Control Method of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on Hall Position Sensor
A permanent magnet synchronous motor, Hall position technology, applied in motor generator control, electronic commutation motor control, control system and other directions, can solve the problem of excessive estimation result deviation, torque and current fluctuation, torque fluctuation, etc. The effect of increasing starting torque, reducing torque fluctuation, and reducing torque fluctuation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
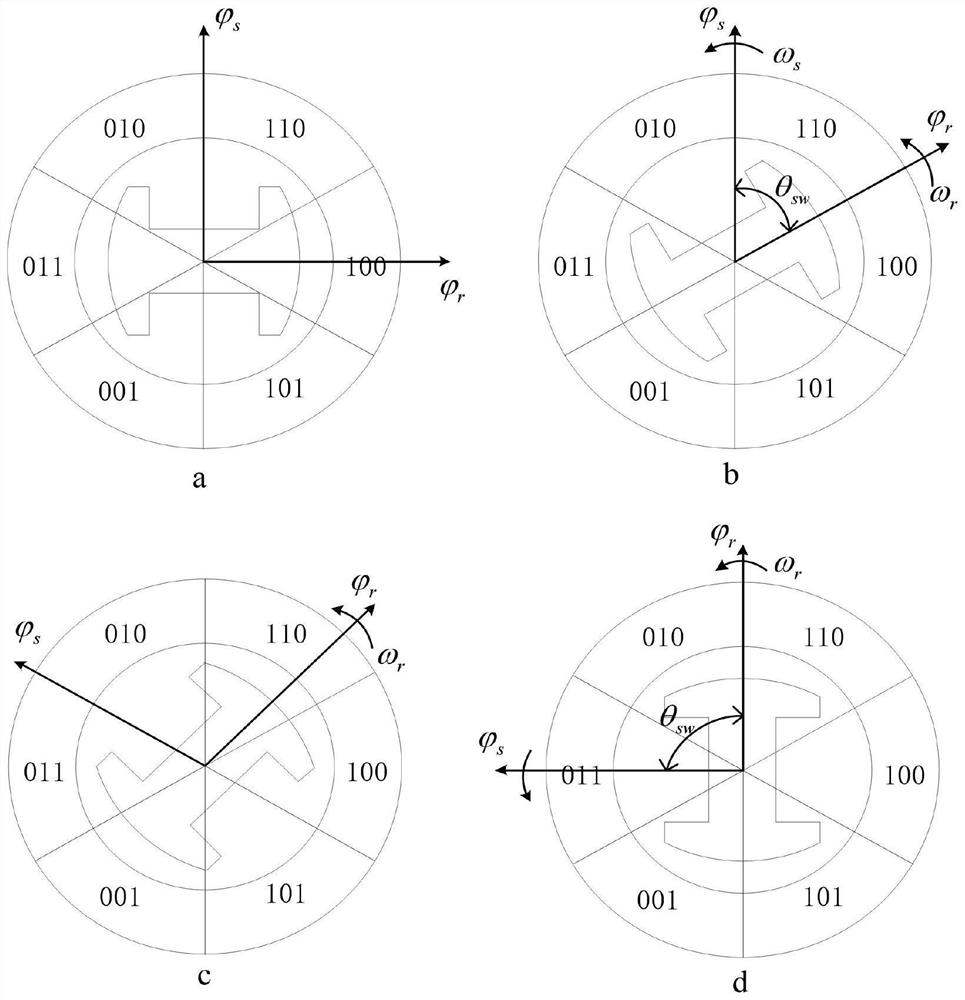
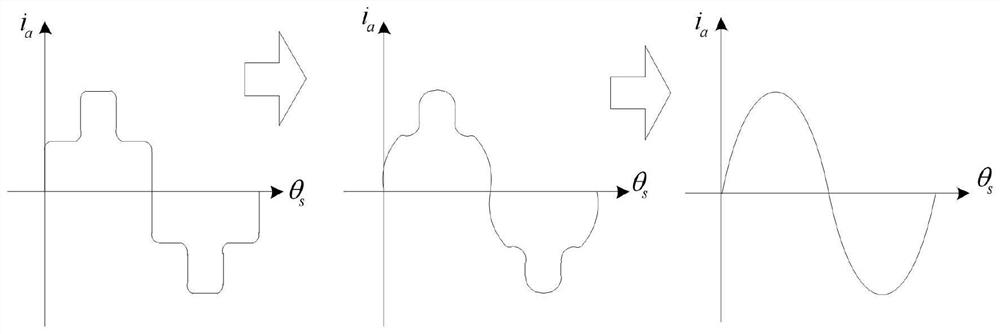
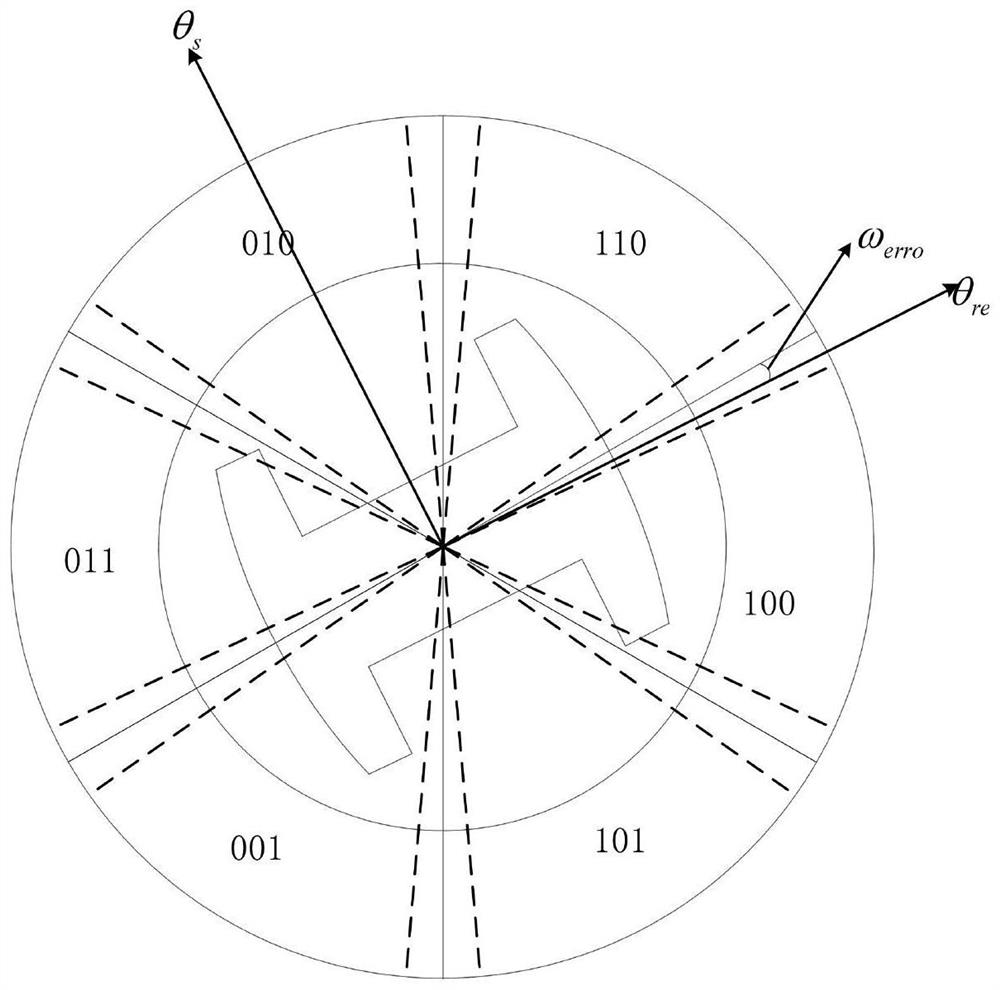
[0057] In this embodiment, the control method of the permanent magnet synchronous motor based on the Hall position sensor adopts the Nanpu 1.2KW permanent magnet synchronous motor as the controlled object, and the specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0058] 1) Open the three-phase electric circuit of the motor, drag it up at the rated speed, then connect the negative pole of the oscilloscope probe to the W phase, and the positive pole to the V pole to obtain the back electromotive force waveform.
[0059] 2) Connect the outputs A, B, and C of the Hall position sensor of the motor to the positive pole of the oscilloscope test lead, and the negative pole of the test lead to the negative pole of the Hall position sensor power supply, and compare it with the back electromotive force waveform obtained in step 1.1 to obtain the position sensor. Along the corresponding six discrete electrical angles θ r1 =27.6°, θ r2 =92.4°, θ r3 =147.2°, θ r4 =207.5°, θ r5 =272.3°, θ ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com