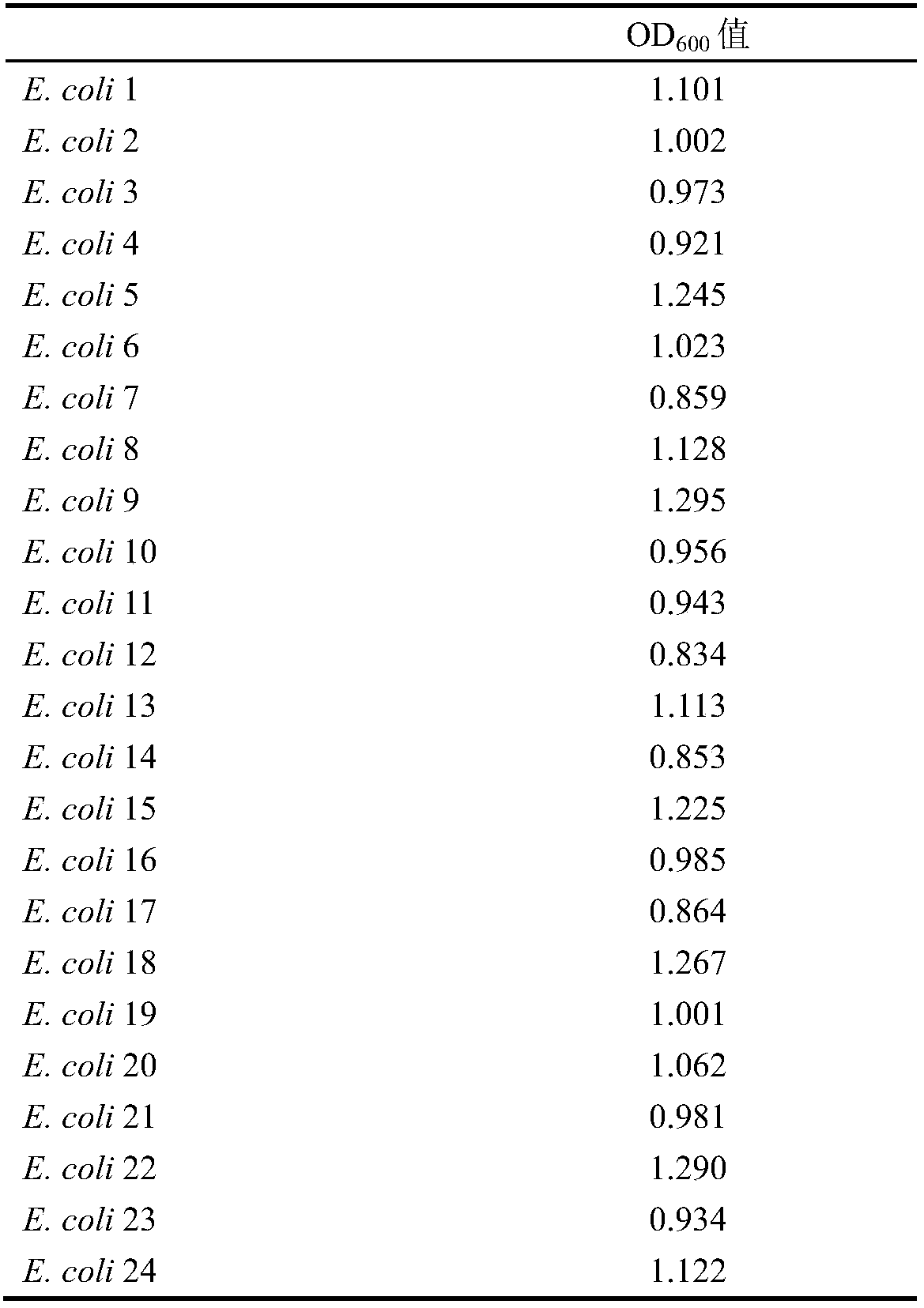Method for rapidly determining antibiotic resistance of Escherichia coli in biofilm
A technology of antibiotic resistance and biofilm, which is applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., to achieve the effect of easy repeatability, less supporting equipment, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
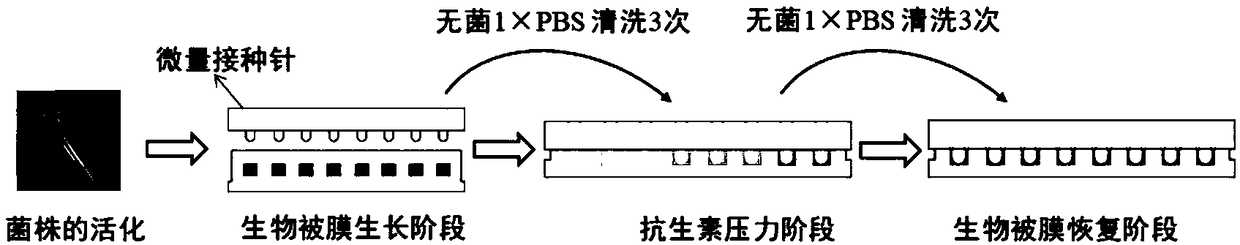
[0032] A method for constructing Escherichia coli in a biofilm resistant to polymyxins, the experimental flow chart is as follows figure 1 As shown, the order is: the activation of the strain; the biofilm growth stage; the antibiotic stress stage; the biofilm recovery stage. The steps of the method include:
[0033] (1) Biofilm growth stage
[0034] Take out the Escherichia coli stored in the glycerol tube from the -80°C refrigerator, place it on the ice box, and thaw it for about 5 minutes. In the aseptic operating table, use a sterile inoculation loop to draw a line on the LB agar plate, place it in a constant temperature incubator, and incubate at 37°C for 16-18h. Pick a single colony and put it in 9mL LB broth, place it in a shaker at 37°C and 200rpm and culture it for 16-18h.
[0035] Centrifuge the cultured thalline at 3000rpm, 10min, and 25°C, remove the supernatant (the supernatant is the centrifuged medium), and adjust the concentration of the bacterial solution wi...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Embodiment 2 plate coating method determines Escherichia coli optimal culture temperature
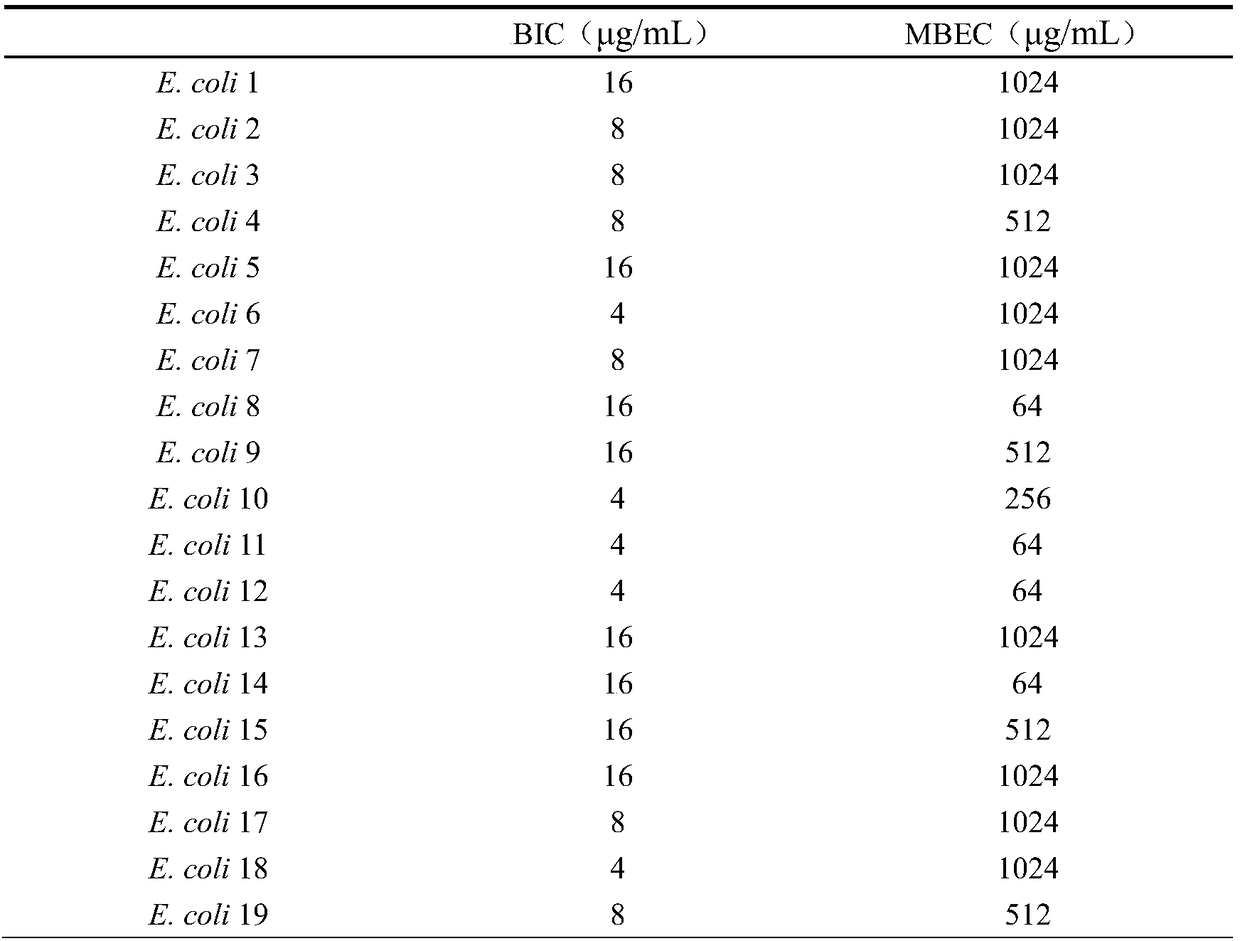
[0057] According to the above-mentioned method of activating and diluting, the OD value of the thalline was adjusted to the bacterium solution of OD600 value=0.5 McFarland, (the bacterial concentration was about 1×10 9 cfu / mL) for the cultivation of biofilms. Take 10 μL of the above-mentioned E. coli culture solution and add it to a 24-well plate containing 990 μL fresh LB (3% NaCL) medium, and use the fresh LB well plate not inoculated with the bacteria solution as a blank control, and make 3 parallels for each strain. Select four different temperatures (15°C, 25°C, 37°C and 45°C) and culture them statically for 24 hours to measure the amount of biofilm formation. The 24-well plate was sealed with plastic wrap to prevent moisture from evaporating.
[0058] After the cultivation, the bacterial solution in the well plate was first discarded, and the non-adhered bacteria were was...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com