Superlattice material as well as preparation method and application thereof
A superlattice and two-dimensional material technology, applied in the growth of polycrystalline materials, the application of conductive/insulating/magnetic materials on magnetic films, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problem of miniaturization and low power consumption that are difficult to meet Storage application requirements and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
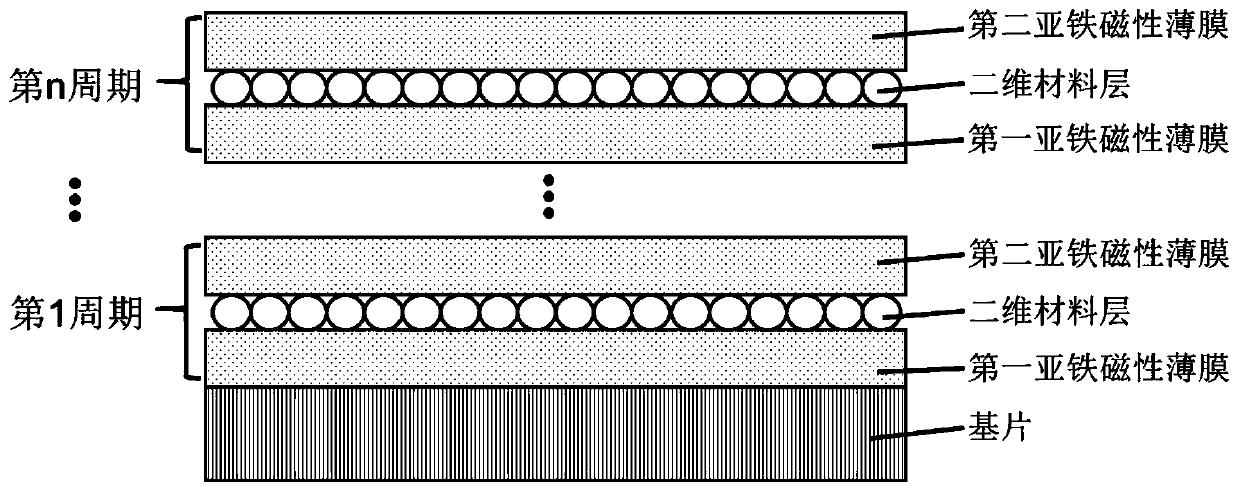
[0037] The present invention also provides a method for preparing the superlattice material described in the above technical solution, comprising the following steps:
[0038] The first ferrimagnetic thin film, the two-dimensional material layer and the second ferrimagnetic thin film are sequentially stacked and grown on the substrate to obtain a superlattice material.
[0039] In the present invention, unless otherwise specified, all raw material components are commercially available products well known to those skilled in the art.
[0040] In the present invention, the substrate is preferably pretreated before growing the first ferrimagnetic thin film; the pretreatment is preferably cleaned with acetone, alcohol and deionized water in sequence; the cleaning It is carried out under ultrasonic conditions; the present invention does not have any special limitation on the ultrasonic conditions.
[0041] In the present invention, the method for growing the first ferrimagnetic th...
Embodiment 1
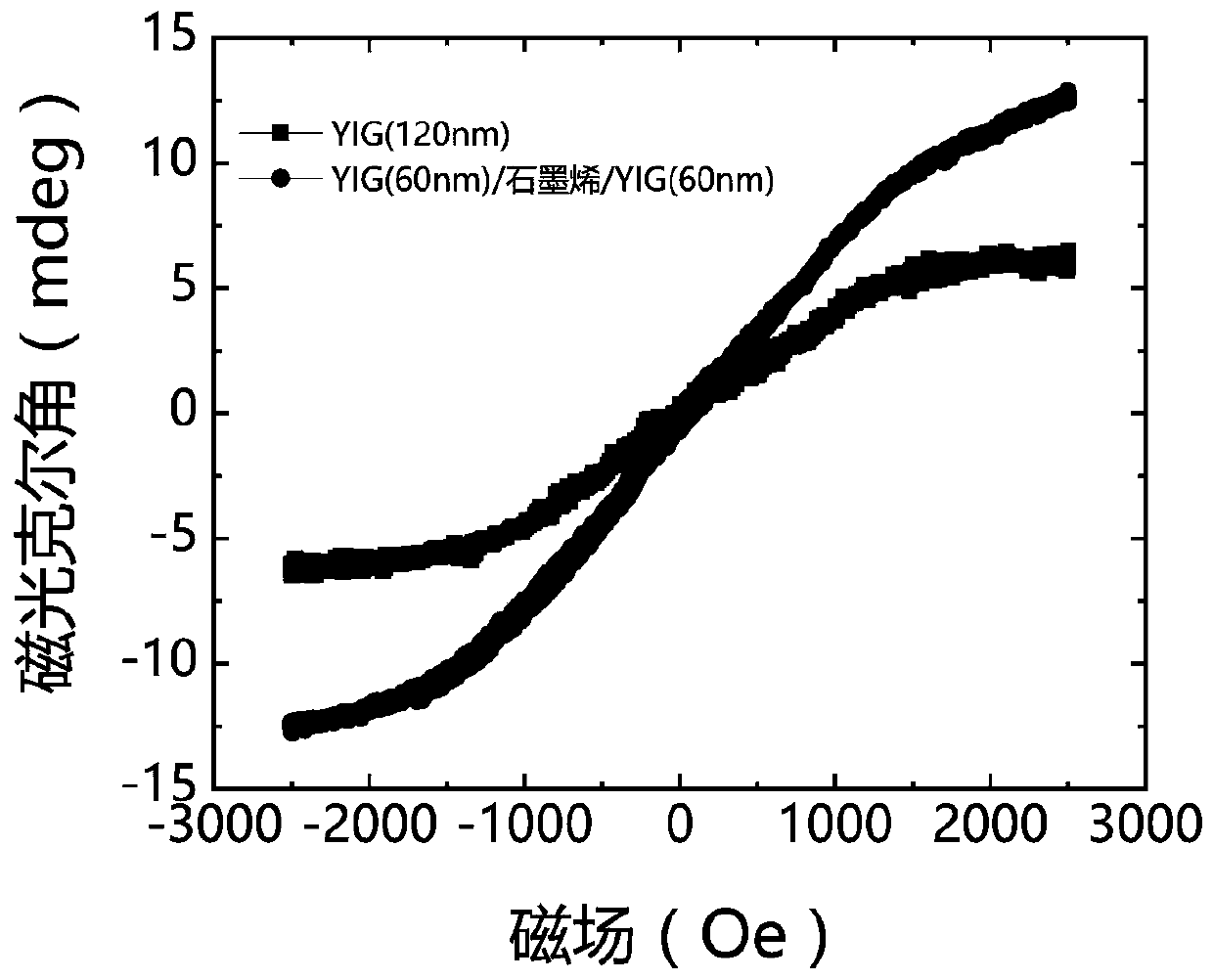
[0063] A superlattice material: the substrate material is a gadolinium gallium garnet (GGG) single crystal substrate, the material of the first ferrimagnetic thin film is yttrium iron garnet (YIG) (60nm), and the material of the two-dimensional material layer is Monolayer graphene, the material of the second ferrimagnetic film is yttrium iron garnet (YIG) (60nm);
[0064] Preparation:
[0065] 1) Use acetone, alcohol and deionized water in sequence to clean the substrate material under ultrasonic conditions;
[0066] 2) Put the substrate in the pulsed laser deposition chamber, and set the target base distance (7cm); at ≤10 -6 In a vacuum environment of Pa, heat the substrate to 750°C at a heating rate of 10°C / min; inject oxygen into the cavity (atmospheric pressure of 1.0Pa); then, turn on and set the laser parameters (laser energy is 300mJ; The laser frequency is 5 Hz); open the substrate baffle, deposit for 20 minutes, close the substrate baffle after the deposition is com...
Embodiment 2
[0073] A superlattice material: the substrate material is a gadolinium gallium garnet (GGG) single crystal substrate, the material of the first ferrimagnetic film is thulium iron garnet (TmIG) (60nm), and the material of the two-dimensional material layer is Monolayer graphene, the material of the second ferrimagnetic film is thulium iron garnet (TmIG) (60nm);
[0074] The preparation method refers to Example 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com