Magnetic fluorescent probe-based food escherichia coli colony visual detection and automatic counting method
A technology of Escherichia coli and fluorescent probes, applied in the field of microbial detection, can solve the problems of low reproducibility, time-consuming, and large randomness of results in immunoassays and molecular biology methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
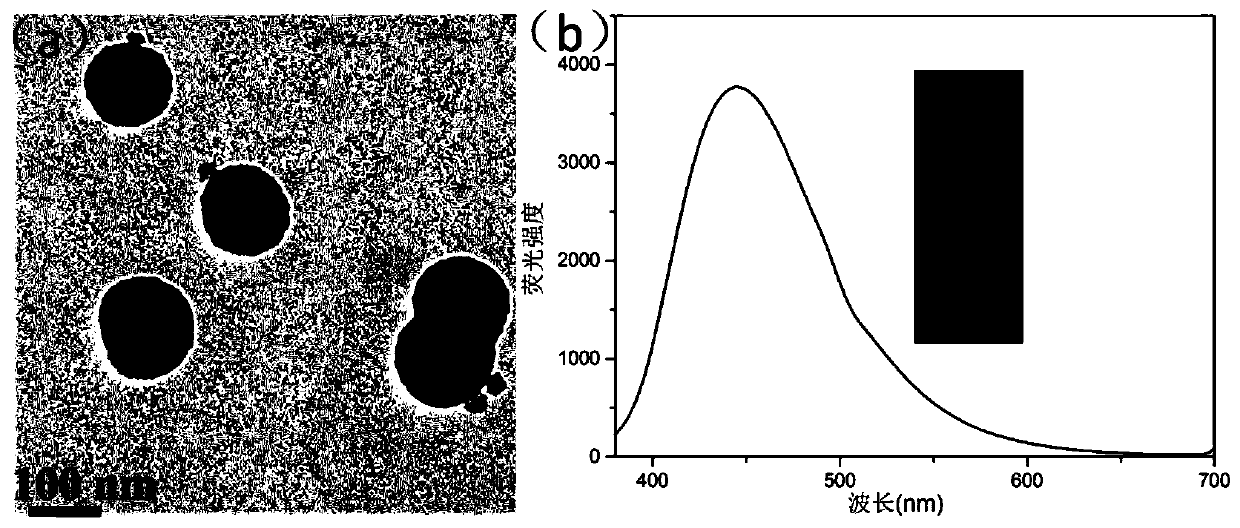
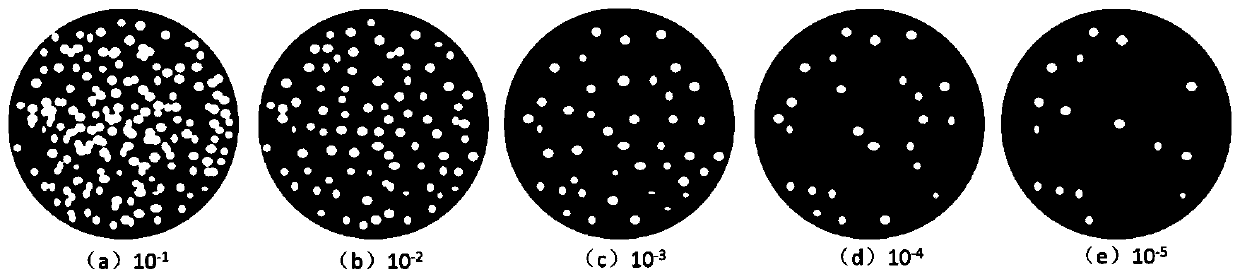
[0047] In the present invention, the bacterial strains in the milk are solid-state cultured at first to obtain the colony plate of the bacterial strain; then the prepared specific magnetic fluorescent probe is added to the colony plate, and the magnetic fluorescent probe that does not react with E. coli is magnetically separated; Plate image; the final image processing realizes the automatic counting of E. coli colonies.
[0048] Step 1, magnetic nanosphere Fe 3 o 4 @SiO 2 - Preparation of cDNA:
[0049] Add 1.08g of ferric chloride hexahydrate, 1.8g of sodium acetate trihydrate and 0.25g of trisodium citrate into 50mL of ethylene glycol in sequence, and stir magnetically for 9 hours at 40°C to form a uniform and transparent solution, then transfer it to the reaction kettle in 200°C for 10 h, and finally the obtained mixture was washed three times with deionized water and ethanol, magnetically separated to obtain a black product, and vacuum dried at 60°C for 10 h to obtain ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com