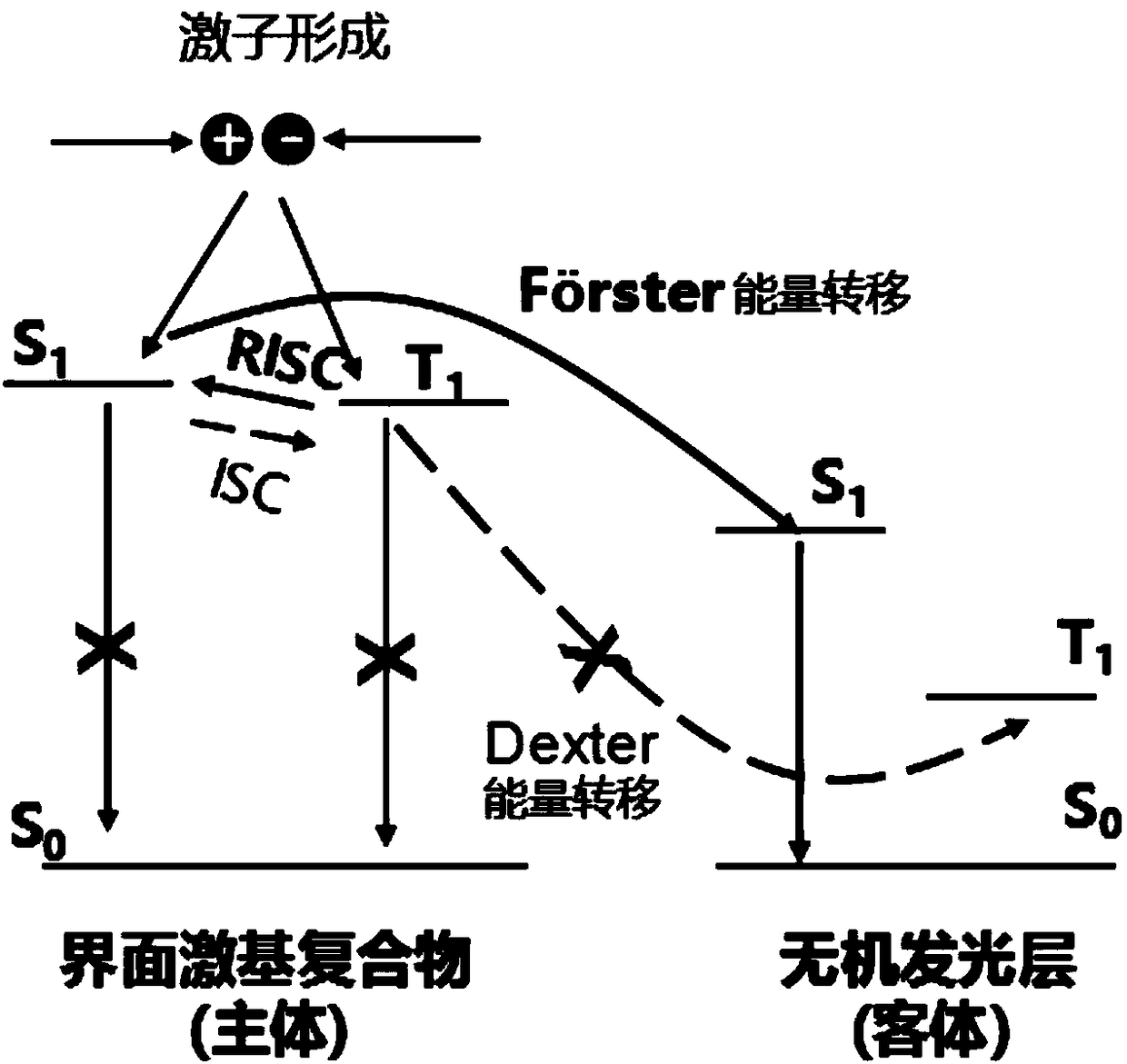
[0043] The organic electron donor molecules carried by the electron donor layer 04 and the organic electron acceptor molecules carried by the electron acceptor layer 05 form an interface exciplex.
[0044] It should be noted that the interface excitons corresponding to exciplexes are also called electron-hole pairs, which consist of one electron and one hole. Among them, electrons are inj...
Embodiment 2
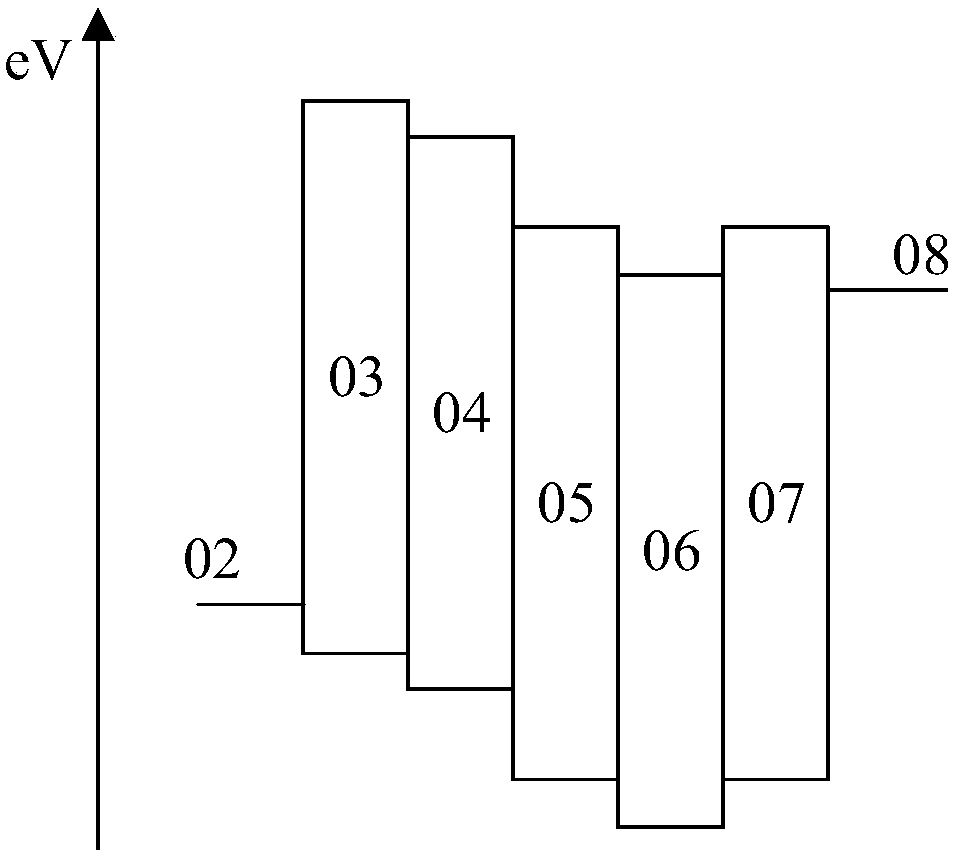
[0067] Figure 4a-Figure 4c For a schematic diagram of the energy level structure of an electroluminescent device provided in Example 2 of the present application, see Figure 4a-Figure 4c , on the basis of the electroluminescent device provided in Example 1, this embodiment provides three electroluminescent devices with optimized structures, specifically as follows:
[0068] The first optimization structure: see Figure 4a ,exist figure 1 On the basis of the electroluminescence device shown, it further includes: an electron blocking layer 09 .
[0069] The electron blocking layer 09 is located between the hole transport layer 03 and the electron donor layer 04 .
[0070] The second optimization structure: see Figure 4b ,exist figure 1 On the basis of the shown electroluminescent device, it further includes: a hole blocking layer 10 .
[0071] The hole blocking layer 10 is located between the phosphorescent layer 06 and the electron transport layer 07 .
[0072] The th...
Embodiment 3
[0078] Figure 5 For a structural schematic diagram of an electroluminescent device provided in Example 3 of the present application, see Figure 5 , the electroluminescent device may specifically include in turn: a substrate 51, a cathode 58, an electron transport layer 57, an inorganic light-emitting layer 56, an electron acceptor layer 55, an electron donor layer 54, a hole transport layer 53, and an anode 52, wherein:
[0079] The organic electron donor molecules carried by the electron donor layer 55 and the organic electron acceptor molecules carried by the electron acceptor layer 54 form an interface exciplex.
[0080] Wherein, the material of the electron transport layer 57 can be an organic electron transport material, zinc oxide ZnO, titanium oxide TiO 2 , one or more of nickel oxide NiO.
[0081] It should be noted that, compared with conventional devices, the inverted structure device used in this embodiment, on the one hand, has changed the positions of cathode ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com