Novel candida-killing polypeptide CFP1 and preparation method thereof
A new type of technology for Candida, which is applied in the field of new Candida-killing polypeptides and its preparation, and can solve the problems of unstable expression products, low product yields, and difficult purification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0014] Preparation of Example 1 FCP1
[0015] The target peptide was synthesized by the solid-phase Fmoc method from the C-terminus to the N-terminus. The carboxyl group of the first Fmoc-Gln(Trt)-OH at the C-terminus of the polypeptide is activated and combined with the resin, the Fmoc-protecting group is removed, combined with the second carboxyl-activated Fmoc-His(Trt)-OH, and then removed The Fmoc-protecting group was removed and the cycle repeated until all amino acids were added. Cut the peptide on the resin with the cutting solution, collect the cutting solution, dry it in a centrifuge tube, wash the precipitate with ice ether 2 to 3 times, centrifuge to remove the supernatant, and dry the precipitate. The obtained crude product was purified by HPLC.
Embodiment 2
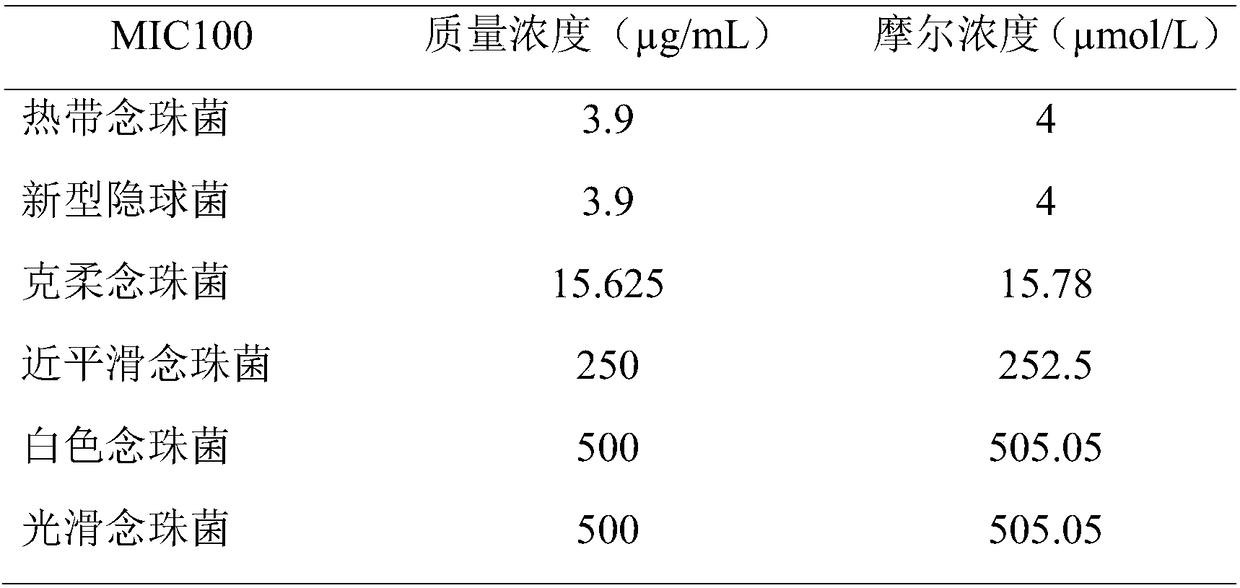
[0016] Embodiment 2 MTT method measures FCP1 antimicrobial spectrum
[0017] 1) Weigh and dissolve protein. Prepare the FCP1 phosphoric acid solution, set the initial concentration in the first column to 250 μg / mL, and set the final concentration to 0.488 μg / mL. It is necessary to prepare 1mg / mL FCP1 stock solution. Take an appropriate amount (<10μl) of DMSO to dissolve 1mg FCP1, then add 20mmol / L pH6.0 sodium phosphate buffer to dissolve to 1ml, and filter the solution through a 0.22μm sterile filter membrane to sterilize.
[0018] 2) Using a pipette gun, add 100 μL of 20 mmol / L sodium phosphate buffer solution at pH 6.0 to each well of the 96-well plate to dilute FCP1.
[0019] 3) Use a pipette to pipette 100 μL of 1 mg / mL FCP1 stock solution into each well of the first row of the 96-well plate.
[0020] 4) Repeatedly blow and suck the solution in the first row in the board for 6-8 times, mix well without splashing.
[0021] 5) Draw 100 μL from the first row and add it t...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Example 3 FCP1 kills Candida tropicalis
[0033] 1) Weigh and dissolve protein. Prepare 1 mg / mL stock solution of FCP1. Take an appropriate amount (<10μl) of DMSO to dissolve 1mgFCP1, then add 20mmol / L pH6.0 sodium phosphate buffer to dissolve to 1ml, and filter the solution through a 0.22μm sterile filter membrane to sterilize.
[0034] 2) Using a pipette gun, add 100 μL of 20 mmol / L sodium phosphate buffer solution at pH 6.0 to each well of the 96-well plate to dilute FCP1.
[0035] 3) Use a pipette to pipette 100 μL of 1 mg / mL FCP1 stock solution into each well of the first row of the 96-well plate.
[0036] 4) Repeatedly blow and suck the solution in the first row in the board for 6-8 times, mix well without splashing.
[0037] 5) Draw 100 μL from the first row and add it to the second row, repeat blowing and mixing for 6 to 8 times, and then draw 100 μL to the third row. Repeat this step to the eighth row.
[0038] 6) Discard the 100 μL sucked out of the eight...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com