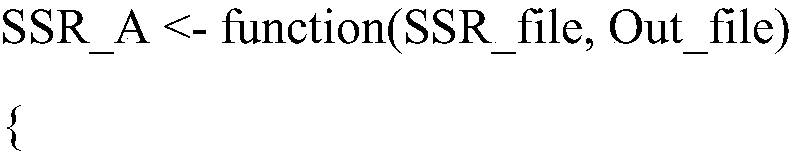Method for developing polymorphic microsatellite molecular markers on basis of multi-sample high-throughput sequencing
A microsatellite marker and molecular marker technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve problems such as low efficiency, and achieve the effect of promoting research and improving efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] In this embodiment, taking hexaploid wild camellia oleifera as an example, the specific implementation of the method of the present invention is given.
[0028] Step 1. Sample collection of wild tea leaves. In this example, wild camellia oleifera pieces were collected from Jinggangshan (26.55°N, 114.15°E) and Lushan (29.61°N, 115.98°E), among which, Jinggangshan is the center of the distribution area of wild camellia oleifera, and Mount Lu is the northern edge of the distribution area of wild camellia oleifera . In this example, 4 samples of Camellia oleifera chips at different altitudes were collected in Jinggang Mountain and Mount Lushan, and 3-5 fresh Camellia oleifera chips were collected for each sample. The collected Camellia oleifera pieces are required to have no obvious damage, and they should be stored in liquid nitrogen immediately after collection, and stored in a -80°C refrigerator after arriving in the laboratory.
[0029]Step 2: High-throughput tran...
Embodiment 2
[0038] A method for developing polymorphic microsatellite molecular markers based on multi-sample high-throughput sequencing, the method performs the following steps on the basis of obtaining high-throughput sequencing data of multiple sample genomes of the species to be tested:
[0039] Step 1. Increase the specificity of microsatellite markers: according to the method disclosed in Example 1, the potential amplifiable microsatellite loci are screened, and then the forward and reverse primers are screened for all sequencing reads at the potentially amplifiable microsatellite loci in a single sample In order to increase the specificity of the primers, the microsatellite loci that only appear once in the
[0040] Step 2, exclude complex microsatellite sites: use R script (Simple_SSR) to screen simple microsatellite sites in the sites obtained in step 1.
[0041] Step 3, calculate the number of alleles of each microsatellite locus in each sample, and screen the loci with high PCR...
Embodiment 3
[0045] A method for developing polymorphic microsatellite molecular markers based on multi-sample high-throughput sequencing, comprising the following steps:
[0046] 1) Take several samples of the target species and perform high-throughput sequencing on the genome;
[0047] 2) From the high-throughput sequencing data of each sample, screen potential amplified microsatellite loci;
[0048] 3) From the potentially amplifiable microsatellite loci obtained through the screening in step 2), screening the microsatellite loci whose primer pairs only appear once in all the sequencing reads of the potential amplifiable microsatellite loci of a single sample;
[0049] 4) For the screening results obtained in step 3), use the R script Simple_SSR to perform screening, and the screening results obtained are simple microsatellite sites;
[0050] 5) For the simple microsatellite sites obtained in step 4), use the R script SSR_A to detect the number of alleles in a single sample, and remove...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com