Real-time fluorescence radiation differential super-resolution microscopy method based on parallel spot scanning and device
A real-time fluorescence and super-resolution technology, applied in the field of super-resolution microscopy, can solve the problem of reduced imaging speed and achieve the effect of improving imaging speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] A real-time fluorescence radiation differential super-resolution microscopy method based on parallel spot scanning provided in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0060] (1) After the laser beam emitted by the laser is collimated, it is divided into S polarized light and P polarized light by a polarization beam splitter (PBS);
[0061] (2) Using a quarter-wave plate to modulate the S-polarized light into a circularly polarized solid spot;
[0062] (3) Perform phase modulation on the P polarized light, and modulate it into vortex polarized light;
[0063] (4) Utilizing a quarter-wave plate to further modulate the modulated P-polarized light into a circularly polarized hollow spot;
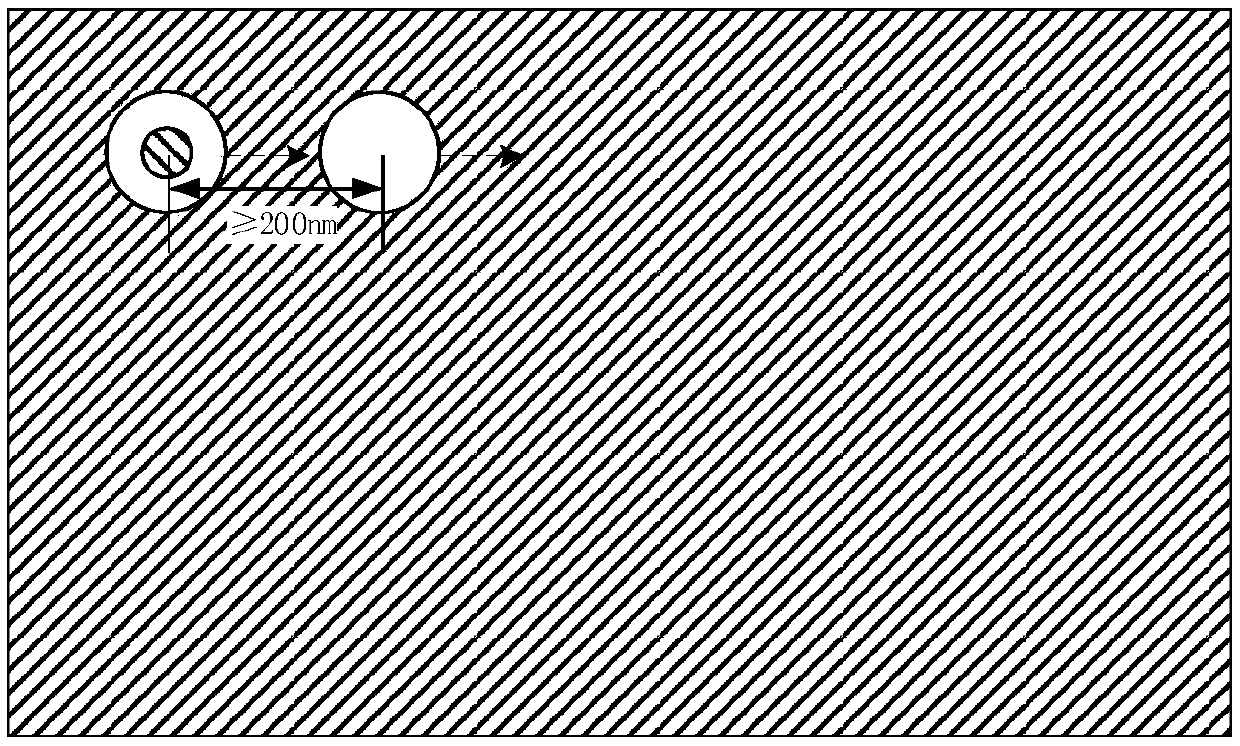
[0064] (5) According to the circular hole diffraction limit formula, in order to ensure that the solid spot and the hollow spot will not interfere with each other, the beam deflection device is used to make the excitation light of the solid spot and the excitation light of the ho...
Embodiment 2
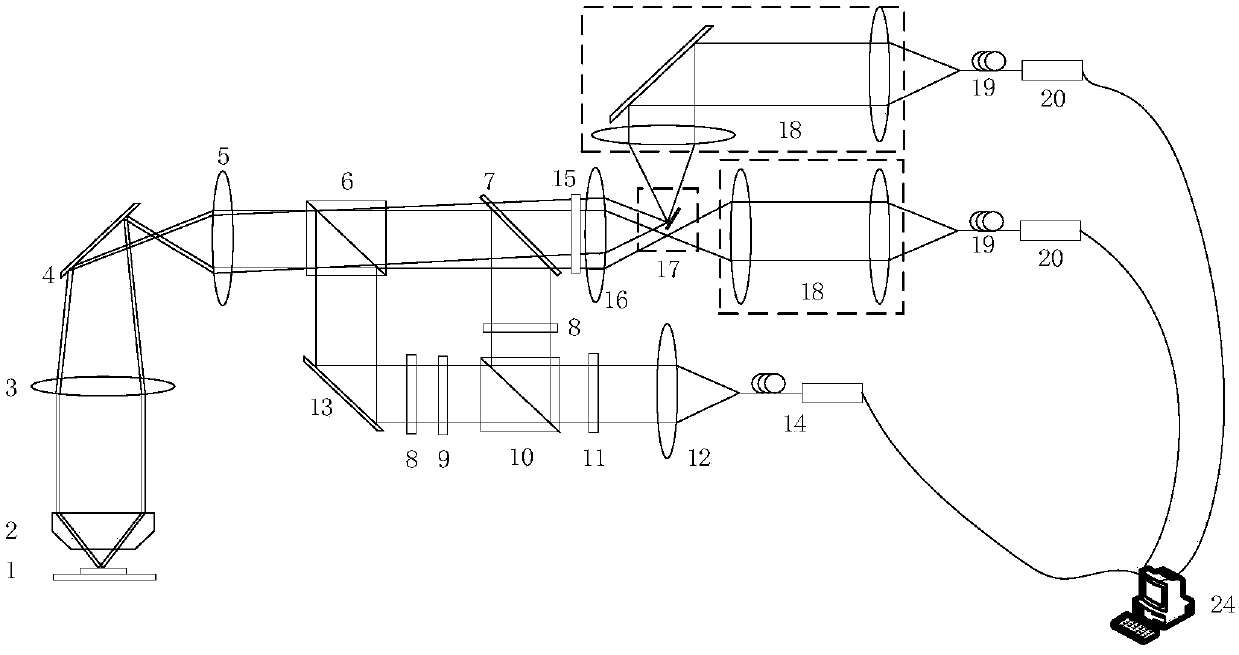
[0072] Such as figure 1 As shown, a real-time fluorescent radiation differential super-resolution microscopy device based on parallel spot scanning provided in this embodiment includes a laser 14, an excitation light modulation optical path sub-module, an object stage 1 carrying a fluorescent sample to be measured, and projecting light to Microscope frame and detection optical path sub-module of stage 1;
[0073] The excitation light modulation optical path sub-module includes:
[0074] A beam expander 12 for expanding the light beam of the point light source emitted by the laser 14 into parallel light;
[0075] A half-wave plate 11 for modulating the polarization direction of the outgoing light from the beam expander 12;
[0076] A polarizing beam splitter 10 for splitting the output light from the half-wave plate 11 into P polarized light and S polarized light;
[0077] A vortex phase plate 9 for performing 0-2π phase modulation on P-polarized light;
[0078] A quarter-w...
Embodiment 3
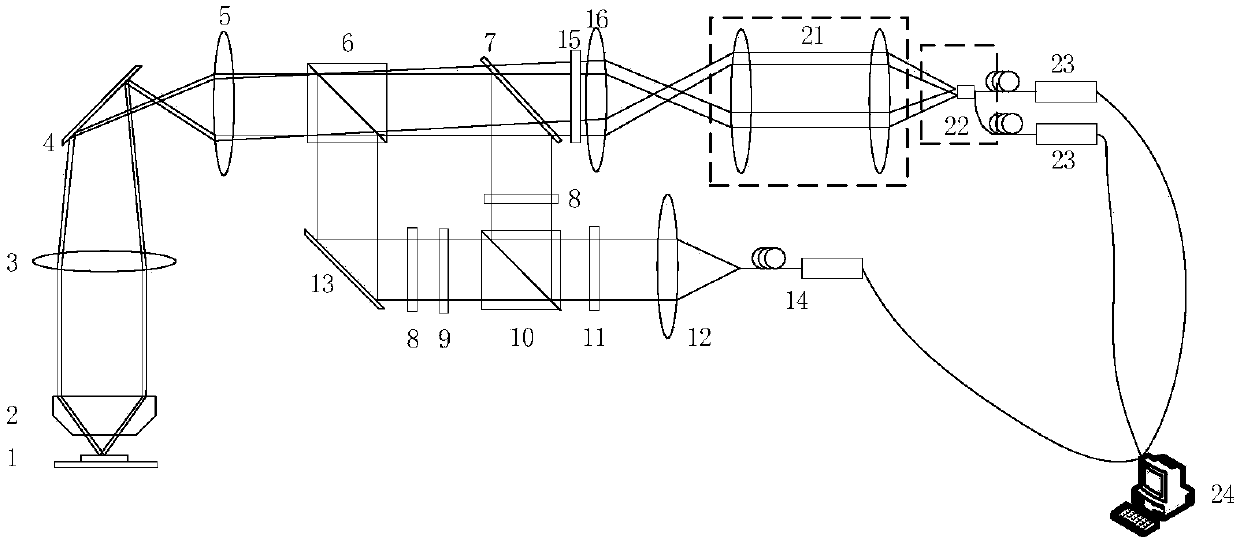
[0097] Such as figure 2 As shown, a real-time fluorescent radiation differential super-resolution microscopy device based on parallel spot scanning provided in this embodiment includes a laser 14, an excitation light modulation optical path sub-module, an object stage 1 carrying a fluorescent sample to be measured, and projecting light to Microscope frame and detection optical path sub-module of stage 1;
[0098] The excitation light modulation optical path sub-module includes:
[0099] A beam expander 12 for expanding the light beam of the point light source emitted by the laser 14 into parallel light;
[0100] A half-wave plate 11 for modulating the polarization direction of the outgoing light from the beam expander 12;
[0101] A polarizing beam splitter 10 for splitting the output light from the half-wave plate 11 into P polarized light and S polarized light;
[0102] A vortex phase plate 9 for performing 0-2π phase modulation on P-polarized light;
[0103] A quarter-...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Focal length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com