Energy perturbation cross-bidirectional detection method based on rare earth nickel-based perovskite compounds
A detection method and perovskite technology, applied in the direction of material resistance, can solve problems such as limited space for optimization, and achieve the effect of broad application prospects and considerable application value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
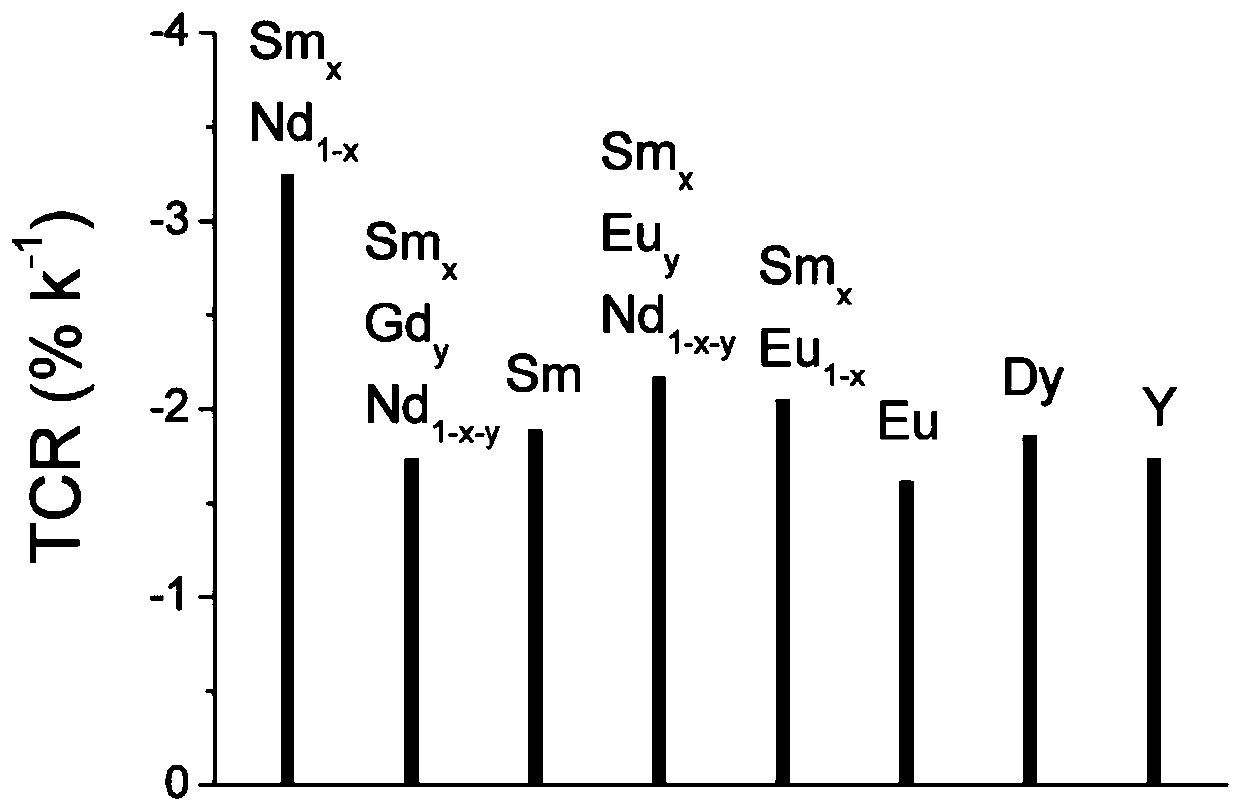
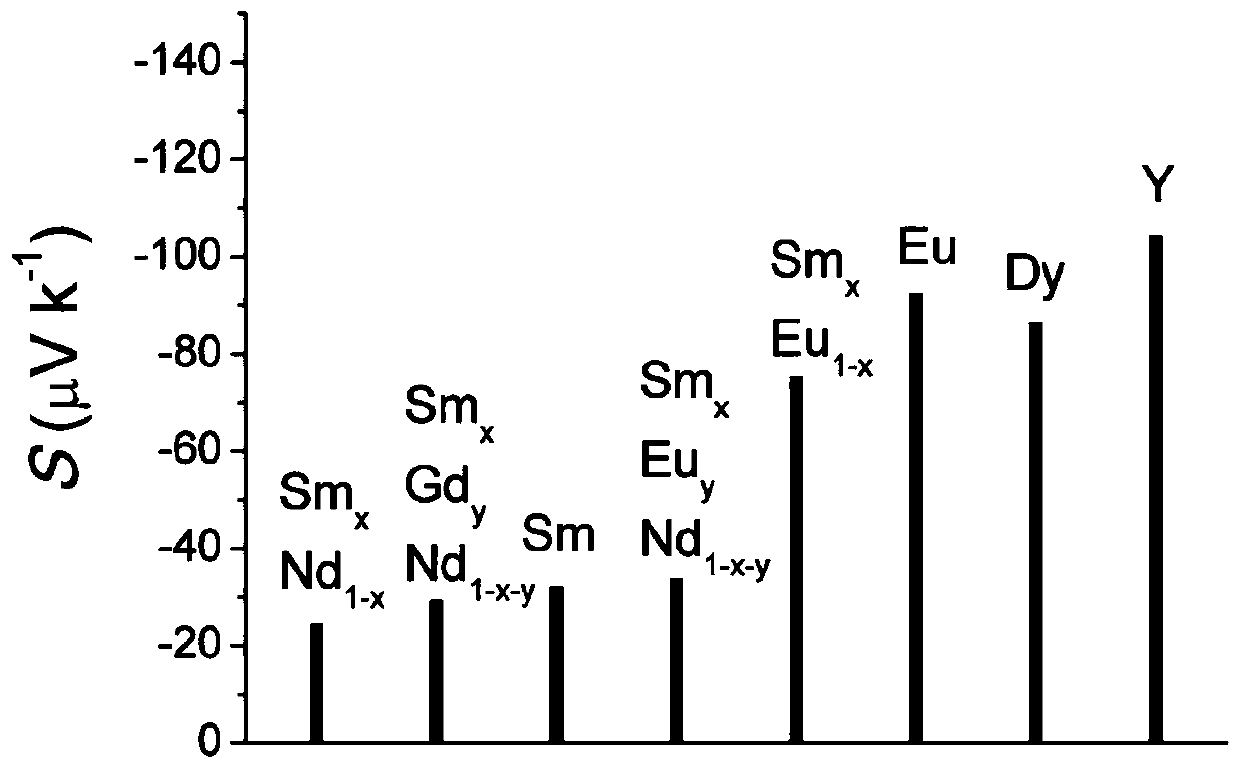
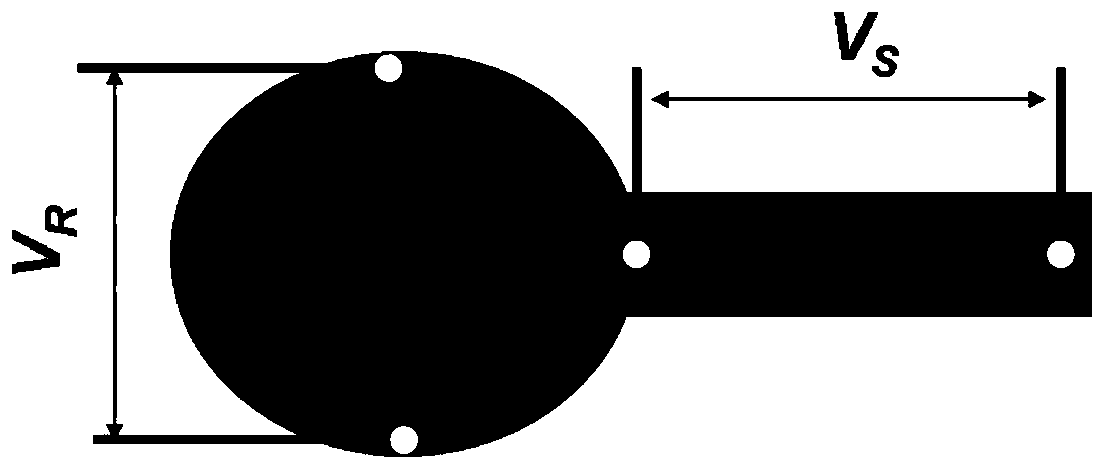
[0057] use figure 1 , figure 2 The samarium, neodymium, nickel and oxygen with properties such as the temperature coefficient of resistance and the Seebeck coefficient shown are used as energy sensitive materials, according to image 3 Devices were fabricated from the structures shown. Follow the direction indicated by the arrow (along V R Direction) through a current, read V R value, when V S value close to zero. Energy perturbation is applied to the center of the circular structure of the device by light waves, so that V R 3% change; at the same time measure the Seebeck voltage V caused by the temperature rise due to localized light absorption S Read a voltage signal of approximately 20 microvolts. After removing the energy disturbance, V R back to the original value and V S Back to zero. In active detection, the signal response time is short, and in passive detection, the signal-to-noise ratio can be achieved. Therefore, through the comprehensive utilization of a...
Embodiment 2
[0059] use figure 1 , figure 2 The ytterbium nickel oxide material with properties such as the resistance temperature coefficient and the Seebeck coefficient is used as an energy sensitive material, according to image 3 Devices were fabricated from the structures shown. Follow the direction indicated by the arrow (along V R Direction) through a current, read V R value, when V S value close to zero. Local heating of the center of the circular structure of the device increases the temperature by 10K, making V R 18% change; at the same time measure the Seebeck voltage V caused by the temperature rise due to localized light absorption S Read a voltage signal of approximately 180 microvolts. After stopping heating and standing for 30 minutes, V R back to the original value and V S Back to zero. In active detection, the signal response time is short, and in passive detection, the signal-to-noise ratio can be achieved. Therefore, through the comprehensive utilization of a...
Embodiment 3
[0061] use figure 1 , figure 2 Dysprosium-nickel-oxygen materials with properties such as the temperature coefficient of resistance and Seebeck coefficient shown are used as energy-sensitive materials, according to Figure 4 Devices were fabricated from the structures shown. Follow the direction indicated by the arrow (along V R Direction) through a current, read V R value, when V S value close to zero. A microwave perturbation signal is applied to the center of the circular structure of the device, resulting in V R 2% change; at the same time measure the Seebeck voltage V caused by the temperature increase due to localized light absorption S1 , V S2 , V S3 Voltage signals of about 30 microvolts, 32 millivolts, and 28 millivolts are respectively generated. stop microwave signal incident, V R back to the original value and V S1-S3 Back to zero. In active detection, the signal response time is short, and in passive detection, the signal-to-noise ratio can be achieve...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com