Microfluid analysis box
A microfluidic and microfluidic structure technology, applied in the field of microfluidics, can solve the problems of extremely high processing precision, high hydrophilic treatment requirements, reduced product reliability, portability, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
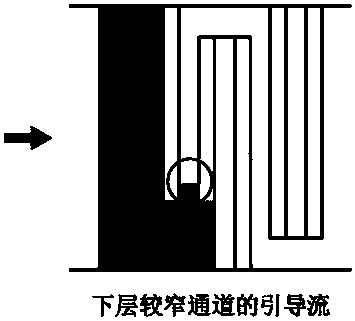
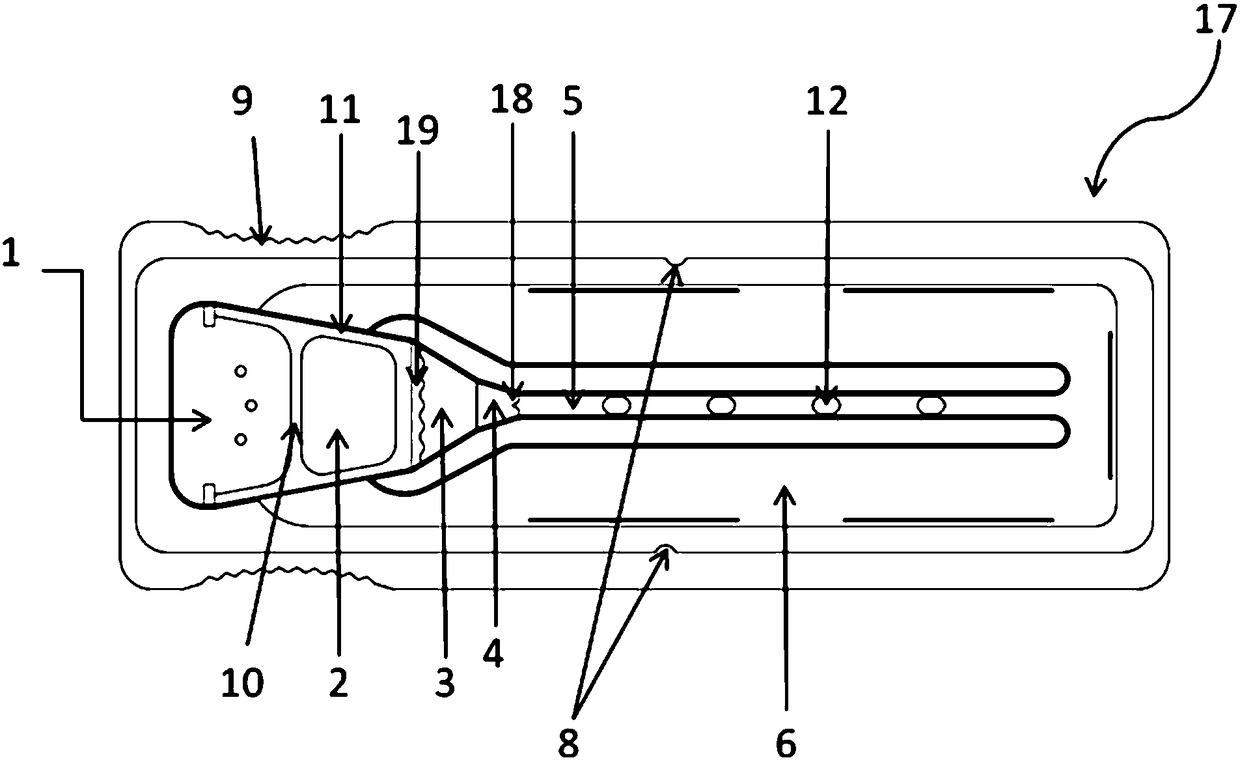
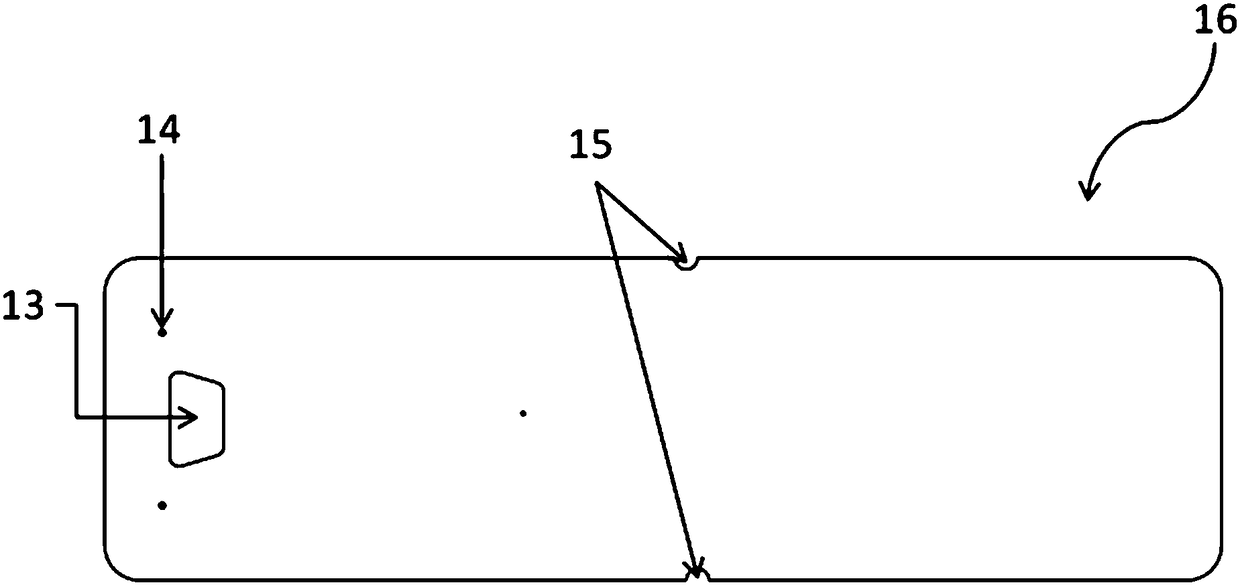
[0064] to attach Figure 5 The analysis box shown is an example, the operator can hold the structure 9 that is easy to grasp by hand and from the sample injection hole 13 of its upper cover 16 (see the attached figure 2 ) add the liquid sample containing the analyte to the sample receiving area 1 of the base 17 (see attached figure 1 ), the liquid sample flows into the sample storage area 2 through the isolation rod 10, then flows into the incubation area 3 through a wave-shaped structure 19, and enters the time valve 4 after combining with the detection reagent fixed on the microcolumn in the incubation area 3. The time valve is a staggered stagnation bar structure (see accompanying drawing 3), and the side view of each stagnation bar is stepped (referring to the accompanying drawing Figure 3B -a), the liquid containing the sample-detection reagent combination flows through the drainage structure 18 at a uniform speed in the diversion groove to the detection channel 5 and ...
Embodiment 2
[0066] to attach Figure 5 The analysis box shown is an example, the operator can hold the structure 9 that is easy to grasp by hand and from the sample injection hole 13 of its upper cover 16 (see the attached figure 2 ) add the liquid sample containing the analyte to the sample receiving area 1 of the base 17 (see attached figure 1 ), the liquid sample flows into the sample storage area 2 through the isolation rod 10, then flows into the incubation area 3 through a wave-shaped structure 19, and enters the time valve 4 after combining with the detection reagent fixed on the microcolumn in the incubation area 3. This time valve is a block bar structure (see accompanying drawing 3), and the side view of each block bar is trapezoidal (see accompanying drawing 3). Figure 3B -C), the distance between each blocking column is that the liquid containing the sample-detection reagent combination flows through the drainage structure 18 at a uniform speed in the diversion groove to th...
Embodiment 3
[0068] The microfluidic real-time detection chip is formed by bonding an upper cover 16 and a base 17 . The capillary channel has a width of 2 mm and a depth of 200 μm. Wherein the base 17 includes an incoming sample receiving area 1, an isolation rod 10, a sample storage area 2, a wave-shaped structure 19, an incubation area 3, a time valve 4, a drainage structure 18, a detection channel 5 and two detection sites 12 therein, and Waste area 6. The fluid sample is added dropwise from the left sampling port 13, and after being filtered through the filter membrane of the upper cover 16 and base 17 in the sample loading area, the serum in the sample storage area 2 is drained by the wave-shaped structure 19 and quickly enters the incubation area 3. The substance to be detected in the filtered fluid sample is evenly mixed with the reagent in the incubation zone 3, and then enters the body time valve 4. The time valve 4 has the characteristics of reducing the sample flow rate and c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com