Preparation method for composite material with magnetic field regulating martensitic transformation
A martensitic transformation and composite material technology, which is applied in the field of preparation of composite materials with magnetic field regulated martensitic transformation, can solve the problem that the magnetic field-induced martensitic transformation in the temperature region is inefficient, affecting the application of materials, Unfavorable materials and other problems, to achieve the effect of widening the temperature range affected by the magnetic field, reducing the complexity of the equipment and increasing the efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1: Mn with a sintering temperature of 500°C and a sintering pressure of 25MPa 48 co 4 Ni 28 Ga 20 and Tb 0.27 Dy 0.73 Fe 1.9 Samples with a mass ratio of 20:1.
[0037] The preparation method is as follows
[0038] Step 1: Weigh two groups of metal elements Mn, Co, Ni and Ga, and Tb, Dy and Fe with a purity of 99.99% with an electronic balance;
[0039] The second step: Weigh the good metal element and put it into the electric arc furnace. Pump the vacuum in the electric arc furnace to 2×10 -3 Pa, further up to 1x 10 -6 Fill it with argon after Pa is below;
[0040] The third step: smelting simple metal with electric arc (current is 85A). After repeated smelting for 4 times, uniform ingot-like samples were prepared to obtain Mn 48 co 4 Ni 28 Ga 20 Ingot and Tb0.27 Dy 0.73 Fe 1.9 Ingot casting; (note, the subscript numbers of alloys represent the atomic number ratio)
[0041] The fourth step: the prepared Mn 48 co 4 Ni 28 Ga 20 Spindle same ...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2: Mn with a particle size of 30 microns, a sintering temperature of 500°C, and a sintering pressure of 25 MPa 48 co 4 Ni 28 Ga 20 and Tb 0.27 Dy 0.73 Fe 1.9 Samples with a mass ratio of 20:1.
[0047] The other steps are the same as in Example 1, except that the particle size of the precursor material is changed from 10 microns to 30 microns, and the material obtained under the same other conditions is relatively denser, but the phase change is extremely small.
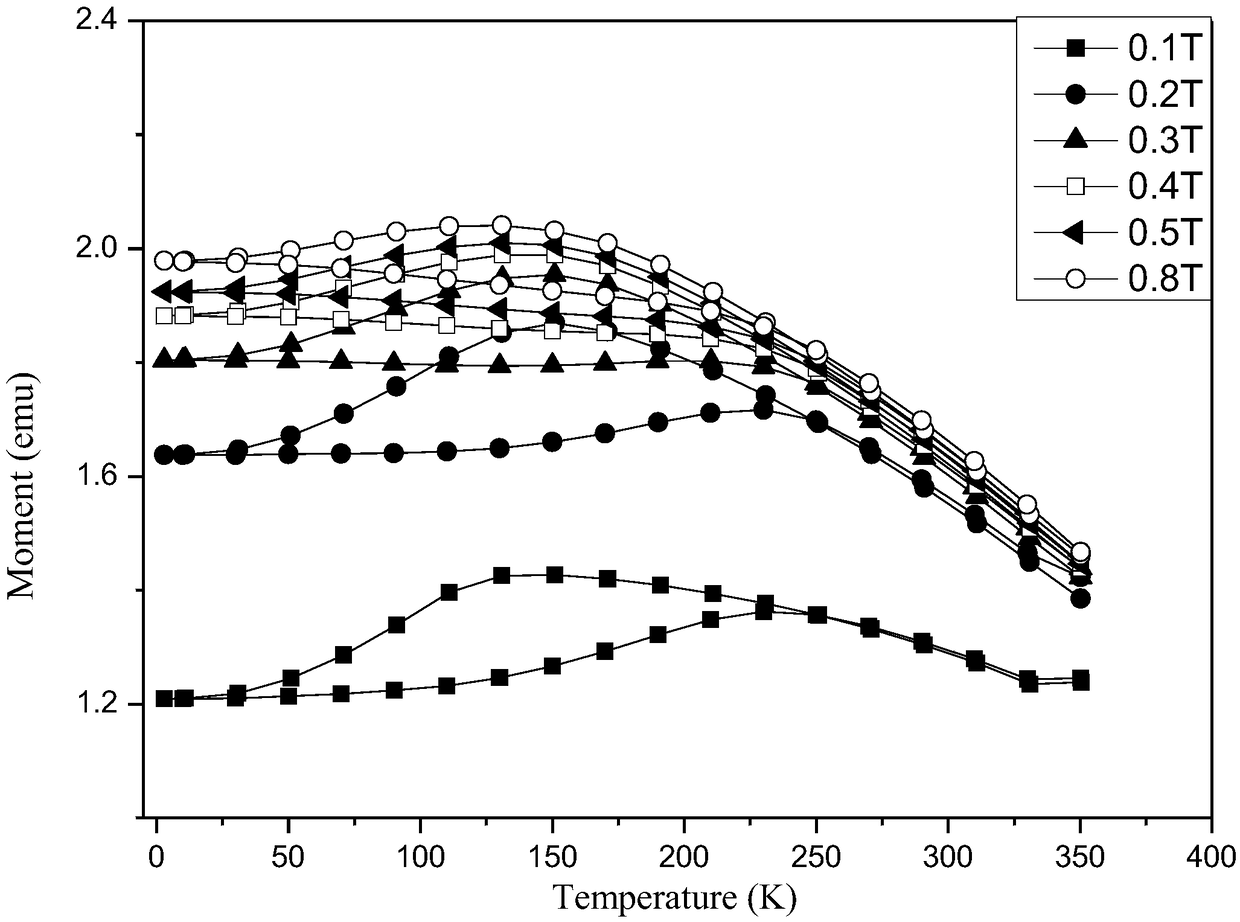
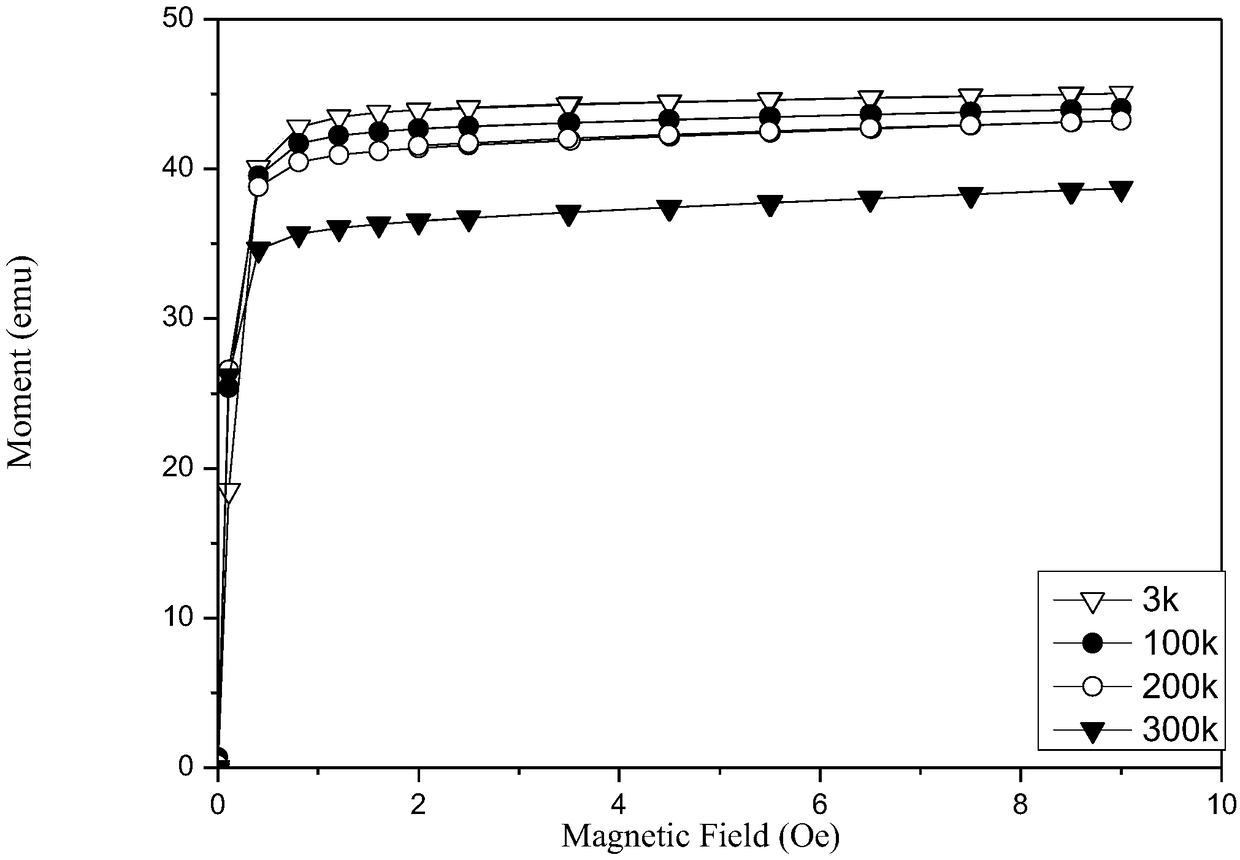
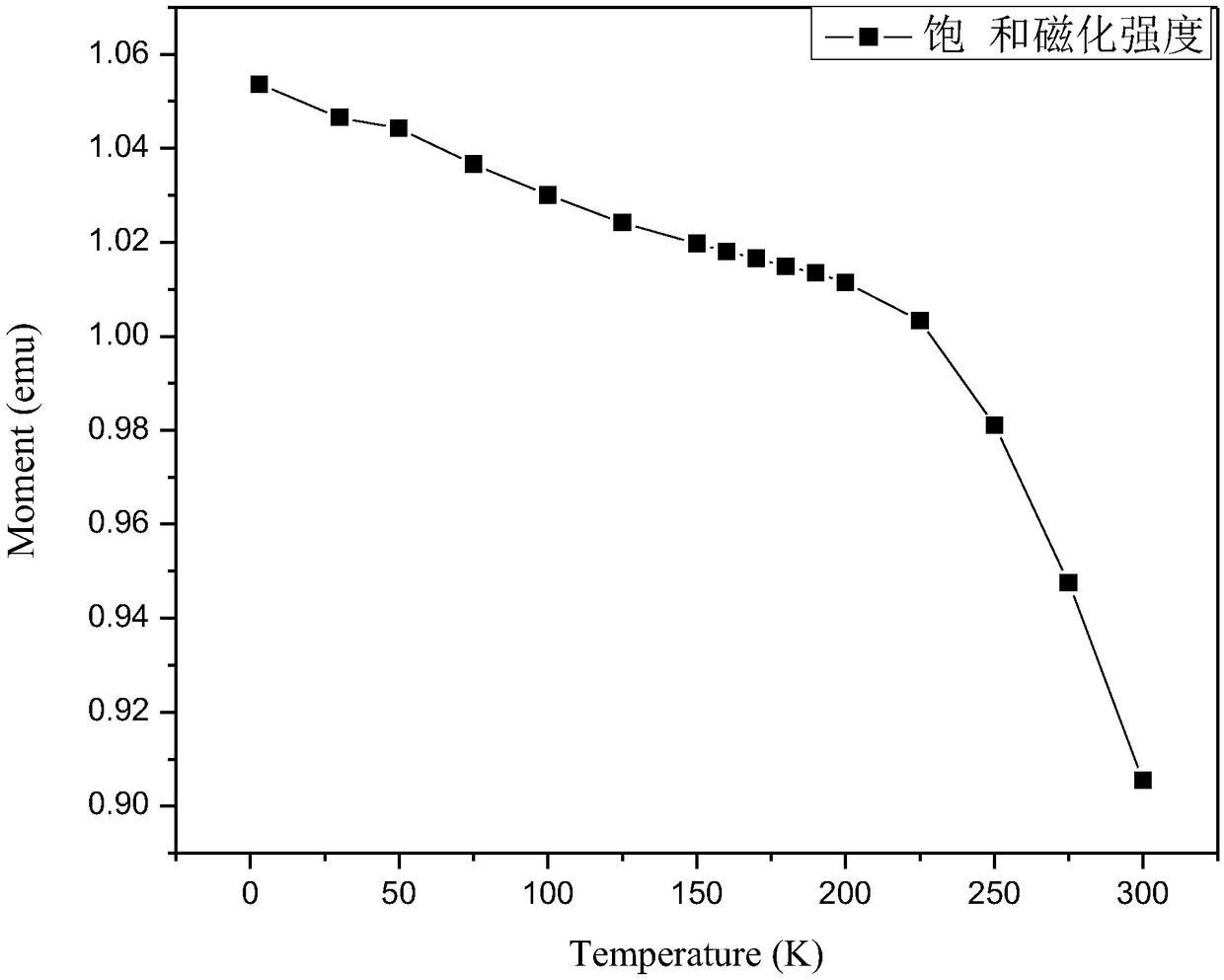
[0048] The influence efficiency of the magnetic field on the martensitic phase transformation obtained from the MT curve measurement is 6K / T, and the material is a typical magnetic field-induced martensitic phase transformation material. Under the 7T magnetic field, the influence range of the magnetic field on the martensitic transformation is: 46K-88K, and the temperature zone width is 42K.
Embodiment 3
[0049] Example 3: Mn with a particle size of 50 microns, a sintering temperature of 500°C, and a sintering pressure of 25 MPa 48 co 4 Ni 28 Ga 20 and Tb 0.27 Dy 0.73 Fe 1.9 Samples with a mass ratio of 20:1.
[0050] The other steps were the same as in Example 1, except that the particle size of the precursor material was changed from 10 microns to 50 microns, and the material obtained under the same conditions was very densely sintered but the martensitic transformation was small.
[0051] The influence efficiency of the magnetic field on the martensitic phase transformation obtained by MT curve measurement is 1K / T, and the material is a typical magnetic field-induced martensitic phase transition material. Under the 7T magnetic field, the influence range of the magnetic field on the martensitic transformation is: 49K-56K, and the temperature zone width is 7K.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com