Radiation pneumonitis CT (Computed Tomography) quantitative detection method used for radiobiology experiment
A quantitative detection method, technology of radiation pneumonitis, applied in measuring devices, scientific instruments, material analysis using wave/particle radiation, etc., can solve the problems of combined cardiotoxicity, affecting the accuracy of results, affecting the accuracy and reliability of models, etc. , to achieve the effect of increasing accuracy, reducing dependence, reducing experimental cost and effort
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Embodiment 1 radiation biology (mice) experiment uses radiation pneumonitis CT quantitative detection method
[0036]A conventional medical linear accelerator was used to irradiate the whole lung field of mice to complete the modeling of radiation pneumonitis in mice. Mice were under anesthesia and well fixed.
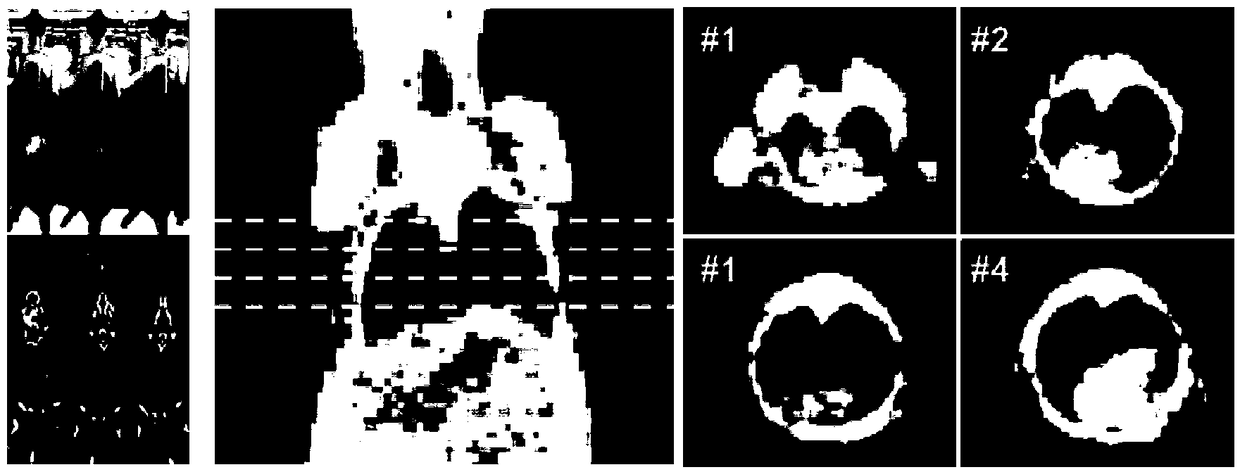
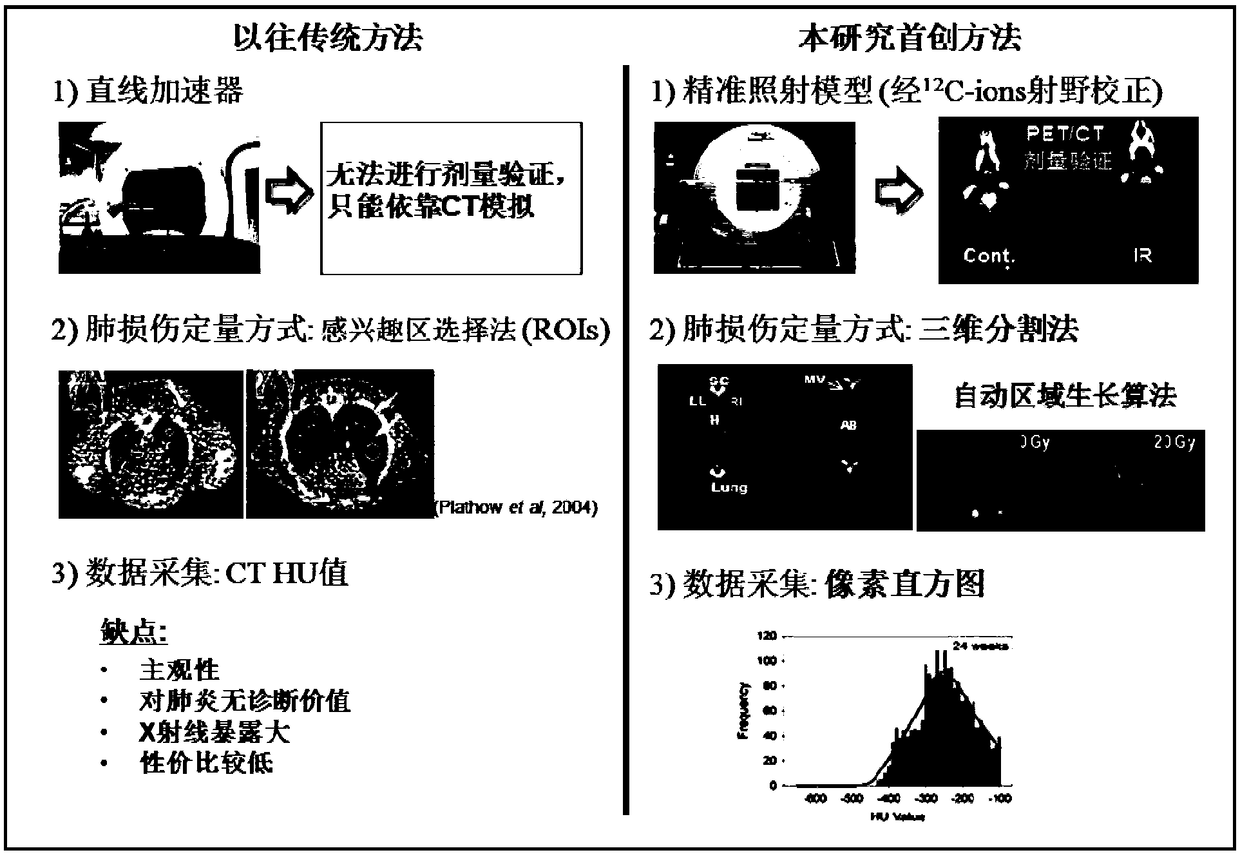
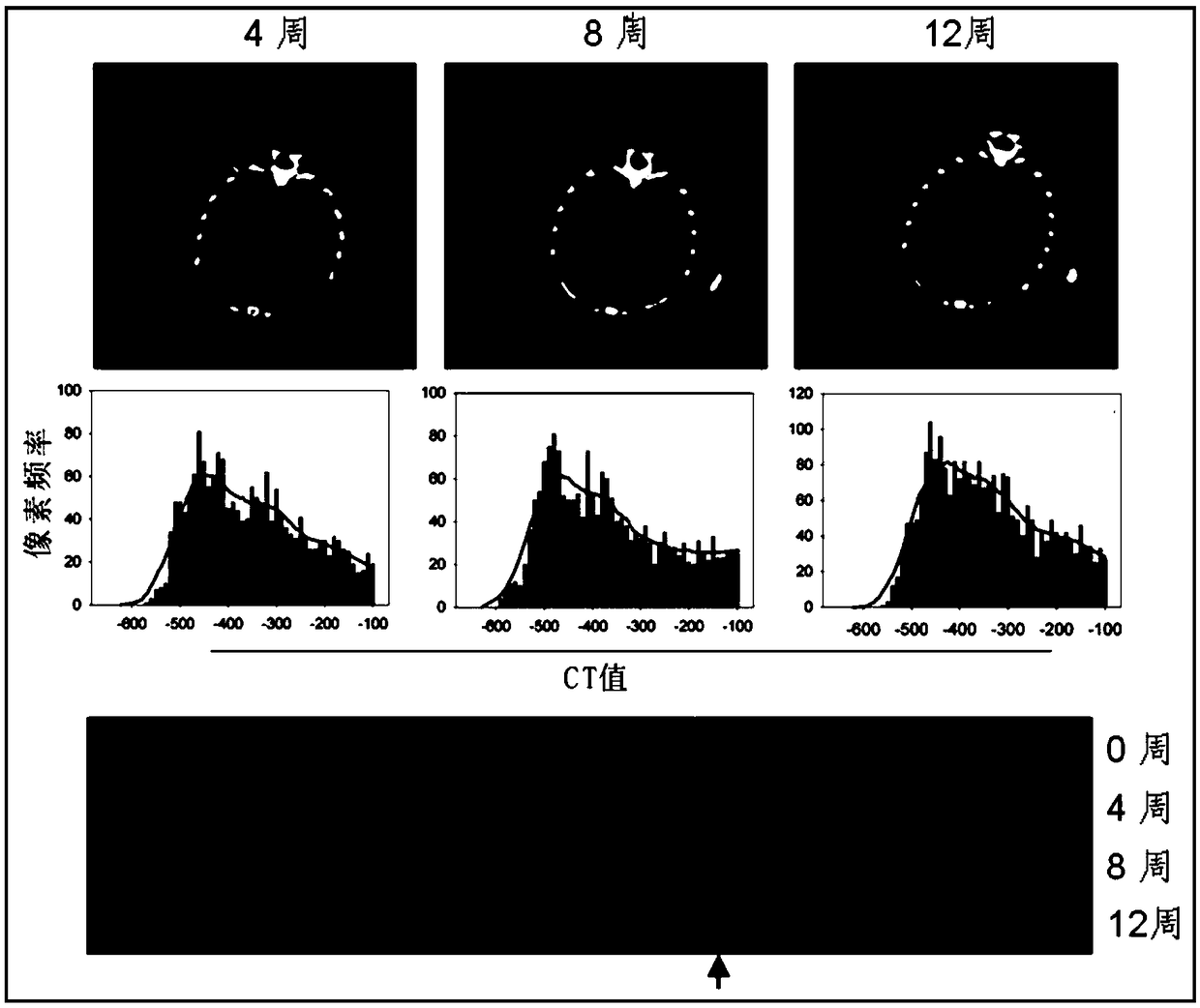
[0037] refer to figure 1 At different time points after the whole lung field of mice was irradiated, images were collected using conventional medical computed tomography (CT) equipment with low-dose scanning parameters; followed by 3D image reconstruction and 3D lung segmentation based on automatic region growing.
[0038] refer to figure 2 , an intuitive comparison between the CT non-invasive quantitative detection technology of the present invention and the traditional method. In the past, traditional CT image evaluation usually used Regions of interests (ROIs), its main disadvantages include: high subjectivity (relying on the experimenter’s subjective out...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Example 2: Quantitative detection of pneumonia was carried out 12 weeks after C57BL6 at the age of 8-10 weeks received whole lung field irradiation. The specific methods are as follows:
[0044] 1. Irradiation and grouping of animal experiments: C57BL6 female mice aged 8-10 weeks were used and raised at SPF level. Light for 12h, free access to food and water.
[0045] 2. After induction of anesthesia by isoflurane before irradiation, transfer to a dedicated mouse chest irradiation device and fix it properly. The whole lung field was irradiated by conventional medical linear accelerator.
[0046] 3. Give a single dose of 20Gy irradiation.
[0047] 4. The blank control group did not receive X-ray irradiation (0Gy). 12 mice were randomly assigned to each group of the control group and each dose of the experimental group;
[0048] 5. CT scans were performed every 4 weeks before and after irradiation (time points of 0, 4, 8, and 12 weeks respectively); low-dose scanning ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com