A reactive polyurethane hot-melt material for 3D printing and its preparation method
A technology of 3D printing and hot-melt materials, applied in polyurea/polyurethane adhesives, additive processing, adhesive types, etc., can solve the problems of high production cost, insufficient strength, toughness, etc., and reach the processing molding temperature Low cost, easy to large-scale production, and the effect of simple and easy process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
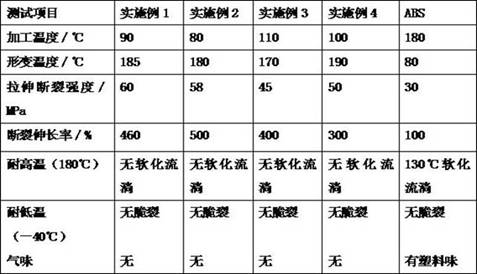
[0019] This example provides a method for preparing a reactive polyurethane hot-melt material for 3D printing. The specific steps are as follows: in parts by mass, 40 parts of adipic acid-1,4-butanediol (PBA), 20 parts of polypropylene glycol, 20 parts of polycaprolactone (molecular weight 20000), 3-hydroxyethyl-1 and 3-oxazolidine are placed in the reactor, 3-hydroxyethyl-1 and 3-oxazolidine A total of 2 parts, heated to 120 ° C, dehydrated under vacuum for 1 hour under stirring, then added 18 parts of isocyanate (MDI), reacted for 2 hours under stirring, and vacuumed, when NCO reached the theoretical value, under the condition of nitrogen protection Pour out the product and seal the package to obtain a reactive polyurethane hot-melt material for 3D printing.
Embodiment 2
[0021] This example provides a method for preparing a reactive polyurethane hot-melt material for 3D printing. The specific steps are as follows: in parts by mass, 40 parts of 1,6-hexanediol sebacate, 25 parts 12 parts of polypropylene glycol, 12 parts of polycaprolactone (molecular weight 50000), and 3 parts of salicylaldimine are placed in a reaction kettle, heated to 110 ° C, and vacuum dehydrated for 1 hour under stirring, then 20 parts of IPDI are added, and stirred React for 2 hours, and vacuumize. When the NCO reaches the theoretical value, pour out the product under nitrogen protection conditions, seal the package, and obtain a reactive polyurethane hot-melt material for 3D printing.
Embodiment 3
[0023] This example provides a method for preparing a reactive polyurethane hot-melt material for 3D printing. The specific steps are as follows: in parts by mass, 30 parts of adipic acid-1,4-butanediol (PBA), 15 parts of polytetrahydrofuran diol, 48 parts of polycaprolactone (molecular weight 200000), 2-phenyl-3-hydroxyethyl-1, 3-oxazolidine are placed in the reaction kettle, 2-phenyl-3 -2 parts of hydroxyethyl-1 and 3-oxazolidine in total, heated to 120°C, dehydrated under vacuum for 1 hour with stirring, then added 5 parts of MDI, reacted with stirring for 2 hours, and vacuumed, when NCO reached the theoretical value , the product was poured out under nitrogen protection conditions, sealed and packaged to obtain a reactive polyurethane hot-melt material for 3D printing.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength at break | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com