A Target Arrival Angle Estimation Method Based on Dynamic Update of Spatial Discrete Grid
A discrete grid and space discrete technology, applied in directions such as direction finders using radio waves, radio wave direction/bias determination systems, etc. It can solve problems such as increasing correlation, and achieve the effect of solving discrete grid mismatch, reducing computational complexity and improving estimation accuracy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
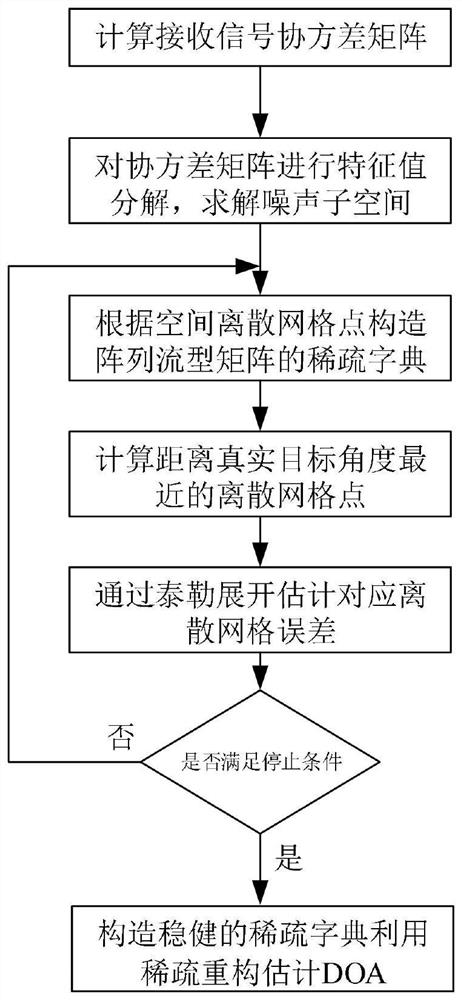
[0062] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing, the method provided by the present invention is described in more detail:
[0063] Step 1. Calculate the covariance matrix of the array antenna
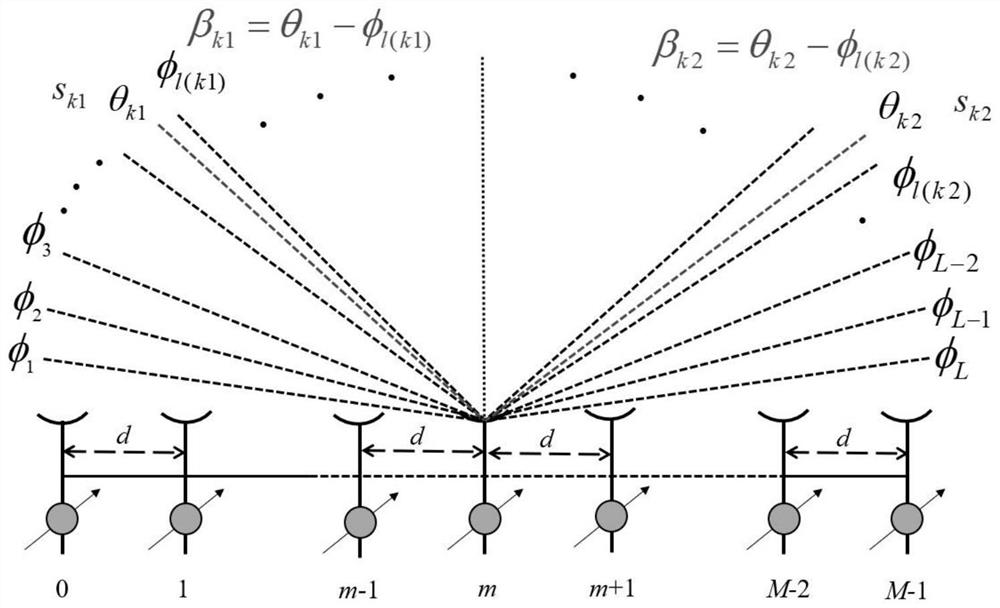
[0064] Assume that the position of the antenna element of the uniform linear array is d=[d 0 ,d 1 ,...,d M-1 ] T , without loss of generality assuming that the first antenna is d 0 =0, then d m =(m-1)d. If there are K far-field and uncorrelated targets irradiated on the linear array, assume that the direction of arrival of the target wave is θ=[θ 1 ,θ 2 ,...,θ K ] T , where θ k is the incoming wave direction of the k-th target, then the target baseband received signal in the t-th snapshot can be expressed as:
[0065]
[0066] in is the steering vector corresponding to the k-th target, A=[a(θ 1 ),...,a(θ K )] is an array manifold matrix. n(t) is additive white Gaussian noise with a mean of 0 and a variance of
[0067] According to the mathematical model of t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com