Production system for utilizing solid waste to produce thermal insulation building blocks or composite wall slabs
A technology for thermal insulation blocks and composite wall panels, which is applied in manufacturing tools, ceramic molding workshops, ceramic molding machines, etc., can solve the problems of poor sound insulation, low production efficiency, and high energy consumption in the production process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
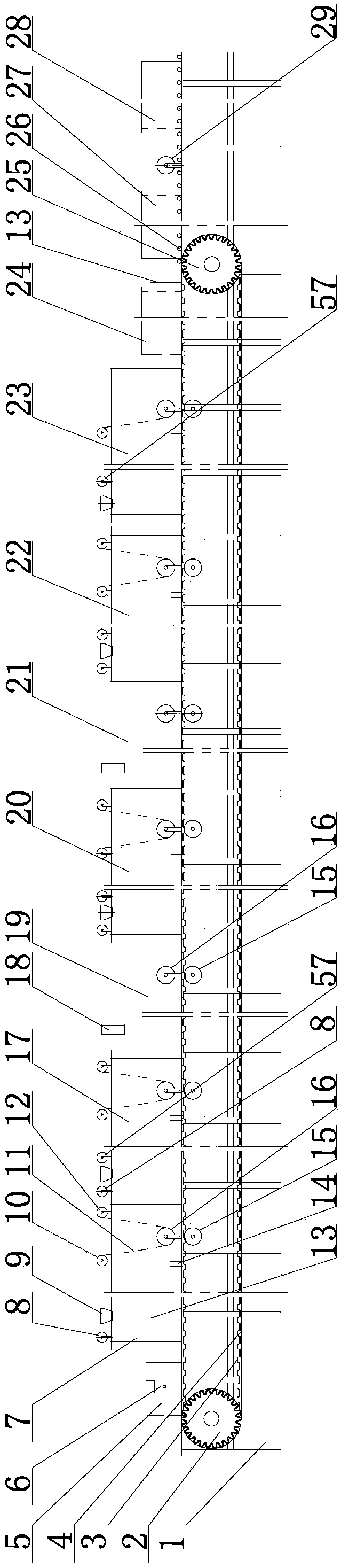
[0075] Such as Figure 1-4 As shown, the production system using solid waste residues to manufacture thermal insulation blocks or composite wallboards includes a spraying release agent area 5, a production area, a steam curing area, a post-treatment area 28, and a transmission device running through each area, which are arranged sequentially from front to back;
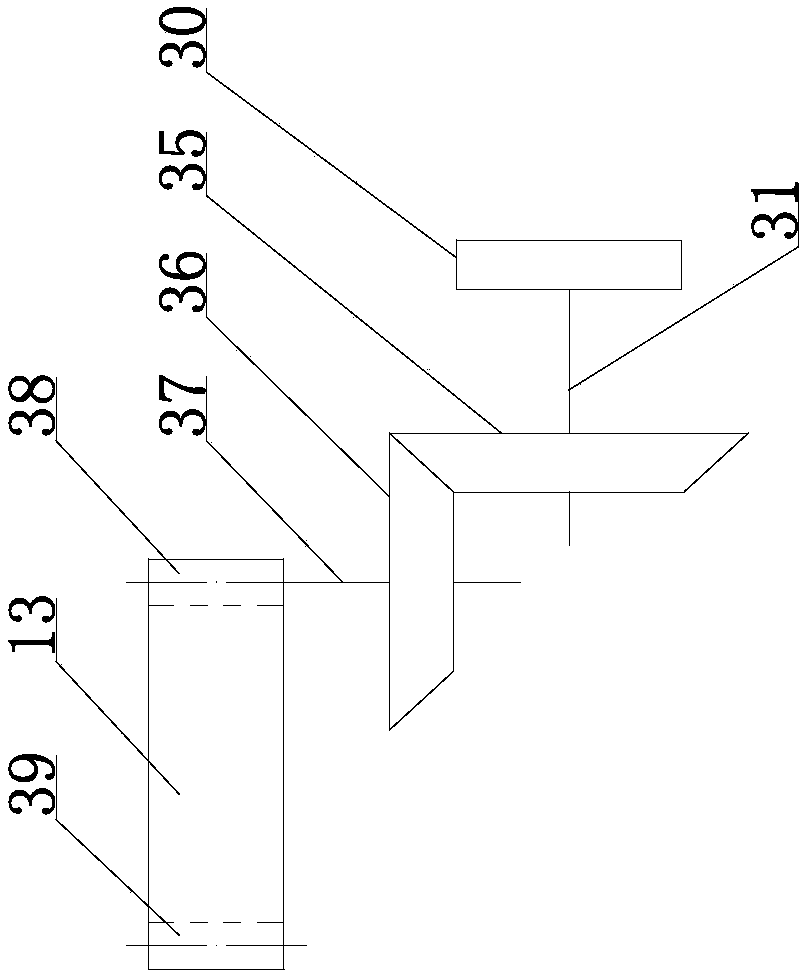
[0076] The transmission device comprises a sprocket chain plate conveying device and a lower belt 4, the sprocket chain plate conveying device comprises a driving sprocket 25, a chain plate 3 and a driven sprocket 2, and the driving sprocket 25 and the driven sprocket 2 are installed in a fixed position. On the bracket 1, the driving sprocket 25 is driven by the driving device, the driven sprocket 2 is linked with the driving sprocket 25 through the chain plate 3, and the lower belt 4 is attached to the outer periphery of the chain plate 3;
[0077] A spraying release agent device 6 is set in the spray release agent a...
Embodiment 2
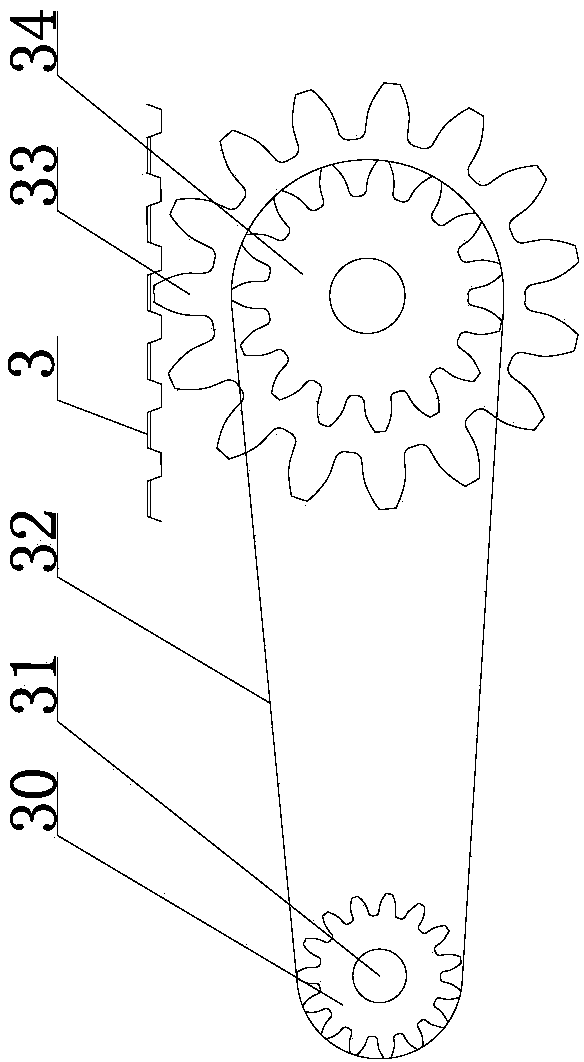
[0094] The structure of this production system and the process of producing panels are roughly the same as those of Embodiment 1, except that: the spraying release agent area 5, the outer surface production area 7, the outer leaf plate production area 17, and the lower insulation board filling area 19 The shaping belts 13 on both sides are flat belts, and the shaping belts 13 on both sides of the middle leaf plate production area 20, the upper insulation plate filling area 21, the inner leaf plate production area 22, the interior surface production area 23, and the pre-steaming area 24 are convex surfaces belts (such as Figure 10 shown), the lower belt 4 attached to the chain plate 3 is a belt with convex surfaces on both sides (such as Figure 6 shown), or a flat belt, and the pressure roller 16 in the outer surface production area 7 and the outer leaf plate production area 17 is a pressure roller with concave surfaces at both ends (such as Figure 11 shown), or flat roller...
Embodiment 3
[0097] The structure of this production system and the second embodiment and the process of producing panels are roughly the same, the difference is that there is no interior surface production area 23 in the production area; spraying release agent area 5, exterior surface production area 7, and outer leaf plate production The shaping belts 13 on both sides of the area 17 and the lower insulation board filling area 19 are plane belts, the middle blade production area 20, the upper insulation board filling area 21, the inner blade production area 22, and the two sides of the steam curing front area 24. The shaping belt 13 For belts with raised surfaces (such as Figure 10 shown), the lower belt 4 attached to the chain plate 3 is a belt with convex surfaces on both sides (such as Figure 6 shown), or a flat belt, and the pressure roller 16 in the outer surface production area 7 and the outer leaf plate production area 17 is a pressure roller with concave surfaces at both ends (s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com