Microbial cell exchanging method and optical tweezer device thereof
A technology of microbial cells and optical tweezers, applied in the field of biological cells, can solve problems such as reducing experimental efficiency, increasing time, and increasing the experimental burden of operators, and achieves the effects of wide range of uses, high precision and controllable production quality.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment
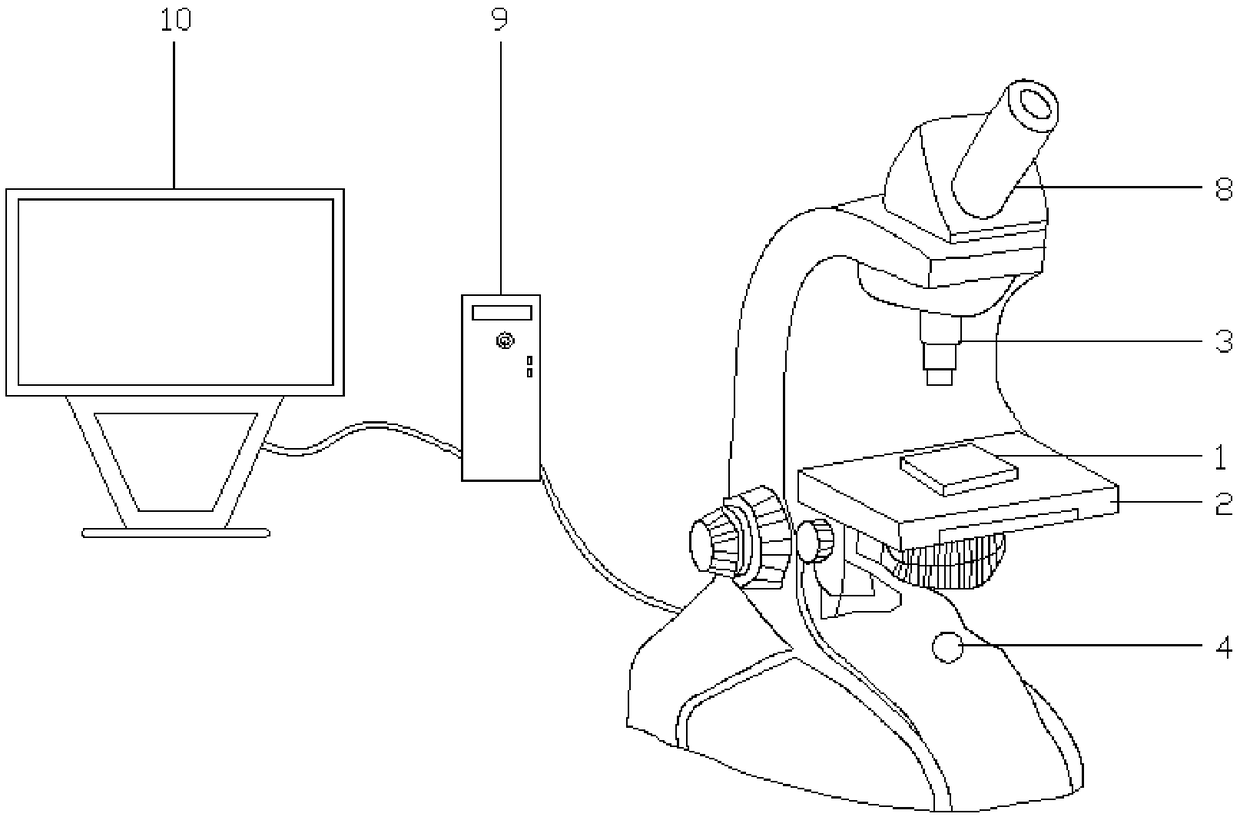
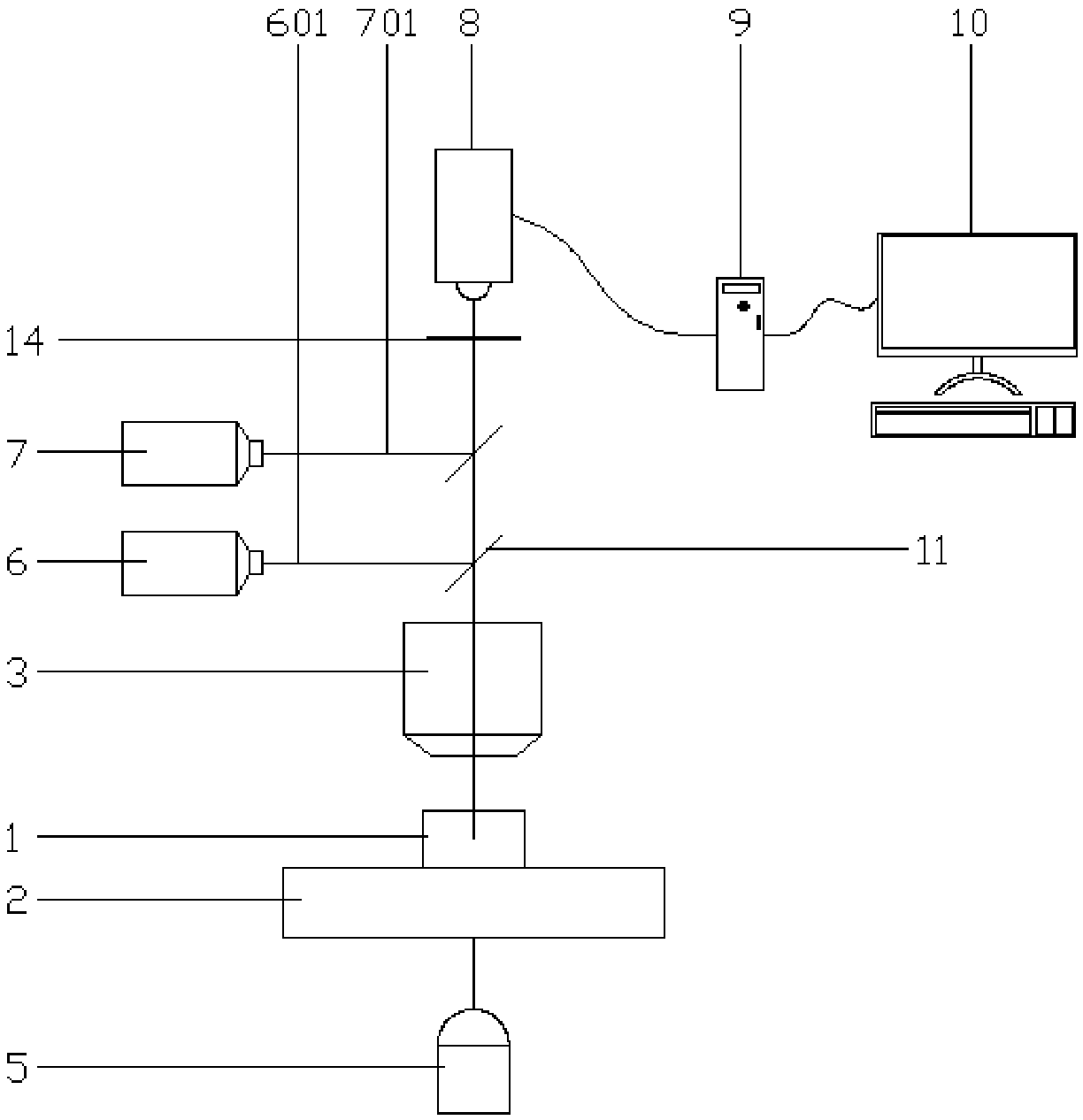
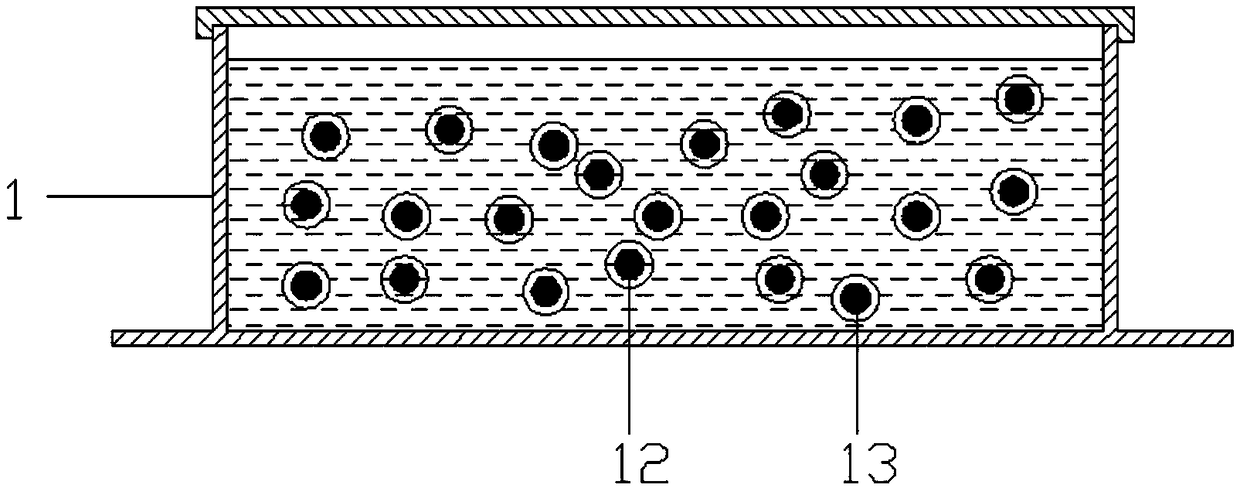
[0055] In actual use, wash the mushrooms and ganoderma of the same mass to clean the residues on the mushrooms and ganoderma; cut the washed mushrooms and ganoderma into small pieces, put them into different cell stirring sample chambers, and add 0.8 - 1.6 times the quality of the culture medium, close the cell stirring sample chamber; run the cell stirring sample chamber at a speed of 800-2800 rpm, run for 10-12 minutes, chop and beat the mushrooms or ganoderma lucidum in the sample chamber; Filter the slurry obtained in step 3 through a 250-500 mesh filter screen, collect the filtered filtrate and the residue remaining on the filter screen respectively, and obtain the filtered mushroom filtrate and Ganoderma lucidum filtrate; the obtained mushroom filtrate and Ganoderma lucidum filtrate The filtrate is poured into both sides of the cell culture chamber 1 with the culture medium in a small amount; adjust the microscope objective lens 3 so that it can clearly see the mushroom c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com