Fusobacterium nucleatum as marker to predict curative effect of PD-L1 antibody therapy of colorectal cancer and application of maker
A technology of Fusobacterium nucleatum and PD-L1, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of unclear, less than 30% effective rate, unsatisfactory immunotherapy effect, etc., to achieve good therapeutic effect and prolong survival period.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] This embodiment is a method and steps for detecting whether a colorectal cancer patient carries Fusobacterium nucleatum, including:
[0041] (1) Fusobacterium nucleatum DNA was extracted from the feces of patients with colorectal cancer;
[0042] The stool genomic DNA extraction kit (product number DP328) produced by Tiangen Biochemical Technology (Beijing) Co., Ltd. was used to extract DNA from the stool of colorectal cancer patients. The specific steps are as follows:
[0043] 1. Weigh 180-220mg of stool sample into a 2ml centrifuge tube and place the tube on ice.
[0044] 2. Add 500 μl Buffer SA, 100 μl Buffer SC, 15 μl Proteinase K, and 0.25 g of grinding beads to the sample, shake intermittently for 1 min until the sample is fully mixed.
[0045] 3. Incubate at 70°C for 15 minutes, shake 2-3 times during incubation.
[0046] 4. Vortex for 15 sec, centrifuge at 12,000 rpm (~13,400×g) for 3 min, transfer the supernatant to a new centrifuge tube, add 10 μl of RNase ...
Embodiment 2
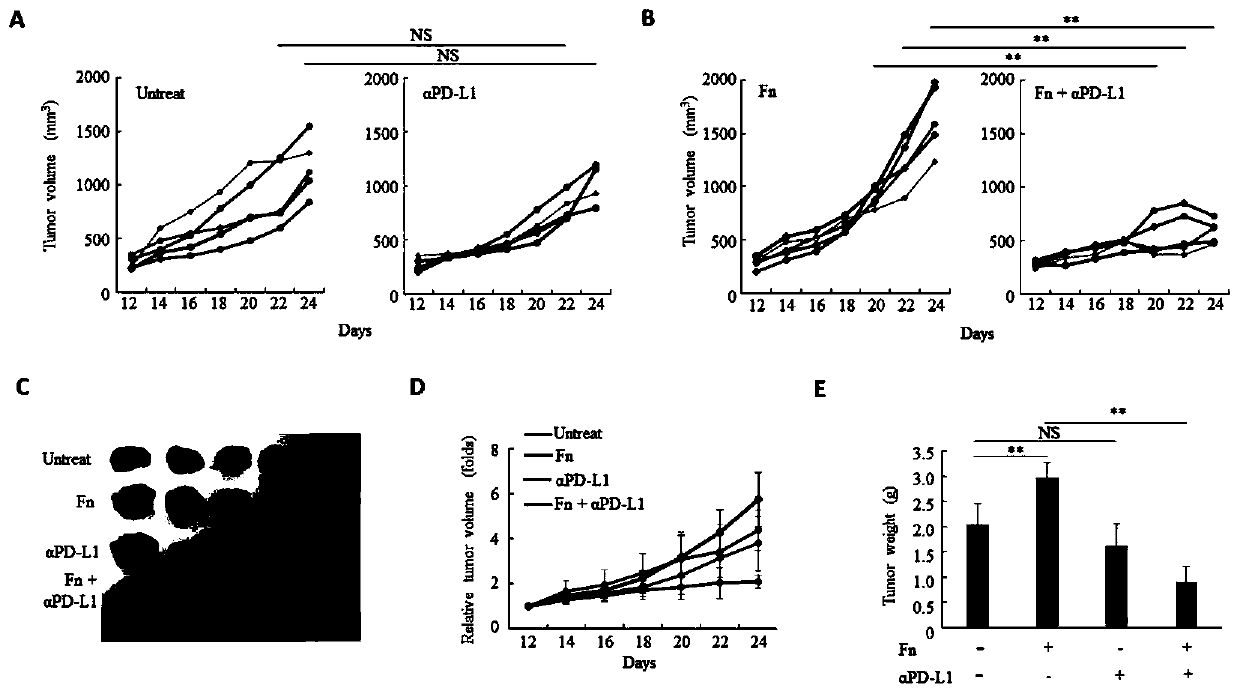
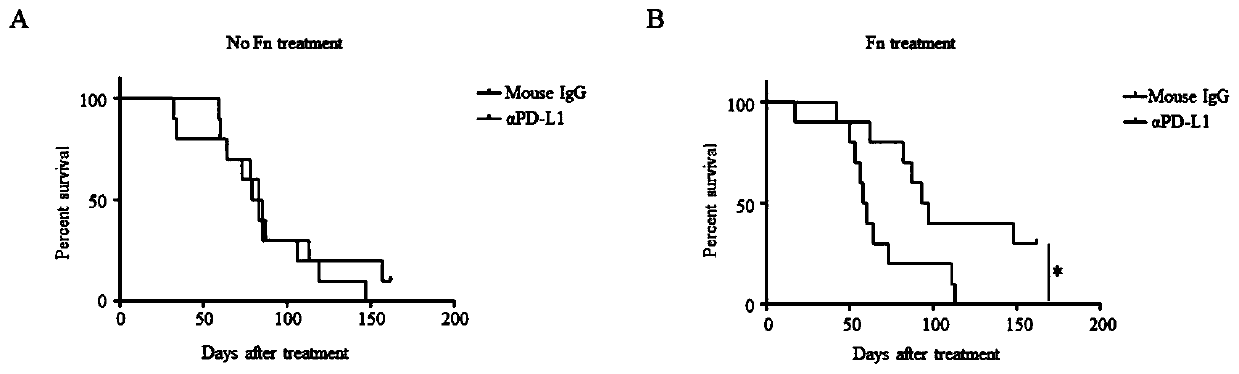
[0111] This example verifies the relationship between Fusobacterium nucleatum and the immunotherapeutic effect of colorectal cancer PD-L1 antibody, and the experimental steps are as follows:
[0112] Use the mouse colon cancer cell line CT26.WT to form tumors subcutaneously in BalB / C mice, inject Fusobacterium nucleatum into the tumor at multiple points, and then inject anti-mouse PD-L1 antibody intraperitoneally, and observe the changes in tumor size. After the tumor tissue of mice with Fusobacterium nucleatum was treated with PD-L1 antibody, the tumor was significantly inhibited, while the tumor tissue without Fusobacterium nucleatum was not sensitive to PD-L1 antibody treatment. The results were as follows: figure 1 As shown, this indicates that Fusobacterium nucleatum enhances the immune efficacy of PD-L1 antibody in colorectal cancer.
Embodiment 3
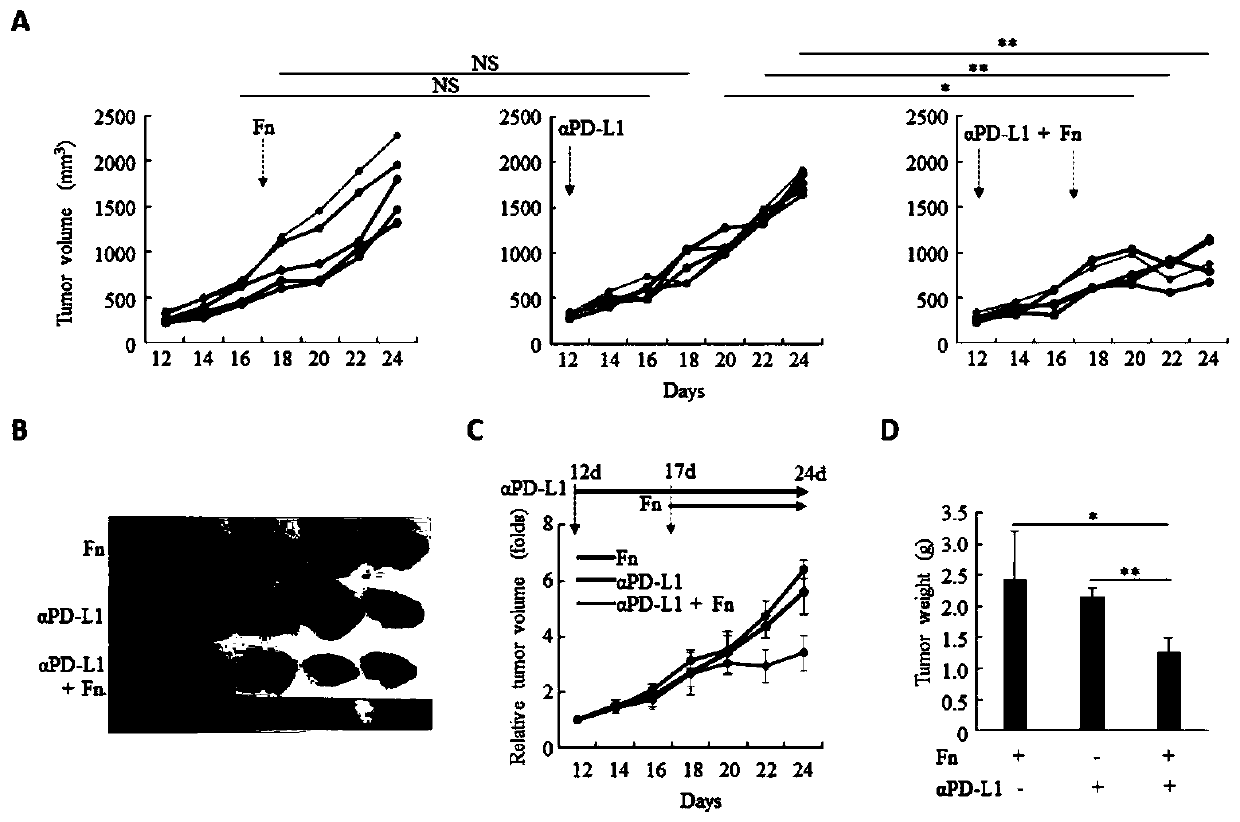
[0114] This example verifies the effect of transplanting Fusobacterium nucleatum on the curative effect of PD-L1 immunotherapy-insensitive colorectal cancer, and the experimental steps are as follows:
[0115] After subcutaneous tumor formation of CT26.WT cells, PD-L1 antibody immunotherapy, compared with the untreated group, the tumor volume did not shrink significantly, indicating that CT26.WT is not sensitive to PD-L1 antibody immunotherapy, and then transplanted in tumors with Fusobacterium nucleatum, it was found that the tumor volume after PD-L1 antibody immunotherapy after transplantation of Fusobacterium nucleatum was significantly reduced, and the results were as follows figure 2 As shown, this illustrates that transplantation of Fusobacterium nucleatum enhances the efficacy of colorectal cancer that is insensitive to PD-L1 immunotherapy.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com