Method for determining bacterial amount in sodium alginate microcapsule
A technology of sodium alginate and determination method, which is applied in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, color/spectral property measurement, etc., can solve the problem of high cost of qPCR method, long determination time of glucosamine method, ergosterol It can solve problems such as the measurement of discomfort in the method, and achieve the effect of simple and easy operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1 Determination of the amount of bacteria in the microcapsules of Monascus
[0026] (1) Configuration of various reagents:
[0027] ① Anaerobic sodium citrate solution: accurately weigh 0.2moL sodium citrate, dilute the volume to 1L with deionized water after boiling and cooling, and remove oxygen again by 100W ultrasound for 20min.
[0028] ②27wt% anaerobic sulfuric acid solution: slowly add 98wt% concentrated sulfuric acid to the deionized water after boiling and cooling to dilute the concentrated sulfuric acid concentration to 27wt%, and then remove oxygen again by 100W ultrasound for 20min.
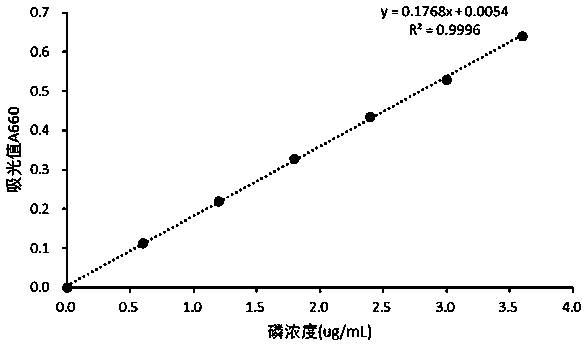
[0029] ③Standard phosphorus solution: Bake potassium dihydrogen phosphate at 110°C to constant weight, accurately weigh 0.8775g, dissolve in a small amount of distilled water, transfer to a 500ml volumetric flask, and dilute it 20 times before use.
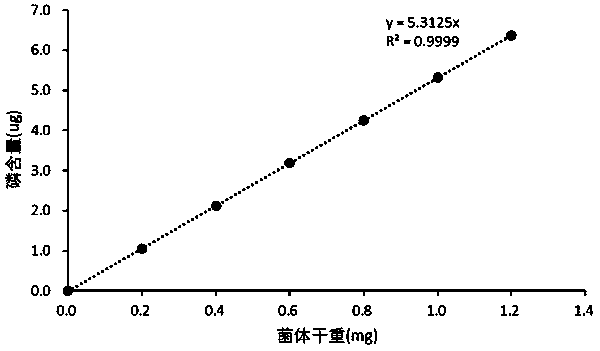
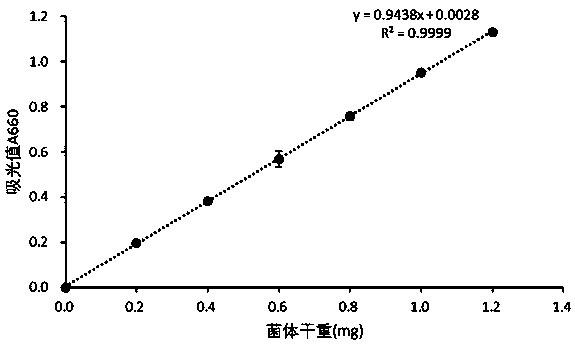
[0030] (2) Dissolution of sodium alginate microcapsules: place the sodium alginate microcapsules in a 75-fold volume of 0.2mol / L an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com