Photovoltaic pavement system
A photovoltaic and pavement technology, applied to roads, roads, pavement details, etc., can solve the problems of base layer damage, easy water permeability, poor flatness, etc., and achieve the effects of avoiding deformation and damage, uniform heating area, and good ventilation performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
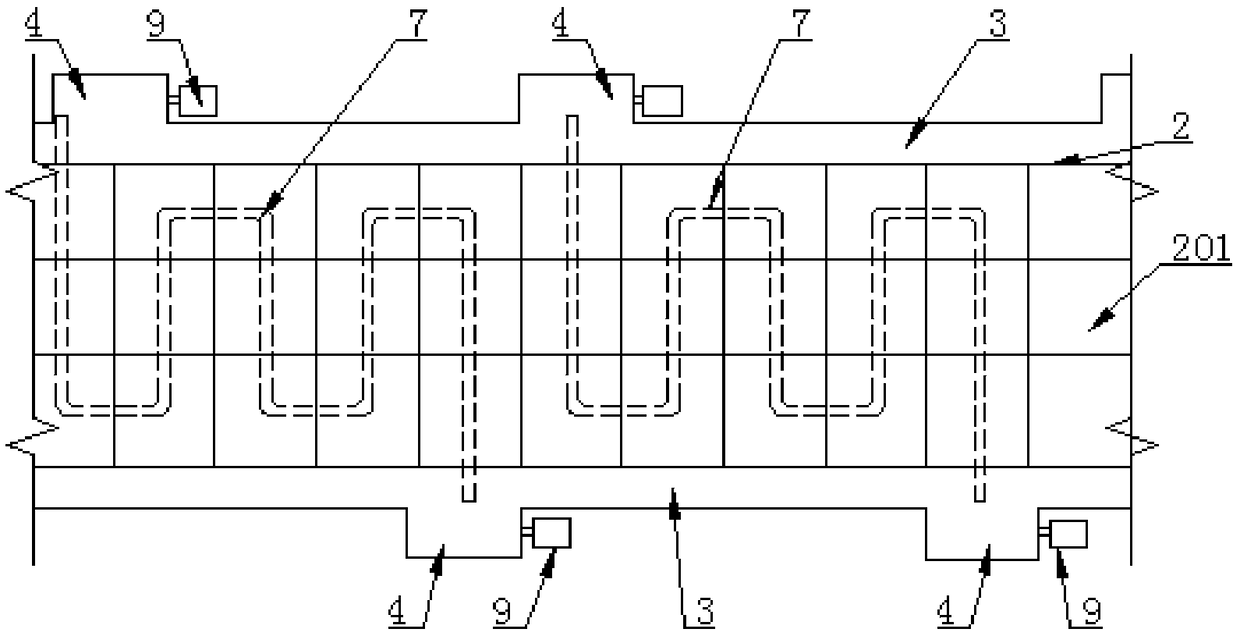
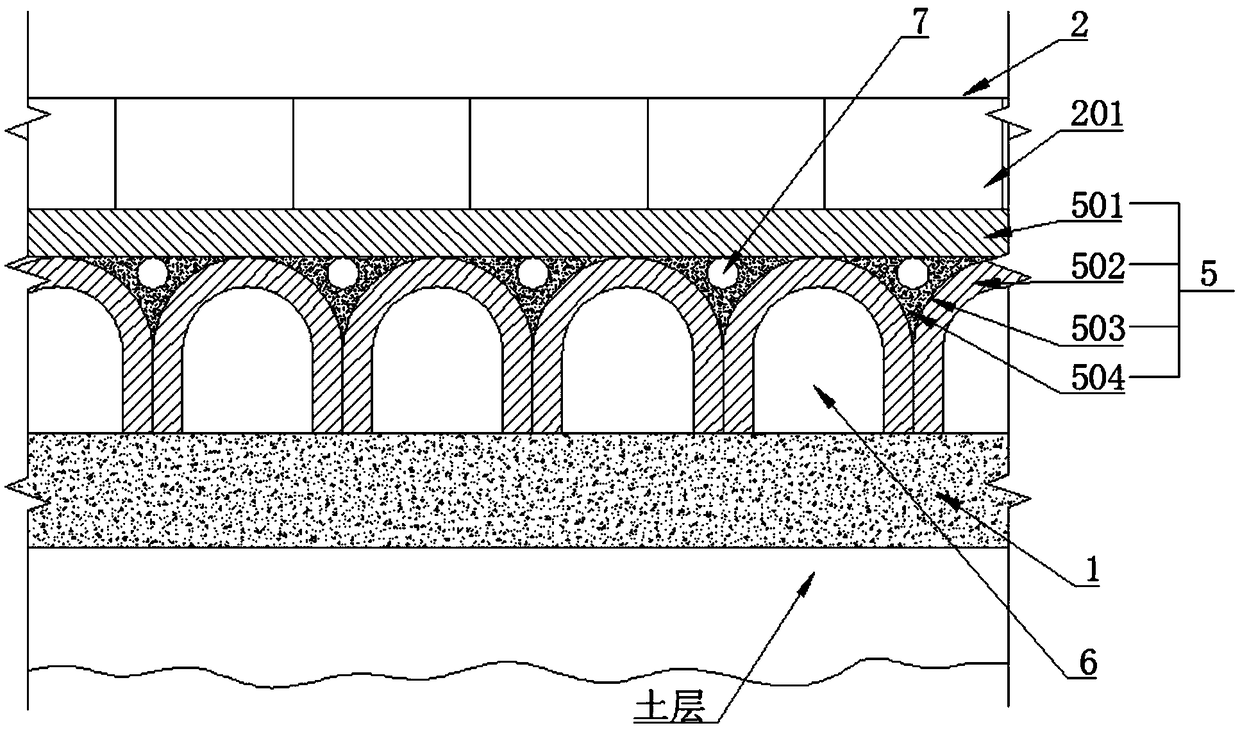
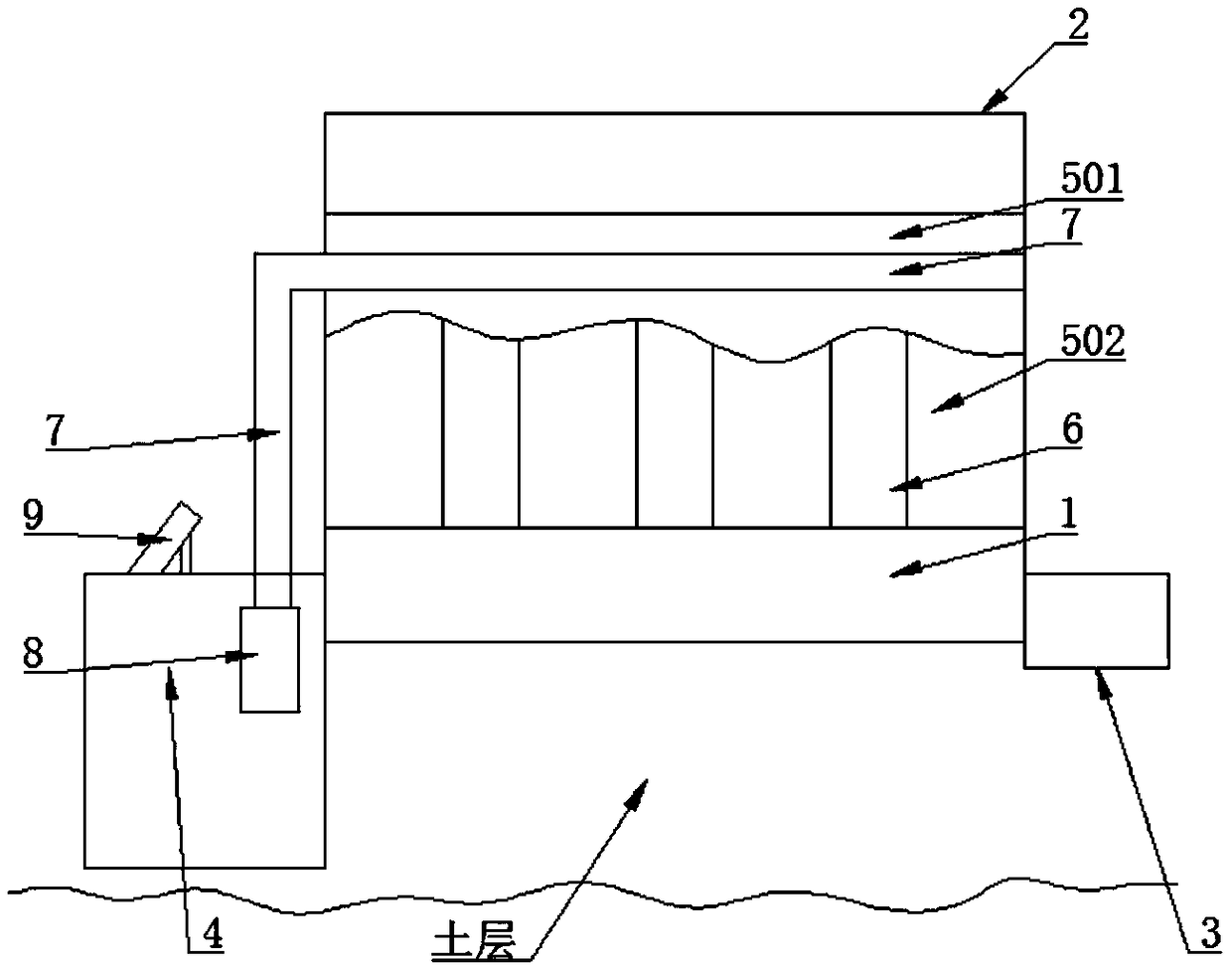
[0035] Such as Figure 1-3 As shown, a photovoltaic pavement system includes a master control unit, a subgrade 1, a photovoltaic pavement 2, and drainage grooves 3 on both sides of the photovoltaic pavement 2. The photovoltaic pavement 2 is composed of several photovoltaic panel modules 201 arranged in a row. 3 Water collection pools 4 are arranged at intervals; a support part 5 is provided on the roadbed 1, and a water collection channel 6 is formed between the roadbed 1 and the support part 5; the photovoltaic panel module 201 is laid on the support part 5 A circulating water pipe 7 is provided between the photovoltaic panel module 201 and the support part 5, and a heat collector 9 is provided at the sump 4, and the circulating water pipe 7 passes through the first water pump 8 and the heat collector 9 connected.
[0036] When the present invention is in use, the load brought by the vehicle running on the photovoltaic road surface 2 is directly transmitted to the photovolta...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Such as Figure 4 As shown, a photovoltaic pavement system. The structure and principle of this embodiment are similar to those of Embodiment 1. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the photovoltaic panel module 201 sequentially includes a tempered glass layer 2011, Photovoltaic panel 2012, substrate 2013, an insulating buffer layer 2014 is provided above the substrate 2013, a boss 20131 is provided on the substrate 2013, and the boss 20131 passes through the insulating buffer layer 2014, photovoltaic panel 2012 and tempered The glass layers 2011 are bonded together. Firstly, the insulating buffer layer 2014 not only has a certain buffering effect on the load transmitted by the tempered glass layer 2011, but also prevents the electric energy on the photovoltaic panel 2012 from being transmitted to the support portion 5, reducing the occurrence of safety accidents.
Embodiment 3
[0042] Such as Figure 5 As shown, a photovoltaic pavement system. The structure and principle of this embodiment are similar to those of Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2 is that the arch support 502 is provided with A water level sensor 11, the water level sensor 11 is electrically connected with the master control unit.
[0043] The sump 4 is provided with a second water pump 12, and the second water pump 12 is electrically connected to the master control unit.
[0044] The water in the water collecting channel 6 not only has the effect of cooling, but also has a certain supporting effect. A water level sensor 11 is set on the arch support 502, and the water level sensor 11 is electrically connected with the master control unit. The water in the water collecting channel 6 is used to support the photovoltaic pavement 2 within a certain water level. When the water level in the water collecting channel 6 is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com