Calcium-zinc compound stabilizer as well as preparation method and application thereof
A calcium-zinc composite and stabilizer technology, applied in the field of chemical stabilizers, to achieve the effects of no three wastes, reduced production costs, and good thermal stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
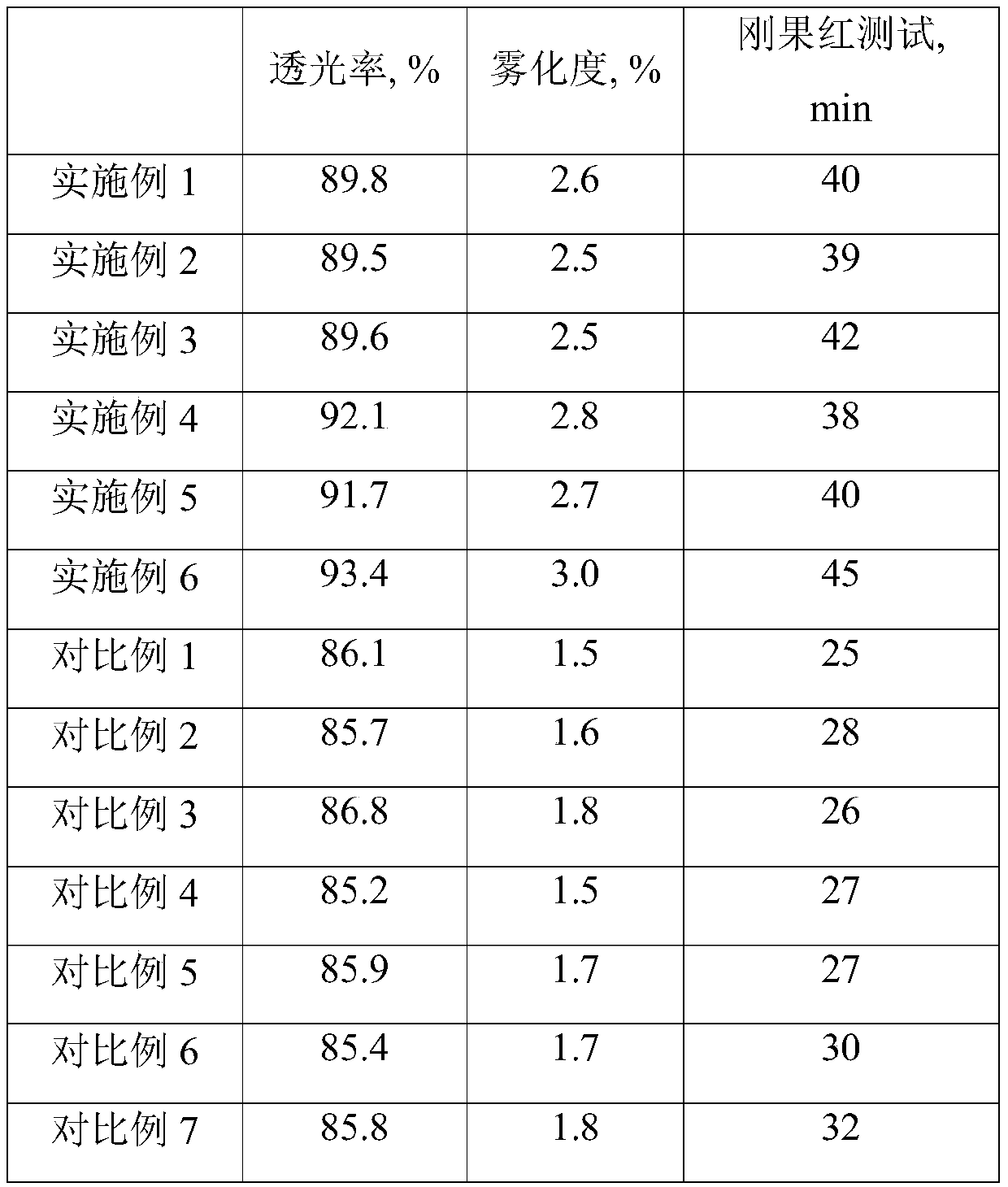
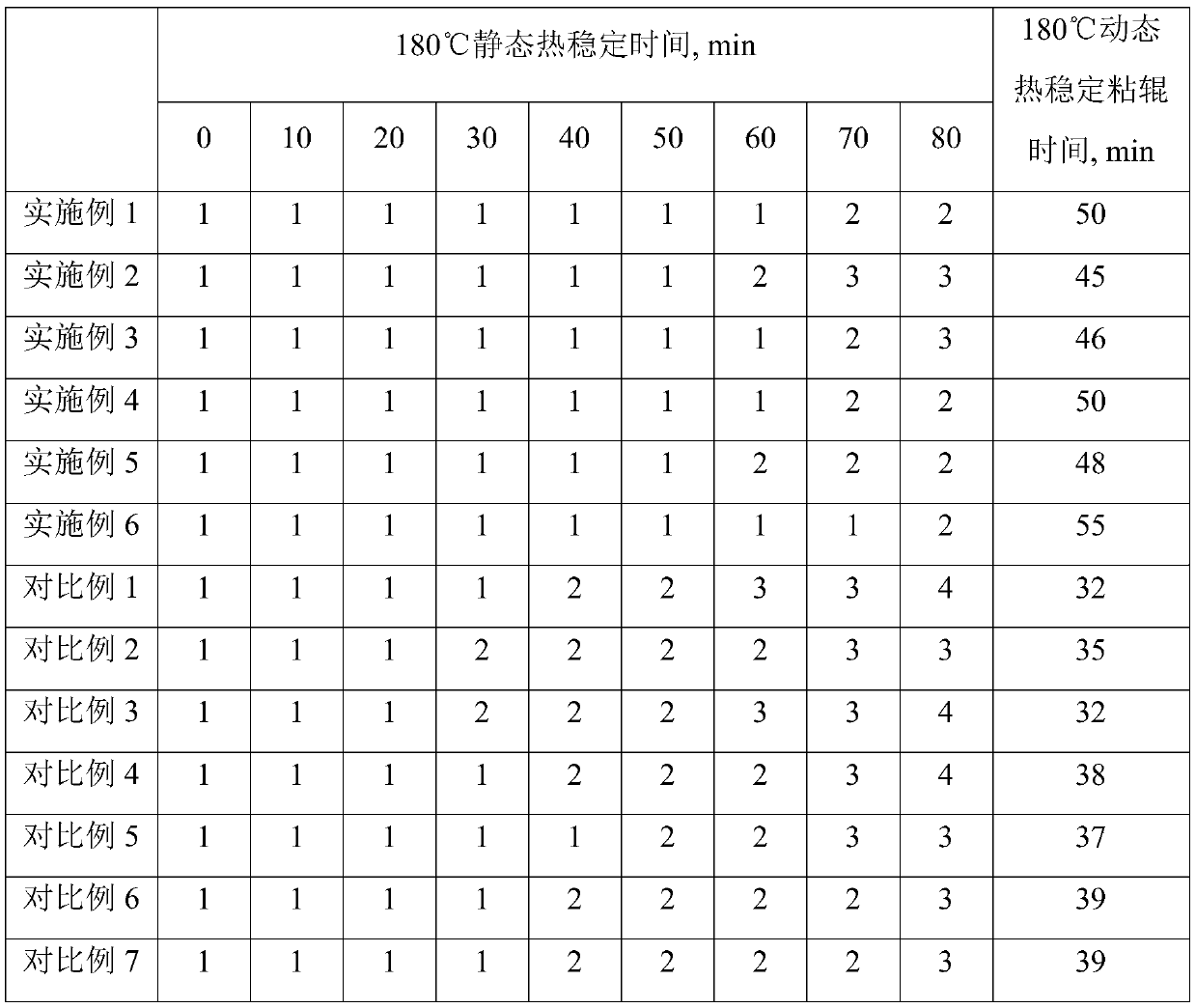
[0061] This embodiment provides a calcium-zinc composite stabilizer, which is composed of the following raw materials in mass percentage: isooctanoic acid: 10%, benzoic acid: 10%, ultrafine zinc oxide: 4.2%, ultrafine calcium oxide: 6.5%, non-toxic Phosphite: 8%, DINCH: 35%, ATBC: 1%, TXIB: 0.3%, methyl chloride: 25%; the average particle size of ultrafine zinc oxide is 30nm; the average particle size of ultrafine calcium oxide is 40nm, non-toxic phosphite is 4,4-diisoylidene bisphenol (12-14) carbon alkyl ester of phosphite;
[0062] The preparation method of above-mentioned calcium-zinc composite stabilizer specifically comprises the following steps:
[0063] S1. Carry out dehydration and salification treatment of isooctanoic acid, benzoic acid, zinc oxide and calcium oxide in the above ratio, and obtain calcium salt and zinc salt respectively; wherein, the process parameters of dehydration and salification treatment are: the reaction temperature is 100°C, The reaction time...
Embodiment 2
[0066] This embodiment provides a calcium-zinc composite stabilizer, the main difference from Example 1 is that it consists of the following raw materials in mass percentage: isooctanoic acid: 30%, benzoic acid: 2%, ultrafine zinc oxide: 0.5%, ultrafine Fine calcium oxide: 1.2%, non-toxic phosphite: 15%, DINCH: 20%, ATBC: 5%, TXIB: 3%, chloromethyl ester: 23.3%; the average particle size of ultrafine zinc oxide is 80nm; The average particle size of superfine calcium oxide is 80nm;
[0067] The preparation method of the above-mentioned calcium-zinc composite stabilizer refers to the operation steps of Example 1, the main difference is that in step S1, the process parameters of the dehydration and salt-forming treatment are as follows: the reaction temperature is 120° C., and the reaction time is 15 minutes.
Embodiment 3
[0069] This embodiment provides a calcium-zinc composite stabilizer, the main difference from Example 1 is that it consists of the following raw materials in mass percentage: isooctanoic acid: 22%, benzoic acid: 4%, ultrafine zinc oxide: 3%, ultrafine Fine calcium oxide: 1.9%, non-toxic phosphite: 10%, DINCH: 25%, ATBC: 2%, TXIB: 0.1%, chloromethyl ester: 32%; the average particle size of ultrafine zinc oxide is 50nm; The average particle size of superfine calcium oxide is 50nm;
[0070] The preparation method of the above-mentioned calcium-zinc composite stabilizer refers to the operation steps of Example 1, the main difference is that in step S1, the process parameters of the dehydration and salt-forming treatment are as follows: the reaction temperature is 110° C., and the reaction time is 20 minutes.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com